Definition:
The so-called linked list means that in the process of storing data in a node, there is also an attribute to point to the next linked list node. Such a data storage method is called linked list
Advantages and disadvantages of linked list:
Advantages: easy to store and delete
Disadvantage: it's troublesome to query
We use java to implement the following linked list structure:
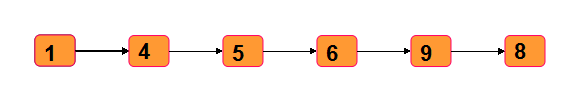
First, define the node class:
package LinkTest; /** * Link list node class * @author admin * */ public class Node { private int value;//Store data private Node next;//Next node /** * Define constructor * @param vlaue * @param value */ public Node(int value){ this.value=value; } public int getValue() { return value; } public void setValue(int value) { this.value = value; } public Node getNext() { return next; } public void setNext(Node next) { this.next = next; } }
Then define a linked list class:
*Note: two methods are defined for traversing the linked list, one is common method and the other is recursive method, which can be traversed
package LinkTest; /** * Linked list * @author admin * */ public class Link { private Node current; private Node root; public void insert(int vlaue){ Node newNode=new Node(vlaue); if(this.current==null){ this.current=newNode; this.root=this.current; }else{ this.current.setNext(newNode); this.current=this.current.getNext(); } } //Ordinary traversal public void getList(){ this.current=this.root; while(this.current!=null){ System.out.print(this.current.getValue()); this.current=this.current.getNext(); if(this.current!=null){ System.out.print("------->"); } } } //Recursive traversal public void getList2(){ DG(this.root); } //Recursive Method public void DG(Node node){ System.out.print(node.getValue()+"----->"); if(node.getNext()!=null){ DG(node.getNext()); }else{ return; } } }
Test class:
package LinkTest; /** * Test class * @author admin * */ public class Test { public static void main(String[] args){ Link l=new Link(); l.insert(1); l.insert(4); l.insert(5); l.insert(6); l.insert(9); l.insert(8); l.getList(); } }
Test class run results:
1------->4------->5------->6------->9------->8
In this way, we use java to implement a simple linked list structure.