1. Permission viewing and reading
File permission is one of the lowest security setting methods of the system. It ensures that files can be operated by available users
1. Permission view
| command | function |
|---|---|
| ls -l file | ##View file permissions ls -l =ll |
| ls -ld dir | ##View directory permissions ls -ld =ll -d |
2. Permission reading
The attributes of a file are called meta data“
A metadata that records content with a byte“
File permission information
- | rw-r--r-- | . | 1 | root | root | 0 |Apr 12 10:57 |westos [1] [2] [3] [4] [5] [6] [7] [8] [9]
Directory permission information
d | rw-r--r-- | . | 2 | root | root | 0 | Apr 12 10:57 |westosdir
[1] [2] [3] [4] [5] [6] [7] [8] [9]
[1] Indicates the file type
-Ordinary file
[root@foundation50 mnt]# ls -l westos -rw-r--r--. 1 root root 0 Aug 12 23:29 westos
d directory
[root@foundation50 mnt]# ls -ld westosdir/ drwxr-xr-x. 2 root root 6 Aug 12 23:29 westosdir/
l soft connection (understood as shortcut)
[root@foundation50 mnt]# ls -l /home/westos/Desktop/westos l rwxrwxrwx. 1 root root 6 Aug 12 23:29 /home/westos/Desktop/westos -> westos
Block b equipment
[root@foundation50 Desktop]# ls -l /dev/sdb brw-rw----. 1 root disk 8, 16 Aug 13 10:37 /dev/sdb
c character device (the device that displays characters, / dev/pts/0 is characterized in that when the content is written to / dev/pts/0, it will be displayed on the screen
[root@foundation50 mnt]# ls -l /dev/pts/0 crw--w----. 1 westos tty 136, 0 Aug 12 23:27 /dev/pts/0
s socket socket (equivalent to a door of the program and the interface into the program)
p pipe|
[2] User rights
u user g belongs to group o others
rw-|r--|r-- u g o
[3] selinux startup of the system (kernel enhanced firewall, security context)
ls -Z olelee view the security context of the file and create the file when selinux is closed Will disappear
[4] If it is a directory, it indicates the number of sub files in the directory; if it is a file, it indicates the number of hard connections
Soft connection:
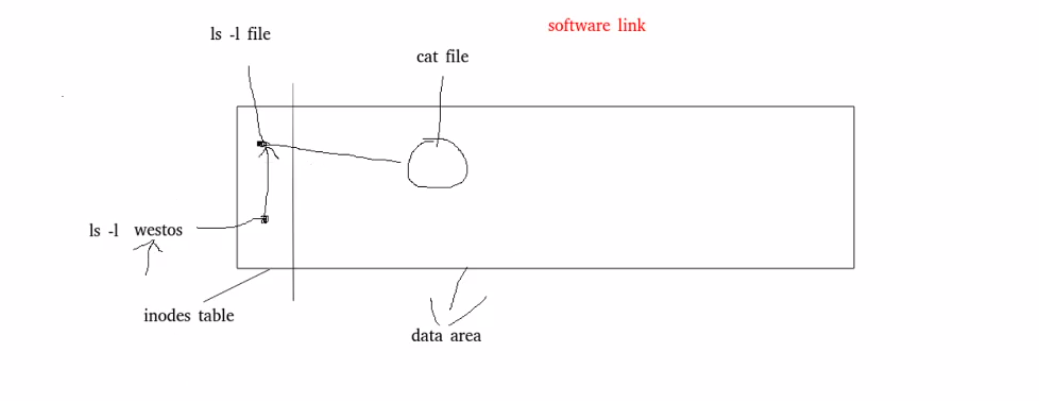
Hard connection:
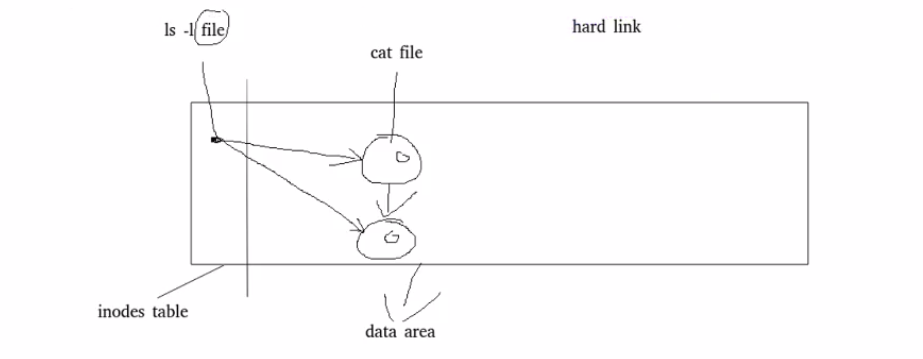
catalog: [root@foundation50 mnt]# ls -ld westosdir/ drwxr-xr-x. 2 root root 6 Aug 13 11:13 westosdir/ [root@foundation50 mnt]# mkdir westosdir/westos [root@foundation50 mnt]# ls -ld westosdir/ drwxr-xr-x. 3 root root 20 Aug 13 11:16 westosdir/ File: [root@foundation50 mnt]# ls -l westos -rw-r--r--. 1 root root 0 Aug 13 11:14 westos [root@foundation50 mnt]# cp westos oldlee [root@foundation50 mnt]# ls -i westos oldlee view node number 868637908 oldlee 868636607 westos [root@foundation50 mnt]# rm -fr oldlee [root@foundation50 mnt]# ln westos oldlee hardwired [root@foundation50 mnt]# ls -l westos -rw-r--r--. 2 root root 0 Aug 13 11:14 westos The number changes from 2 to 1 [root@foundation50 mnt]# ls -l oldlee -rw-r--r--. 2 root root 0 Aug 13 11:14 oldlee [root@foundation50 mnt]# ls -i westos oldlee view the node number. One node corresponds to two data areas 868636607 oldlee 868636607 westos
[5] File owner
[6] File owning group
[7] For files: file content size
[root@foundation50 mnt]# echo 1 > westos [root@foundation50 mnt]# LS - L westos 1 character plus a newline character -rw-r--r--. 2 root root 2 Aug 13 11:46 westos
For the directory: the metadata size of the sub file or subdirectory of the directory (| rw-r – R -- |. 1 | root | root | 0 | Apr 12 10:57 | westos, each of the first 8 is recorded with one byte, and several bytes of the file name is several)
[root@foundation50 mnt]# ls -ld westosdir/ drwxr-xr-x. 2 root root 6 Aug 13 16:01 westosdir/ The original data size is 6(. ..) [root@foundation50 mnt]# touch westosdir/11 create a file in the westosdir directory [root@foundation50 westosdir]# The attribute size of ls -l 11 file 11 is 10 -rw-r--r--. 1 root root 0 Aug 13 16:03 11 [root@foundation50 mnt]# ls -ld westosdir/ drwxr-xr-x. 2 root root 16 Aug 13 16:03 westosdir/ The metadata size is 10+6=16
[8] The time when the file was last modified, including the time when the file attribute and file content were last modified
[root@foundation50 mnt]# ls -l westoslee -rw-r--r--. 2 root root 2 Aug 13 11:46 westoslee [root@foundation50 mnt]# Echo 123 > westoseee modify file contents [root@foundation50 mnt]# ls -l westoslee -rw-r--r--. 2 root root 4 Aug 13 16:28 westoslee Time change [root@foundation50 mnt]# MV westoselee Lee the time when the file name is modified will also be changed
3. File user group management
| command | function |
|---|---|
| chown username file | Change file owner |
| chgrp groupname file | Change file ownership group |
| chown username:groupname file | Change the owner and ownership group of the file at the same time |
| chown/chgrp -R user/group dir | Change the owner or group of the directory itself and the contents in the directory |
Establishment of experimental environment
[root@foundation50 Desktop]# cd /linux/
[root@foundation50 linux]# mkdir westosdir
[root@foundation50 linux]# touch westos{1..3}
[root@foundation50 linux]# touch westosdir/westosfile{1..3}
Monitoring command: watch ls -R /linux
[root@foundation50 ~]# chown lee /linux/westos1 change file owner
[root@foundation50 ~]# Chgrp Liu / Linux / westos1change file ownership group
[root@foundation50 ~]# chown lee.liu /linux/westos2 also change the file owner group
[root@foundation50 ~]# chown lee:liu /linux/westos3 also change the file owner group
[root@foundation50 ~]# chown lee /linux/westosdir / change i directory file itself
[root@foundation50 ~]# chgrp liu /linux/westosdir/
[root@foundation50 ~]# chown -R lee /linux/westosdir / change the owner of the directory itself and the contents of the directory (including files and directories)
[root@foundation50 ~]# chgrp -R lee /linux/westosdir/
[root@foundation50 ~]# chown -R root:root /linux/
4. User identity matching
user>group>other
5. Permission type
| command | purpose |
|---|---|
| -Permission not opened | |
| r | Readable for files: file contents can be read for directories: files in directories can be ls listed |
| w | Writable: for files, you can change the contents of the file; For directory: you can create or delete files in the directory |
| x | Executable file: the program recorded in the file can be called with the file name; For directory: you can enter the directory |
[root@foundation50 ~]# ls -l /linux/westos1 -rwx------. 1 lee westos 5 Aug 15 15:35 /linux/westos1 [root@foundation50 ~]# From the id lee, you can see that lee has user rights over the file westos1 uid=1001(lee) gid=1001(lee) groups=1001(lee) [root@foundation50 ~]# Su -- switching users [westos@foundation50 root]$ id westos It can be seen that westos User to file westos1 Enjoy the power of the group uid=1000(westos) gid=1000(westos) groups=1000(westos) [root@foundation50 ~]# usermod -G westos root [root@foundation50 ~]# id root uid=0(root) gid=0(root) groups=0(root),1000(westos) It can be seen that root User pair westos1 This document enjoys the authority of the group Note: the power of the group depends not only on
[lee@foundation50 ~]$ chmod u+r /linux/westos1 [lee@foundation50 ~]$ cat /linux/westos1 [lee@foundation50 ~]$ echo 123 > /linux/westos1 No write permission bash: /linux/westos1: Permission denied [lee@foundation50 ~]$ chmod u+w /linux/westos1 Add write permission [lee@foundation50 ~]$ echo 123 > /linux/westos1 [lee@foundation50 ~]$ cat /linux/westos1 123 [lee@foundation50 ~]$ echo date > /linux/westos1 [lee@foundation50 ~]$ /linux/westos1 bash: /linux/westos1: Permission denied No execution permission [lee@foundation50 ~]$ chmod u+x /linux/westos1 Add execution permission [lee@foundation50 ~]$ /linux/westos1 date The command can be executed Sun Aug 15 15:36:21 CST 2021 [lee@foundation50 root]$ ls -ld /linux/westosdir/ d---------. 2 lee root 63 Aug 13 22:27 /linux/westosdir/ [lee@foundation50 root]$ ls /linux/westosdir/ No right to read ls: cannot open directory '/linux/westosdir/': Permission denied [lee@foundation50 root]$ chmod u+r /linux/westosdir/ Plus the power to read [lee@foundation50 root]$ ls /linux/westosdir/ You can read the files in the directory ls: cannot access '/linux/westosdir/westosfile1': Permission denied ls: cannot access '/linux/westosdir/westosfile2': Permission denied ls: cannot access '/linux/westosdir/westosfile3': Permission denied westosfile1 westosfile2 westosfile3 Note that for the directory, the written program should be based on the executive power. Without the executive power, you can't enter the door for peace talks [lee@foundation50 root]$ chmod u+x /linux/westosdir/ Plus executive power [lee@foundation50 root]$ cd /linux/westosdir/ You can enter the door and check the things in the door [lee@foundation50 westosdir]$ ls westosfile1 westosfile2 westosfile3 [lee@foundation50 westosdir]$ rm -fr westosfile1 No permission to delete file rm: cannot remove 'westosfile1': Permission denied [lee@foundation50 linux]$ chmod u+w westosdir/ Add write permission [lee@foundation50 linux]$ cd westosdir/ [lee@foundation50 westosdir]$ rm -fr westosfile1 Can delete [lee@foundation50 westosdir]$ chmod ugo=--- /linux/westos2 Other users' files cannot be changed chmod: changing permissions of '/linux/westos2': Operation not permitted
6. How to set normal permissions
| command | function |
|---|---|
| chmod | Set file permissions |
6.1. Copy permission
| command | function |
|---|---|
| chmod – reference westos2 westos1 | westos1 permission to copy westos2 |
-rwx------. 1 lee root 5 Aug 15 15:35 westos1 -rw-r--r--. 1 root root 0 Aug 13 16:43 westos2 take westos2 Copy file permissions to westos1 [root@foundation50 ~]# chmod --reference /linux/westos2 /linux/westos1 -rw-r--r--. 1 lee root 5 Aug 15 15:35 westos1 -rw-r--r--. 1 root root 0 Aug 13 16:43 westos2
6.2 right to change documents in character mode
[root@foundation50 ~]# chmod u+x /linux/westos1 [root@foundation50 ~]# chmod u-w /linux/westos1 [root@foundation50 ~]# chmod ug+w /linux/westos1 [root@foundation50 ~]# chmod u-r,g-w,o+x /linux/westos1 [root@foundation50 ~]# chmod u=rx,go=--- /linux/westos1
6.3 setting authority in digital mode
Just remember how many numbers r, w and x Stand for
| command | purpose |
|---|---|
| r | 4 |
| w | 2 |
| x | 1 |
[root@foundation50 ~]# chmod 500 /linux/westos1 wx-|---|--- [root@foundation50 ~]# chmod 630 /linux/westos1 rw-|wx-|--- [root@foundation50 ~]# chmod 777 /linux/westos1 rwx|rwx|rwx [root@foundation50 ~]# chmod 000 /linux/westosdir / change permissions for directories [root@foundation50 ~]# chmod -R 640 /linux/westosdir / change the permissions of the directory and the files in the directory
7. System default permission setting
The meaning of the system itself and shared resources
From the perspective of security, the less resources the system shares, the less open power, and the higher system security
We should not only ensure the security of the system, but also create value for the system, so we should open the power that should be open by default and retain the unsafe power by default
7.1 how to retain power
umask indicates that the system reserves rights
| command | function |
|---|---|
| umask | View reserved rights |
| command | function |
|---|---|
| umask permission value | Temporarily set system reserved power |
File default permission = 777-umask-111 (022 is reserved by the system and 111 is reserved by the file system)
Directory default permission = 777 umask
Note: the greater the umask value, the higher the system security
7.2. umask temporary change
umask 077: setting (after setting, the value of the currently created file and directory is the setting. After exiting the current program, the re establishment will be the same as before, that is, the temporary setting only works for the current program)
Using umask: View
7.3 permanent change (edit the configuration file in the system)
(1) Change shell system configuration file
vim /etc/bashrc ##shell system configuration file 74 if [ $UID -gt 199 ] && [ "`id -gn`" = "`id -un`" ]; then 75 umask 002 #umask for ordinary users 76 else 77 umask 022 -- 077 #umask of root user 78 fi
(2) Change system profile
vim /etc/profile ##System environment profile 59 if [ $UID -gt 199 ] && [ "`id -gn`" = "`id -un`" ]; then 60 umask 002 #umask (directory) for ordinary users 61 else 62 umask 022 -- 077 #The umask * * of root user needs to be set as super user 63 fi (text command: gt It means> ,lt express < ,eq express = ,The unequal sign is nt) ( gn Is the name of the initial group, un Is the user's name)
(3) Call
source /etc/bashrc ##When source is used, the content we change is immediately recognized by the system (only one file can be followed by source, not more than one) source /etc/profile
8. Special permissions
Phenomenon: a user can delete both files in his own directory and files in others' directories. This is unreasonable in production, so the sticky bit is introduced
8.1 stickyid adhesive bit (only for the directory)
If a directory stickyid is enabled, the files in this directory can only be deleted by the file owner, and the files in other directories cannot be deleted
How to set sticky bit permissions
| command | user |
|---|---|
| chmod 1 original permission dir | After setting, the last bit becomes t |
| chmod o+t dir | After setting, the last bit becomes t |
[root@foundation50 Desktop] # mkdir /linux/pub [root@foundation50 Desktop]# chmod 777 /linux/pub/ [root@foundation50 Desktop]# su -- lee uses lee users to create leefile files [lee@foundation50 Desktop]$ touch /linux/public/leefile [lee@foundation50 Desktop]$ su -- linux use linux User establishment linuxfile file [linux@foundation50 Desktop]$ touch /linux/public/linuxfile [linux@foundation50 Desktop]$ rm -fr /linux/public/linuxfile linux Users can delete their own public File in [linux@foundation50 Desktop]$ rm -fr /linux/public/leefile linux Users can delete others in public File in [root@foundation50 Desktop]# chmod o+t /linux/public / enable sticky bit [root@foundation50 Desktop]# ls -ld /linux/public/ drwxrwxrwt. 2 root root 38 Aug 16 22:08 /linux/public/ t When it appears, stick the position to open [root@foundation50 Desktop]# su -- lee [lee@foundation50 Desktop]$ rm -fr /linux/public/leefile You can delete your own files [lee@foundation50 Desktop]$ rm -fr /linux//public/linuxfile other people's files cannot be deleted rm: cannot remove '/linux//public/linuxfile': Operation not permitted error!!
8.2 forced bit sgid
For directory: the newly created files in the directory automatically belong to the group to which the directory belongs
[root@foundation50 Desktop]# mkdir /linux/sc [root@foundation50 Desktop]# chgrp shengchan /linux/sc/ [root@foundation50 Desktop]# chmod 1770 /linux/sc/ [lee@foundation50 Desktop]$ ls -ld /linux/sc/ sc The group of the directory is shengchan drwxrwx--T. 2 root shengchan 18 Aug 17 11:45 /linux/sc/ [root@foundation50 Desktop]# su -- lee switch user lee [lee@foundation50 Desktop]$ id lee uid=1001(lee) gid=1001(lee) groups=1001(lee),1004(shengchan) [lee@foundation50 Desktop]$ touch /linux/sc/file use lee User in sc Create files in the directory [lee@foundation50 Desktop]$ ls -l /linux/sc/file -rw-rw-r--. 1 lee lee 0 Aug 17 15:27 /linux/sc/file sc The newly created file in the directory does not belong to sc In the group to which you belong, but the group created by who is whose group, which is unreasonable!!! [root@foundation50 Desktop]# chmod g+s /linux/sc / open strong positions [root@foundation50 Desktop]# ls -ld /linux/sc/ drwxrws--T. 2 root shengchan 18 Aug 17 11:45 /linux/sc/ s A strong position has been opened [root@foundation50 Desktop]# su -- lee switching users [lee@foundation50 Desktop]$ touch /linux/sc/file1 stay sc create file [lee@foundation50 Desktop]$ ls -l /linux/sc/file1 -rw-rw-r--. 1 lee shengchan 0 Aug 17 15:44 /linux/sc/file1 sc New files in the directory are automatically attributed to sc The group to which the directory belongs
For files:
Only for binary executable files (c programs) (binary files: executable files formed by compiling programs written in source code)
When binary executable files are run, they all run as a file group, regardless of the execution user
[root@foundation50 Desktop]# ls -l /bin/cat the owner of binary cat program is root, and all groups are root -rwxr-xr-x. 1 root root 51856 Jan 11 2019 /bin/cat [root@foundation50 Desktop]# su -- westos switching users [westos@foundation50 Desktop]$ /bin/cat Start program generation process [westos@foundation50 Desktop]$ ps ax -o user,group,command | grep cat see cat You can find out who started the program, which is running as this user group ( ps ((process scan) ax (a = all ,x (indicates running in the background) -o (Indicates what you want to view the process) user ,group ,comm(Process name) | grep cat (To view cat use grep yes cat Filter) gdm gdm /usr/libexec/gsd-print-notifications westos westos /usr/libexec/gsd-print-notifications westos westos /usr/bin/gnome-software --gapplication-service westos westos cat westos westos cat westos westos /usr/bin/nautilus --gapplication-service westos westos /usr/bin/gedit --gapplication-service westos westos /bin/cat westos The program opened is westos Run as group westos westos grep --color=auto cat [root@foundation50 Desktop]# chmod g+s /bin/cat enable force bit [root@foundation50 Desktop]# ls -l /bin/cat -rwxr-sr-x. 1 root root 51856 Jan 11 2019 /bin/cat s Appears, forcing the bit to turn on [root@foundation50 Desktop]# su -- westos switching users [westos@foundation50 Desktop]$ /bin/cat function cat program [westos@foundation50 Desktop]# ps ax -o user,group,command |grep cat view process gdm gdm /usr/libexec/gsd-print-notifications westos westos /usr/libexec/gsd-print-notifications westos westos /usr/bin/gnome-software --gapplication-service westos root cat westos root cat westos root /bin/cat become root,Run as file owning group root root grep --color=auto cat
8.3 adventure bit suid
Adventure bit (done under super user)
Binary only executable (c program)
When binary executable files are run, they are run as the file owner, regardless of the execution user
Setting: chmod 4 original attribute file
chmod 4755 and chmod u + s are the same effect. As a result, when viewing the file with ls -l, the file name changes to red (user + s is red, group + s is yellow, and green when not added)
[westos@foundation50 Desktop]$ /bin/cat [root@foundation50 ~]# ps ax -o user,group,command | grep cat gdm gdm /usr/libexec/gsd-print-notifications westos westos /usr/libexec/gsd-print-notifications westos westos /usr/bin/gnome-software --gapplication-service westos root cat westos root cat westos westos /usr/bin/nautilus --gapplication-service westos westos /usr/bin/gedit --gapplication-service westos root /bin/cat The process started by the user is the user's westos root root grep --color=auto cat [root@foundation50 ~]# chmod u+s /bin/cat enable adventure bit [root@foundation50 ~]# su -- westos [westos@foundation50 ~]# ps ax -o user,group,command | grep cat gdm gdm /usr/libexec/gsd-print-notifications westos westos /usr/libexec/gsd-print-notifications westos westos /usr/bin/gnome-software --gapplication-service westos root cat westos root cat westos westos /usr/bin/gedit --gapplication-service root root /bin/cat Run as file owner,It has nothing to do with the execution user root root grep --color=auto c
9. acl list permission (enable acl)
| user | function |
|---|---|
| setfacl -m u: (specify user) lee:rw (authority) westosfile (for that file or directory) | #Set permissions |
| setfacl -m g:westos:rw westosfile | Set group permissions g to represent groups |
| setfacl -x u:lee westosfile | Delete lee from the list |
| setfacl -x g:caiwu westosfile | Delete financial group from list |
| setfacl -b westosfile | Turn off the list function (it can be turned off whether it is turned on or not) |
| getfacl /linux/westosfile | View permission list |
[root@foundation50 Desktop]# chmod 777 /linux/westos/ [root@foundation50 Desktop]# setfacl -m u:westos:--- /linux/westos / specify westos user permissions [root@foundation50 Desktop]# su -- westos [westos@foundation50 Desktop]$ cd /linux/ [westos@foundation50 linux]$ rm -fr westos/ rm: cannot remove 'westos/': Permission denied [root@foundation50 linux]# setfacl -m u:lee:--- /linux/westos / specify lee user permissions [root@foundation50 linux]# su -- lee [lee@foundation50 linux]$ rm -fr westos/ bash: rm-fr: command not found... [lee@foundation50 linux]$ rm -fr westos/ rm: cannot remove 'westos/': Permission denied [root@foundation50 linux]# setfacl -m g:shengchan:--- /linux/westos / specify group permissions [root@foundation50 linux]# getfacl /linux/westos / view permission list getfacl: Removing leading '/' from absolute path names # file: linux/westos/ # owner: root # group: root user::rwx user:westos:--- user:lee:--- group::rwx group:shengchan:--- mask::rwx other::rwx [root@foundation50 linux]# setfacl -x u:lee /linux/westos / delete lee [root@foundation50 linux]# setfacl -x g:shengchan /linux/westos / delete shengchan group [root@foundation50 linux]# getfacl /linux/westos/ getfacl: Removing leading '/' from absolute path names # file: linux/westos/ # owner: root # group: root user::rwx user:westos:--- group::rwx mask::rwx other::rwx
10. acl permission priority
Owner > ACL special designated user > groups with more permissions > groups with less permissions > others
11. acl mask control
mask is the maximum threshold that can be granted to a specified user
----rwx—+ 1 root caiwu 0 Apr 18 09:03 westosfile
When + appears, this is the permission value of the mask, not the permission value of the representative group
problem
After setting the acl list of files, use chmod to narrow down the file ownership group
The mask will change
Recover: setfacl - M:: permission file
[root@foundation50 Desktop]# mkdir /linux/westosfile
[root@foundation50 Desktop]# ls -ld /linux/westosfile/
drwxr-xr-x. 2 root root 6 Aug 18 10:50 /linux/westosfile/
[root@foundation50 Desktop]# setfacl -m u:westos:rwx /linux/westosfile / specify the user's westos permission and open the acl list
[root@foundation50 Desktop]# ls -ld /linux/westosfile/
drwx**rwx**r-x+ 2 root root 6 Aug 18 10:50 /linux/westosfile/ +Number appears acl List opened
representative
mask
jurisdiction
[root@foundation50 Desktop]# getfacl /linux/westosfile / view acl list
getfacl: Removing leading '/' from absolute path names
# file: linux/westosfile/
# owner: root
# group: root
user::rwx
user:westos:rwx
group::r-x
mask::rwx
other::r-x
[root@foundation50 Desktop]# chmod g-x /linux/westosfile use chmod to reduce the execution permission of the group
[root@foundation50 Desktop]# getfacl /linux/westosfile / view acl list
getfacl: Removing leading '/' from absolute path names
# file: linux/westosfile/
# owner: root
# group: root
user::rwx
user:westos:rwx #effective:rw-
group::r-x #effective:r--
mask::rw-
other::r-x
[root@foundation50 Desktop]# Setfacl - M: RWX / Linux / westosfile / restore msak permissions
[root@foundation50 Desktop]# getfacl /linux/westosfile/
getfacl: Removing leading '/' from absolute path names
# file: linux/westosfile/
# owner: root
# group: root
user::rwx
user:westos:rwx
group::r-x
mask::rwx Restore to rwx
other::r-x
[root@foundation50 Desktop]# setfacl -m g::0 /linux/westosfile / if you want to reduce the permissions of the group, set it with setfacl
[root@foundation50 Desktop]# getfacl /linux/westosfile/
getfacl: Removing leading '/' from absolute path names
# file: linux/westosfile/
# owner: root
# group: root
user::rwx
user:westos:rwx
group::--- Permission set to 0
mask::rwx
other::r-x
12. Default permissions for acl lists
| command | purpose |
|---|---|
| setfacl -m u:lee:rwx /mnt/westosdir | Only valid for the / mnt/westosdir directory itself |
| setfacl -Rm u:lee:rwx /mnt/westosdir | Takes effect for the / mnt/westosdir directory and content that already exists in the directory |
Note: the above commands are valid for existing files, and new files will not be set
| command | purpose |
|---|---|
| setfacl -m d:u:lee:rwx /mnt/westosdir/ | It takes effect for new files in / mnt/westosdir directory; d: Indicates that it only works on newly created |
[root@foundation50 Desktop]# mkdir /linux/westosdir [root@foundation50 Desktop]# touch /linux/westosdir/file [root@foundation50 Desktop]# touch /linux/westosdir/file1 [root@foundation50 Desktop]# touch /linux/westosdir/file2 [root@foundation50 Desktop]# setfacl -m u:westos:rwx /linux/westosdir / only the acl permission is enabled on the directory itself, and the files in the directory are not opened Every 2.0s: ls -lR /l... foundation50.ilt.example.com: Wed Aug 18 15:28:42 2021 /linux/: total 0 drwxrwxr-x+ 2 root root 44 Aug 18 15:24 westosdir /linux/westosdir: total 0 -rw-r--r--. 1 root root 0 Aug 18 15:24 file -rw-r--r--. 1 root root 0 Aug 18 15:24 file1 -rw-r--r--. 1 root root 0 Aug 18 15:24 file2 [root@foundation50 Desktop]# setfacl -Rm u:westos:rwx /linux/westosdir / the directory itself and its files have acl list permissions enabled Every 2.0s: ls -lR /l... foundation50.ilt.example.com: Wed Aug 18 15:35:43 2021 /linux/: total 0 drwxrwxr-x+ 2 root root 44 Aug 18 15:24 westosdir /linux/westosdir: total 0 -rw-rwxr--+ 1 root root 0 Aug 18 15:24 file -rw-rwxr--+ 1 root root 0 Aug 18 15:24 file1 -rw-rwxr--+ 1 root root 0 Aug 18 15:24 file2 [root@foundation50 Desktop]# touch /linux/westosdir/file3 open the acl list and then create a new file Every 2.0s: ls -lR /l... foundation50.ilt.example.com: Wed Aug 18 15:37:35 2021 /linux/: total 0 drwxrwxr-x+ 2 root root 57 Aug 18 15:36 westosdir /linux/westosdir: total 0 -rw-rwxr--+ 1 root root 0 Aug 18 15:24 file -rw-rwxr--+ 1 root root 0 Aug 18 15:24 file1 -rw-rwxr--+ 1 root root 0 Aug 18 15:24 file2 -rw-r--r--. 1 root root 0 Aug 18 15:36 file3 The new file is not open acl list How to make the new file effective acl List permissions?? [root@foundation50 Desktop]# Setfacl - M D: u: westos: RWX / Linux / westosdir / - D means to work on new files [root@foundation50 Desktop]# touch /linux/westosdir/file4 create a new file Every 2.0s: ls -lR /l... foundation50.ilt.example.com: Wed Aug 18 15:42:56 2021 /linux/: total 0 drwxrwxr-x+ 2 root root 70 Aug 18 15:40 westosdir /linux/westosdir: total 0 -rw-rwxr--+ 1 root root 0 Aug 18 15:24 file -rw-rwxr--+ 1 root root 0 Aug 18 15:24 file1 -rw-rwxr--+ 1 root root 0 Aug 18 15:24 file2 -rw-r--r--. 1 root root 0 Aug 18 15:36 file3 -rw-rw-r--+ 1 root root 0 Aug 18 15:40 file4 The new file is also opened acl list
13. attr permissions
Problem: a super user can create and delete files and directories even if he has no authority
Solution: attr permission can restrict all users
Setting method:
| command | function |
|---|---|
| chattr +i file | No changes can be made (no one can change it, but you can see it) |
| chattr +a | Can you add or delete |
| lsattr dir/file | View attr permissions |
| lsatter -d dir | The right to view the directory |
[root@foundation50 Desktop]# mkdir /linux/test [root@foundation50 Desktop]# ls -ld /linux/test/ drwxr-xr-x. 2 root root 6 Aug 18 16:01 /linux/test/ [root@foundation50 Desktop]# touch /linux/test/file [root@foundation50 Desktop]# rm -fr /linux/test/file [root@foundation50 Desktop]# Chatr + A / Linux / test / can be added or deleted [root@foundation50 Desktop]# lsattr -d /linux/test/ -----a-------------- /linux/test/ take effect [root@foundation50 Desktop]# touch /linux/test/file can be established [root@foundation50 Desktop]# rm -fr /linux/test/file cannot be deleted rm: cannot remove '/linux/test/file': Operation not permitted [root@foundation50 Desktop]# Chatr - A / Linux / test / minus a [root@foundation50 Desktop]# rm -fr /linux/test/file to delete the file [root@foundation50 Desktop]# Chatr + I / Linux / test / can't make any changes. You can only see [root@foundation50 Desktop]# lsattr -d /linux/test / view ----i--------------- /linux/test/ [root@foundation50 test]# touch /linux/test/file cannot be created touch: setting times of '/linux/test/file': No such file or directory [root@foundation50 test]# rm -fr /linux/test/file cannot be deleted rm: cannot remove '/linux/test/file': Operation not permitted