Introduction to the author
Author name: Ming Shiyin in programming world
Introduction: CSDN blog expert has been engaged in software development for many years and is proficient in Java and JavaScript. Bloggers also learn and grow step by step from scratch, know the importance of learning and accumulation, and like to fight and upgrade with ADC. Welcome to pay attention and look forward to learning, growing and taking off with you!

introduction
Many Java beginners ask me that it's worrying for the novice to turn around and forget the Java knowledge he has studied very hard. How can Xiaobai grow up quickly and become a big cow?
In fact, there is only one skill to become a big God: "learn more and practice more", so brother Ming sorted out typical practice examples. Through practice, you can quickly improve coding skills and proficiency, so that you can never return on the way to become a big man (remember to practice with your own hands)!
Navigation
✪ introduction to Java white 200 case series directory index
◄ previous 05 Self increasing and self decreasing (+ +, --)
► next article to be updated
Example 1
Process user input integers and print out to the console
package demo.demo6;
import java.util.Scanner;
public class Test1 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//Create a reader instance
Scanner reader = new Scanner(System.in); //Input from standard input - Keyboard
System.out.print("Please enter an integer: ");
//nextInt() reads the next integer from the keyboard
int number = reader.nextInt();
//println() prints the following lines to the output screen
System.out.println("The integer you entered is: " + number);
}
}
The operation results are as follows:
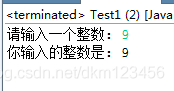
Example 2
Process user input 3 integers, get the maximum value, and print out to the console
package demo.demo6;
import java.util.Scanner;
public class Test2 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//1. Prompt and receive the three integers entered by the user and hand them over to the variable a, B and C to save
System.out.println("Please enter the first integer:");
int a = new Scanner(System.in).nextInt();
System.out.println("Please enter the second integer:");
int b = new Scanner(System.in).nextInt();
System.out.println("Please enter the third integer:");
int c = new Scanner(System.in).nextInt();
int max=0;//Define maximum number
//Let a and b compare first, and assign a large value to max
if(a>b){
max=a;
}else {
max=b;
}
//Let's compare c with max. whoever is big is max
if(c>max){//If c is greater than max, let Max be c, otherwise Max is already the largest
max=c;
}
System.out.println("The largest number is:"+max);
}
}
The operation results are as follows:
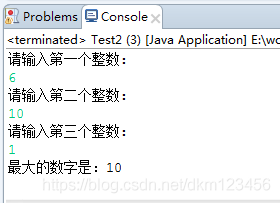
Example 3
Process the user to input multiple integers, input - 1 to end the input, then take the maximum and minimum value, and print out to the console.
package demo.demo6;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.Collections;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.Scanner;
public class Test3 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//Create a reader instance
Scanner reader = new Scanner(System.in); //Input from standard input - Keyboard
System.out.print("Please enter an integer: ");
//nextInt() reads the next integer from the keyboard
int number = reader.nextInt();
List arr = new ArrayList();
while(number!=-1){//When the input is not - 1, it can be input continuously. If - 1 is input, the cycle ends
arr.add(number);
reader = new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.print("Please enter an integer: ");
number = reader.nextInt();
}
int max = 0;//Take maximum
int min = 0;//Take minimum
if(arr.size()>0){
max = (int)Collections.max(arr);//Take maximum
min = (int)Collections.min(arr);//Take minimum
}
//println() prints the following lines to the output screen
System.out.println("The largest integer is: " + max);
System.out.println("The smallest integer is: " + min);
}
}
Operation results:

Summary
This section summarizes the "user input processing". I hope it can be helpful to you. Please help [like] + [collection] + [punch in the comment area]. If you are interested in learning Java with brother Xiao Ming, [pay attention to a wave] won't get lost.
Let me know you by punching in the comment area. Mingge will continue to pay attention to your learning progress!
Navigation
✪ introduction to Java white 200 case series directory index
◄ previous 05 Self increasing and self decreasing (+ +, --)
► next article to be updated