Spring's JDBC module is responsible for database resource management and error handling, which greatly simplifies the operation of the database by the developers, so that the developers can get rid of the tedious database operation, so as to put more energy into writing business logic.
For the Spring framework of database operation, the JdbcTemplate class is provided, which is the basis of the Spring framework data abstraction layer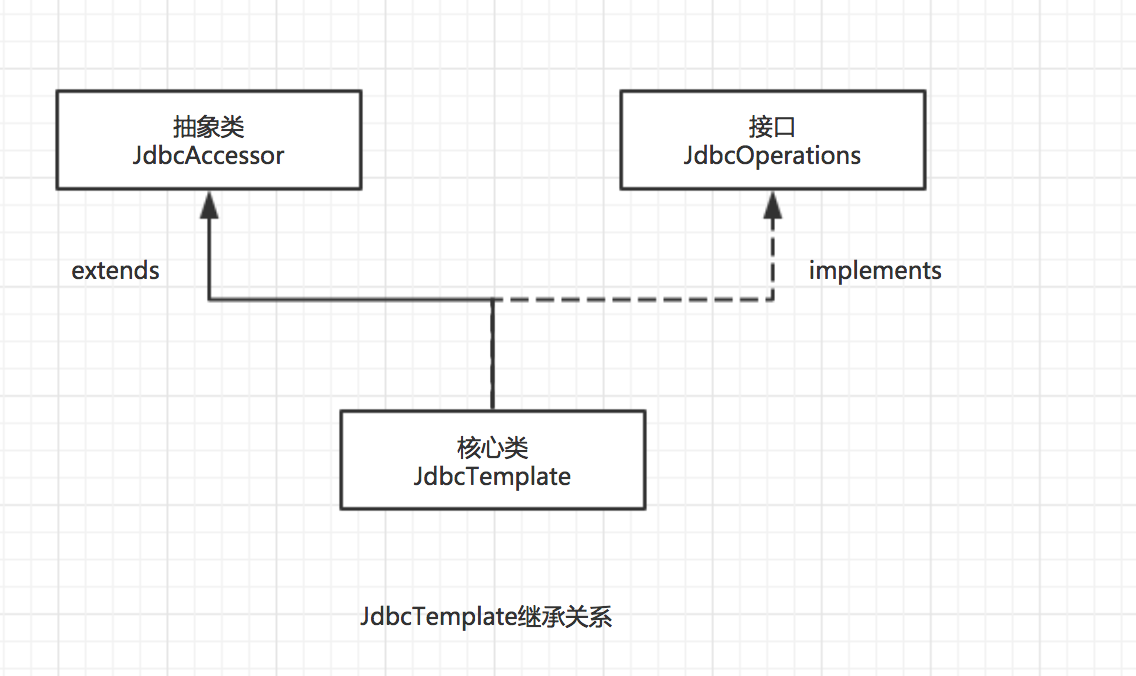
1, Spring JDBC configuration
2. Common usage of Spring JdbcTemplate<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> <beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans-4.3.xsd"> <!-- Configure data sources--> <bean id="dataSource" class="org.springframework.jdbc.datasource.DriverManagerDataSource"> <!-- Database driven --> <property name = "driverClassName" value = "com.mysql.jdbc.Driver" /> <!-- Connect to database URL--> <property name = "url" value = "jdbc:mysql://localhost/spring" /> <!-- User name to connect to the database--> <property name = "username" value = "root" /> <!-- Password to connect to the database--> <property name = "password" value = "kangxg198811" /> </bean> <!-- To configure JDBC Template--> <bean id="jdbcTemplate" class="org.springframework.jdbc.core.JdbcTemplate"> <!-- Data source is required by default --> <property name="dataSource" ref ="dataSource"></property> </bean> </beans>
1. execute()
1.1. Terminal creates spring database
mysql -u root -p
Enter password: password
create database spring;
use spring; 1.2 create test class dbcTemplateTestpackage com.kangxg.jdbc;
import org.springframework.context.ApplicationContext;
import org.springframework.context.support.ClassPathXmlApplicationContext;
import org.springframework.jdbc.core.JdbcTemplate;
public class jdbcTemplateTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ApplicationContext applicationContext = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("applicationContext.xml");
JdbcTemplate jdTemplate = (JdbcTemplate) applicationContext.getBean("jdbcTemplate");
jdTemplate.execute("create table account("+"id int primary key auto_increment,"+"username varchar(50),"+"balance double)");
}
}Enter terminal view
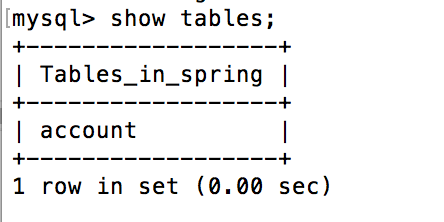
Or go to the sequence Pro database management tool to view
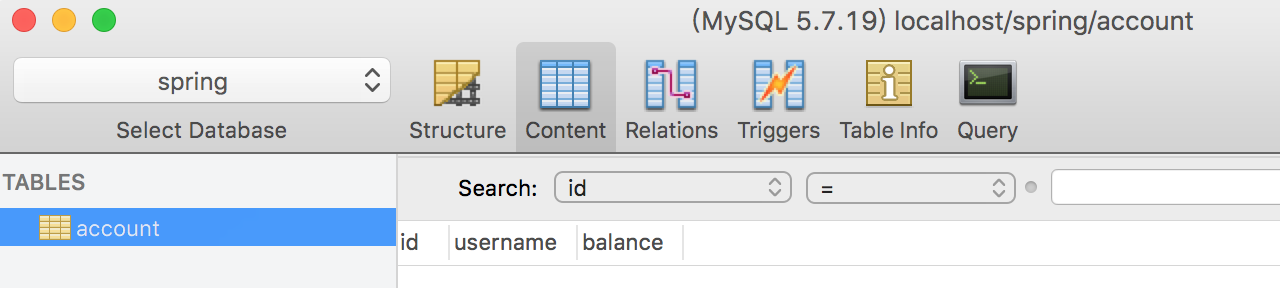
1.4 unit test
Create test class
package com.kangxg.jdbc;
import org.junit.Test;
import org.springframework.context.ApplicationContext;
import org.springframework.context.support.ClassPathXmlApplicationContext;
import org.springframework.jdbc.core.JdbcTemplate;
public class JdbcTemplateJunitTest {
@Test
public void test() {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
//The annotation @Test is disallowed for this Test cannot be resolved to a type
ApplicationContext applicationContext = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("applicationContext.xml");
JdbcTemplate jdTemplate = (JdbcTemplate) applicationContext.getBean("jdbcTemplate");
jdTemplate.execute("create table account("+"id int primary key auto_increment,"+"username varchar(50),"+"balance double)");
System.out.println("Account table account Created successfully");
}
}When the error Test cannot be resolved to a type occurs, move the mouse to @ Test and the error prompt box will be displayed. Select Add Junit4 library to the build path, and eclipse will automatically add Junit4's support package to the project