Article directory
- 1, configuration
- 2. Installation module:
- 3. Reading and writing:
- 4. Read all rows under all worksheets of an Excel table
- 5. Merge all worksheets under an Excel table (or merge multiple Excel tables can also refer to this method)
- 6. Read all columns of all worksheets under an Excel table
- 7. Specify columns to merge all worksheets under Excel tables (or merge multiple Excels)
- Reference resources:
1, configuration
- Windows 10 System
- python3.6
2. Installation module:
pip install openpyxl
3. Reading and writing:
Note 1:
When writing to a date, you need to convert it to a string to write, otherwise the cell opening the date will be displayed as scrambled code.
Note 2:
If the saved excel form exists and your computer is turned on, an error will be reported:
PermissionError: [Errno 13] Permission denied: 'sample.xlsx'

3. demo code:
Referring to the official amendments:
https://pypi.org/project/openpyxl/
import datetime
from openpyxl import Workbook
wb = Workbook()
# grab the active worksheet
ws = wb.active
# Data can be assigned directly to cells
ws['A1'] = 42
# Rows can also be appended
ws.append([1, 2, 3])
# Python types will automatically be converted
data = datetime.datetime.today()
print("data1",data,type(data))
data,time1 = str(data).split(' ')
# Note that I am converting to string writing, if not converting, excel is scrambled, you can try it yourself.
ws['A2'] = data
print(data)
# Save the file
wb.save("sample.xlsx")
4. Read all rows under all worksheets of an Excel table
Sensitive Face-Star Face list0709.xlsx File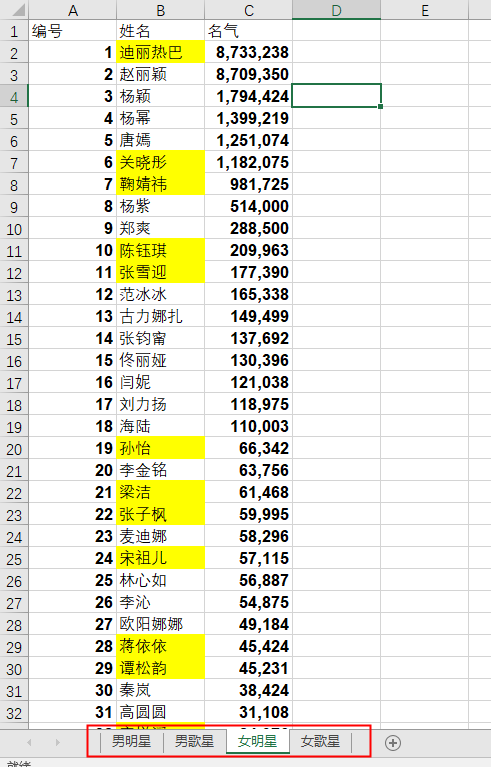
Specific explanations I put in the code, but here's just a few more explanations.
from openpyxl import load_workbook
wb = load_workbook("Sensitive face-Star face list0709.xlsx")
print(wb.sheetnames)
# Read the names of all worksheets
sheetnames = wb.sheetnames
for name in sheetnames:
# Getting the worksheet wb.get_sheet_by_name(name) by the name of the worksheet is equivalent to wb[name]
# sheet = wb.get_sheet_by_name(name)
sheet = wb[name]
# Get the maximum number of rows
print(sheet.max_row)
# Print all attributes
print(dir(sheet))
# Read all rows of a worksheet
rows = sheet.iter_rows()
print(rows, type(rows))
# Traverse all rows
for one in rows:
print(one)
print(dir(one))
# Traverse all columns of all rows
for cell in one:
# Print the values of all columns under each row
print(cell.value)
break
5. Merge all worksheets under an Excel table (or merge multiple Excel tables can also refer to this method)
Hint, I'm just doing a test here. This method can be merged. In fact, it can be modified according to the need. (For example, if you don't need to write the first row of each worksheet, you can judge when you write. If the list is equal to the first row, you don't write it. If you insert a row into the mouth and a whole table, it's ok ay. Others can also refer to this method to get the data dirty merged.)
Bring code directly:
from openpyxl import load_workbook, Workbook
# Instantiate the file to be written
hebing_wb = Workbook()
# Activate worksheet
hebing_ws = hebing_wb.active
wb = load_workbook("Sensitive face-Star face list0709.xlsx")
print(wb.sheetnames)
# Read the names of all worksheets
sheetnames = wb.sheetnames
for name in sheetnames:
# Getting the worksheet wb.get_sheet_by_name(name) by the name of the worksheet is equivalent to wb[name]
# sheet = wb.get_sheet_by_name(name)
sheet = wb[name]
# Get the maximum number of rows
print(sheet.max_row)
max_row = sheet.max_row
# Print all attributes
print(dir(sheet))
# Read all rows of a worksheet
rows = sheet.iter_rows()
print(rows, type(rows))
# Traverse all rows
for one in rows:
one_row = []
for cell in one:
one_row.append(cell.value)
hebing_ws.append(one_row)
# Save the merged table
hebing_wb.save('hebing.xlsx')
After the merger effect display: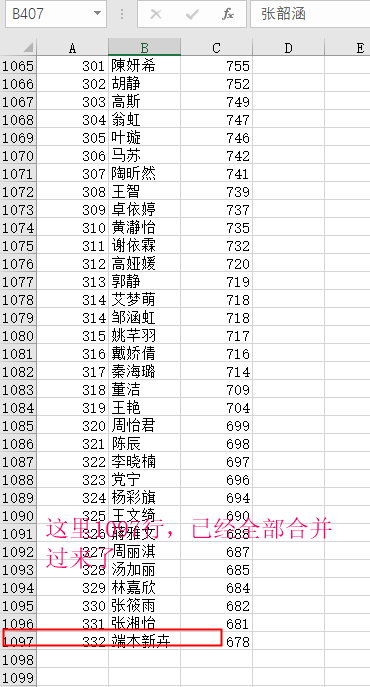
6. Read all columns of all worksheets under an Excel table
Go directly to the code, explain and read the code notes.
from openpyxl import load_workbook
wb = load_workbook("Sensitive face-Star face list0709.xlsx")
print(wb.sheetnames)
# Read the names of all worksheets
sheetnames = wb.sheetnames
for name in sheetnames:
# Getting the worksheet wb.get_sheet_by_name(name) by the name of the worksheet is equivalent to wb[name]
# sheet = wb.get_sheet_by_name(name)
sheet = wb[name]
# Get the maximum number of rows
print(sheet.max_row)
# Print all attributes
print(dir(sheet))
# Read all columns of a worksheet
columns = sheet.iter_cols()
print(columns, type(columns))
# Traverse all columns
for one in columns:
print(one)
# print(dir(one))
# Traversing the cells of all columns
for cell in one:
# Print the values of all cells under each column
print(cell.value)
break
7. Specify columns to merge all worksheets under Excel tables (or merge multiple Excels)
Direct to my code:
from openpyxl import load_workbook,Workbook
# Instantiate the file to be written
hebing_wb = Workbook()
# Activate worksheet
hebing_ws = hebing_wb.active
wb = load_workbook("Sensitive face-Star face list0709.xlsx")
print(wb.sheetnames)
# Read the names of all worksheets
sheetnames = wb.sheetnames
for name in sheetnames:
# Getting the worksheet wb.get_sheet_by_name(name) by the name of the worksheet is equivalent to wb[name]
# sheet = wb.get_sheet_by_name(name)
sheet = wb[name]
# Get the maximum number of rows
print(sheet.max_row)
# Print all attributes
print(dir(sheet))
# Read all columns of a worksheet
columns = sheet.iter_cols()
print(columns, type(columns))
# Traverse all columns
for one in columns:
print(one)
# print(dir(one))
# Traversing the cells of all columns
print(one[0].value)
if one[0].value == 'Full name':
# print("is a name column")
for cell in one:
# Print the values of all cells under each column
# print("is the name column cell",cell.value)
value = cell.value
if value != 'Full name':
print("value2",value)
# Write the name of each worksheet into the new Excel table
hebing_ws.append([value])
# break
# Save the merged table
hebing_wb.save('hebing2.xlsx')
Design sketch: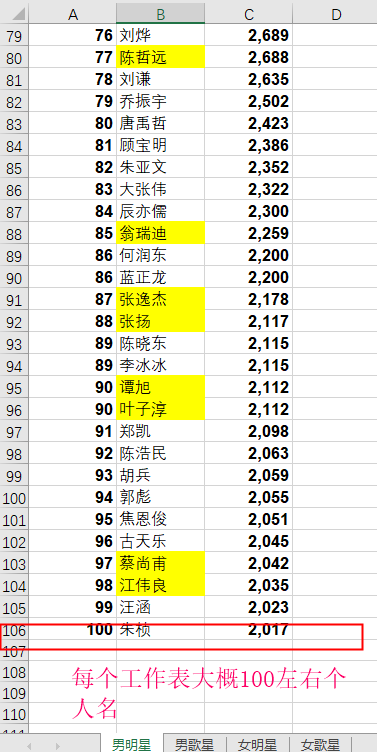
After the merger: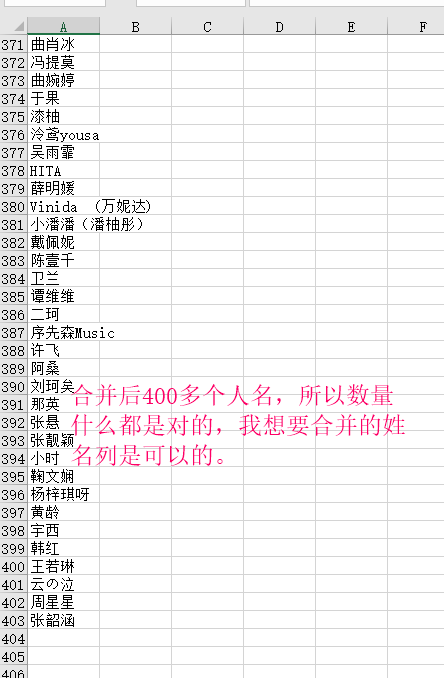
Of course, this effect, if the number is very small and there is no need to merge with code, but if there are many tables that need to be merged and many rows per table, the code operation will be very fast, and the advantage will be reflected.
Reference resources:
https://blog.csdn.net/weixin_43094965/article/details/82226263
https://blog.csdn.net/longshenlmj/article/details/51706010
https://blog.csdn.net/dongfei2033/article/details/79743067
https://pypi.org/project/openpyxl/