1. De duplication query
According to the database tables and data created before, we put forward a demand to query the student numbers of all students who took the exam
select `studentno` from `result` --Query the student numbers of all students with grades
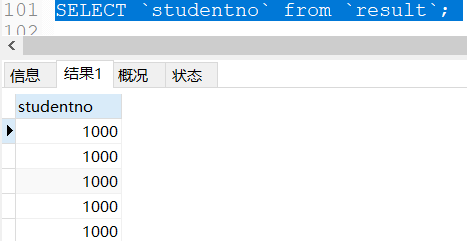
According to the results, we can see that there are a lot of duplicates in the data, so we can use distinct to de duplicate the data.
SELECT DISTINCT `studentno` from `result`;
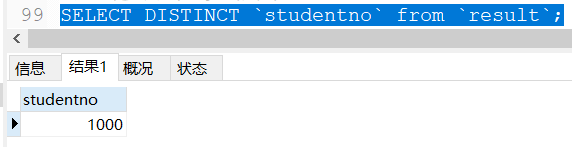
Comparing the two queries, it is obvious that this way of de duplication is more applicable, and only one duplicate data is displayed.
2.where conditional clause
Function: retrieve qualified values in data
Logical operator
| operator | grammar | describe |
|---|---|---|
| and ,&& | a and b,a && b | Logic and |
| or ,|| | a or b,a || b | Logical or |
| not ,! | not a,! b | Logical non |
3. Fuzzy query
| operator | grammar | describe |
|---|---|---|
| is null | a is null | Returns true if a is null |
| is not null | a is not null | Returns true if a is not null |
| between...and... | a between b and c | If a is between b and c, return true |
| Like | a like b | SQL matches. If a matches b, it returns true |
| in | a in (a1,a2,a3,a4...) | If a is in one of (a1,a2,a3...), it returns true |
Fuzzy query example:
- like related operations (capable of fuzzy matching)
#The query name starts with Liu (surnamed Liu) select * from `student` where `studentname` like "Liu%" --%(Represents 0 to any character) #Inquire about students surnamed Liu. Their names are only two words select * from `student` where `studentname` like "Liu_" --_(Represents a character) #Inquire about students surnamed Liu whose names are three words select * from `student` where `studentname` like "Liu__" #Query the students with the word "home" in their names select * from `student` where `studentname` like "%home%"
- In related operations (in can only be matched specifically)
#Query student No. 100110021003
select * from `student` where `studentno` in (1001,1002,1003)
#Query students in Anhui and Beijing
select * from `student` where `address` in ('Anhui','Beijing')
- Null and not null related operations
#Query the students whose address is empty, which may be "" or null select * from `student` where `address` = '' or `address` is null #Query students with birth date, that is, the birth date cannot be blank select * from `student` where `borndate` is not null
4. Associated table query
When we make a query, we may encounter the situation that one table may not meet our requirements. The data we may require to obtain may come from two, three or even more tables. For this, we should use joint table query.
for instance:
According to the database and table we created before, we put forward a demand to obtain the information of the students who took the exam, including the student's name, student number, subject number and score of the student's exam
select * from `student` select * from `result`
We also need to compare the student numbers one by one to find the effect of such query. This method is too troublesome. We need to splice these data in a way to facilitate our view.
Idea:
- Fields from query analysis table:
- Connection method: determine which connection method to use for query (determine the intersection, that is, which data in the two tables are the same)
According to the analysis of the structure of the two tables, we can judge that the condition is: studentNo in the student table = studentNo in the grade table
#Use inner join to join table queries select s.`studentNo`,`studentName`,`subjectNo`,`studentResult` from `student` as s inner join `result` as r where s.`studentNo` = r.`studentNo` #Use right join to join table query select s.`studentNo`,`studentName`,`subjectNo`,`studentResult` from `student` as s right join `result` as r on s.`studentNo` = r.`studentNo` #Use left join to join table query select s.`studentNo`,`studentName`,`subjectNo`,`studentResult` from `student` as s left join `result` as r where s.`studentNo` = r.`studentNo`
- join on join query
- where equivalent query
| operation | describe |
|---|---|
| inner join | If there is at least one match in the table, it will return. If there are both tables, it is enough to determine which table it is |
| left join | Even if no value in the right table matches the left table, all values in the left table will be returned |
| right join | Even if no value in the left table matches the value on the right, all values in the right table will be returned |
If we need to check more than two tables, first query the first two tables, and then connect the query results with the third table.
#Query the student's student number, name, subject and grade (from three tables) SELECT stu.studentno,studentname,sub.subjectname,studentresult from student stu INNER join result res on stu.studentno = res.studentno right join subject sub on stu.studentno = res.studentno
5. Seven join theories:
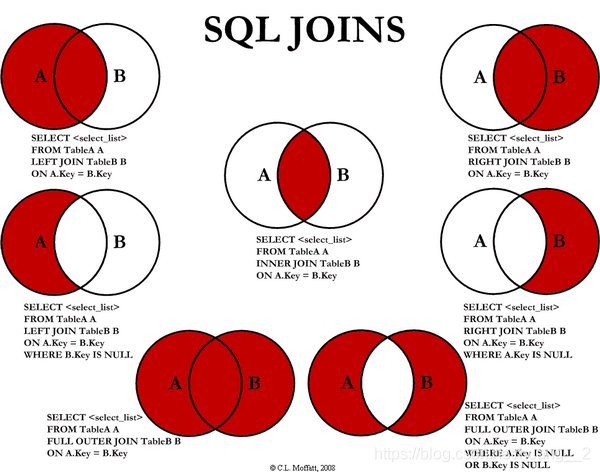
6. Self connection query
Self connection: as the name suggests, it is to connect yourself with yourself. The core is to split a table into two identical tables.
We create a new table category in the existing school database
drop table if exists `category` CREATE TABLE if not exists `category`( `categoryid` INT(3) NOT NULL COMMENT'id', `pid` INT(3) NOT NULL COMMENT'father id 1 if there is no parent', `categoryname` VARCHAR(10) NOT NULL COMMENT'Species name', PRIMARY KEY (`categoryid`) ) ENGINE=INNODB CHARSET=utf8; INSERT INTO `category` (`categoryid`, `pid`, `categoryname`) VALUES (2, 1, "information technology"), (3, 1, "software development"),(5, 1, "Art design"), (4, 3, "database"),(8, 2, "Office information"), (6, 3, "web development"), (7, 5, "ps technology");
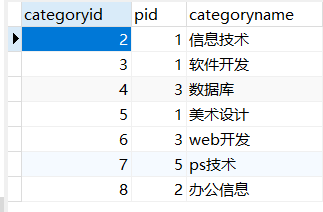
By analyzing this table, we can see that grading is implemented in this table. For example, for web development, its id is 6, but its parent id is 3, and the parent id of software development with id 3 is 1. Let's split the table.
- Parent table
| categoryid | categoryname | pid |
|---|---|---|
| 2 | information technology | 1 |
| 3 | software development | 1 |
| 5 | Art design | 1 |
- Sub table
| categoryid | categoryname | pid |
|---|---|---|
| 4 | database | 3 |
| 8 | Office information | 2 |
| 6 | web development | 3 |
| 7 | Art design | 5 |
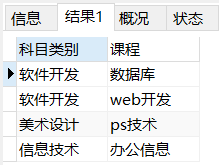
Operation: query the subclass relationship corresponding to the parent class
| Parent class | Subclass |
|---|---|
| information technology | Office information |
| software development | database |
| software development | web development |
| Art design | ps Technology |
We need to query, which should be the query result we want.
For fields that are all in one table, we use self join query.
select a.categoryname Account category,b.categoryname curriculum from category a inner join category b on a.categoryid = b.pid
7. Paging and Sorting Query
(1) Sort query
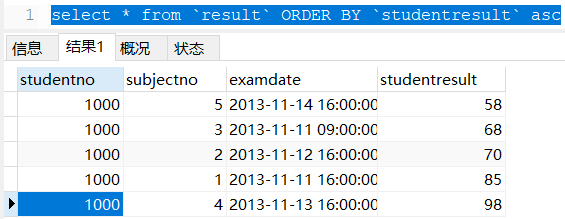
- Ascending (asc):
The query results are sorted in ascending order according to the scores
select * from `result` ORDER BY `studentresult` asc
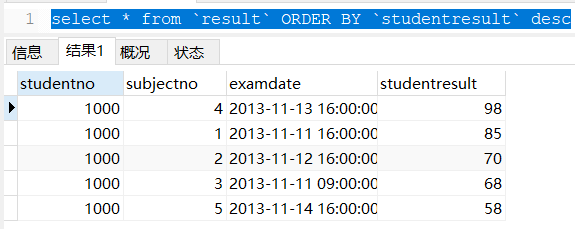
- Descending order (desc):
select * from `result` ORDER BY `studentresult` desc
- order by: sort by that field
- DESC, asc: desc in descending order, asc in ascending order
(2) Paging query
Think about it: why use paging queries?
We look for data in a very large database. If we want to display it all, the pressure of the database will be very large, and it is very inconvenient for us to find data. Therefore, we need to use paging.
- Paging query using limit
SELECT * from subject limit 0,10
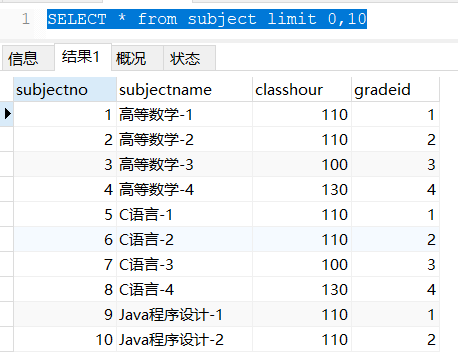
- limit a, b: display b pieces of data from index a
Exercise:
Query all students whose subject score is greater than 60, display the first 10 items and arrange them in descending order. The field only displays student name, subject name and score
SELECT studentname Student name,sub.subjectname Account name,studentresult Student achievement from student stu inner join result res on stu.studentno = res.studentno inner join subject sub where res.subjectno = sub.subjectno and studentresult>60 ORDER BY studentresult desc limit 0,10
8. Sub query and nested query
We were writing sql before. The values in the query conditions are fixed. If the values in the conditions are calculated, it is a sub query.
Essence: nest a query statement under the where condition
Example:
#Query all test results of advanced mathematics-1 (including student number, name, subject number and score), and arrange them in descending order --Use join query select stu.studentno,studentname,res.subjectno,studentresult from student stu inner join result res on stu.studentno = res.studentno inner join subject sub on res.subjectno = sub.subjectno where subjectname = 'Advanced mathematics-1' order by studentresult desc --Use subquery select stu.studentno,studentname,res.subjectno,studentresult from student stu inner join result res on stu.studentno = res.studentno where res.subjectno = (select subjectno from subject where subjectname = 'Advanced mathematics-1') order by studentresult desc
One more question
#Query the student number and name of students whose subject is advanced mathematics-2 and the subject score is not less than 80 #Joint table query method select distinct stu.studentno,studentname from student stu inner join result res on stu.studentno = res.studentno inner join subject sub on res.subjectno = sub.subjectno where subjectname = 'Advanced mathematics-2' and studentresult >= 80 #Subquery method 1 select stu.studentno,studentname from student stu inner join result res on stu.studentno = res.studentno where subjectno = ( select subjectno from subject where subjectname='Advanced mathematics-2' ) and studentresult >=80 #Sub query method 2 select studentno,studentname from student where studentno in ( select studentno from result where subjectno = ( select subjectno from subject where subjectname = 'Advanced mathematics-2' ) and studentresult >= 80 ) #Query the information (student number, name, score) of the top five students whose subjects have the keyword "advanced mathematics" select stu.studentno,studentname,studentresult from student stu inner join result res where subjectno in ( select subjectno from subject where subjectname like "Advanced mathematics%" ) order by studentresult desc limit 0,5