I. objectives
When browsing a web page, you can capture which element you see as a picture, no matter how long it is
II. Tools used and third party libraries
python ,PIL,selenium
pycharm
III. code part
Overall idea of long screenshot:
1. Get element
2. Move, screenshot, move, screenshot to the bottom of the element
3. Cut the screenshot according to the location of the element, and only keep the element in all the pictures
4. stitching
If the driver is in the environment variable, the path is not specified
b=webdriver.Chrome(executable_path=r"C:\Users\Desktop\chromedriver.exe")#Specify driver b.get("https://www.w3school.com.cn/html/html_links.asp") b.maximize_window()#maximize window
Open web site
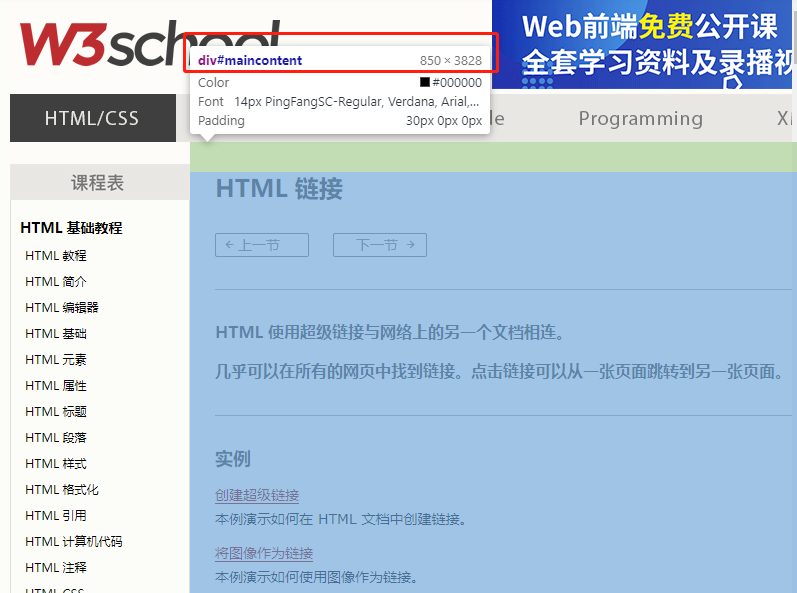
We can see an element with ID of maincontent, with width of 850PX and length of 3828PX. This length must be used to complete the screenshot
el=b.find_element_by_id("maincontent")#Find elements
We also need an important parameter, which is how high pixels can your computer intercept at a time
First, use the following code to get a picture
#fp Is the address where the picture is stored b.get_screenshot_as_file(fp)
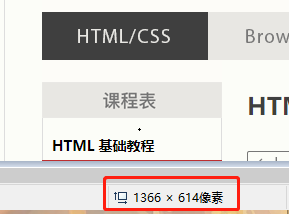
That is to say, the default height of the screenshot on my computer is 614 pixels
So I set a variable:
sc_hight=614
Then set the other variables
count = int(el.size["height"] / sc_hight) # The height of the element divided by the number of times you cut each time start_higth = el.location["y"] # Initial height of element max_px = start_higth + (count - 1) * sc_hight # for The largest in the cycle px last_px = el.size["height"] + start_higth - sc_hight # The lowest position of an element surplus_px = last_px - max_px # Height of remaining edges img_path = [] # Used to store image address
Notes:
1.count is the height of the element / the height of each intercept. For example, in this instance, the height of the element is 3828PX. I need to intercept 614px 6.2 times. After int, it becomes 6, that is to say, 6 times. There is still a little bit left. That will be discussed later
2. Start_hith is the initial height, which has nothing to say
3. Max? PX is the height reached after the end of the cycle
4. Last Pu x is the height at the bottom of the element
5. Surplus? PX is the height that has not been intercepted after six times of movement
Each time the screen moves, move sc_uhigh pixels, and the initial position is (0, Y value of the element)
for i in range(0, count): js = "scrollTo(0,%s)" % (start_higth + i * sc_hight) # For moving the pulley, each time 614 px,The initial value is the initial height of the element b.execute_script(js) # implement js time.sleep(0.5) fp = r"C:\Users\wdj\Desktop\%s.png" % i # Picture address, if running, change it b.get_screenshot_as_file(fp) # Screenshots,Here is the screenshot. It's a complete picture of the web page. You can interrupt and take a look at the picture img = Image.open(fp=fp) img2 = img.crop((el.location["x"], 0, el.size["width"] + el.location["x"], sc_hight)) # Cut pictures img2.save(fp) # Save the picture and cover the complete picture of the web page img_path.append(fp) # Add picture path time.sleep(0.5) print(js) else: js = "scrollTo(0,%s)" % last_px # Scroll to the last position b.execute_script(js) fp = r"C:\Users\wdj\Desktop\last.png" b.get_screenshot_as_file(fp) img = Image.open(fp=fp) print((el.location["x"], sc_hight - surplus_px, el.size["width"] + el.location["x"], sc_hight)) img2 = img.crop((el.location["x"], sc_hight - surplus_px, el.size["width"] + el.location["x"], sc_hight)) img2.save(fp) img_path.append(fp) print(js)
The above is to cut all the elements on the page, cut them, and put the path saved in the image into img [u path]
Last step: paste all screenshots into the newly created image
new_img = Image.new("RGB", (el.size["width"], el.size["height"])) # Create a new picture,Size is the size of the element k = 0 for i in img_path: tem_img = Image.open(i) new_img.paste(tem_img, (0, sc_hight * k)) # Put the picture on,Distance between screenshots k += 1 else: new_img.save(r"C:\Users\wdj\Desktop\test.png") # Preservation
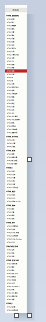
Operation rendering:

It's a complete capture
Supplementary Optimization:
What if it's a small element? It can be captured without a long screenshot
Because it's so simple, I just post the code
start_higth = el.location["y"] js = "scrollTo(0,%s)" % (start_higth) b.execute_script(js) # implement js time.sleep(0.5) fp = r"C:\Users\wdj\Desktop\test.png" # Picture address, if running, change it b.get_screenshot_as_file(fp) img = Image.open(fp=fp) img2 = img.crop((el.location["x"], 0, el.size["width"] + el.location["x"], el.size["height"])) # Cut pictures img2.save(fp)
The effect is as follows:

Full code:
Complete code from selenium import webdriver from PIL import Image import time def short_sc(el,b): start_higth = el.location["y"] js = "scrollTo(0,%s)" % (start_higth) b.execute_script(js) # implement js time.sleep(0.5) fp = r"C:\Users\wdj\Desktop\test.png" # Picture address, if running, change it b.get_screenshot_as_file(fp) img = Image.open(fp=fp) img2 = img.crop((el.location["x"], 0, el.size["width"] + el.location["x"], el.size["height"])) # Cut pictures img2.save(fp) def long_sc(el,b): count = int(el.size["height"] / sc_hight) # The height of the element divided by the number of times you cut each time start_higth = el.location["y"] # Initial height of element max_px = start_higth + (count - 1) * sc_hight # for The largest in the cycle px last_px = el.size["height"] + start_higth - sc_hight # The lowest position of an element surplus_px = last_px - max_px # Height of remaining edges img_path = [] # Used to store image address for i in range(0, count): js = "scrollTo(0,%s)" % (start_higth + i * sc_hight) # For moving the pulley, each time 614 px,The initial value is the initial height of the element b.execute_script(js) # implement js time.sleep(0.5) fp = r"C:\Users\wdj\Desktop\%s.png" % i # Picture address, if running, change it b.get_screenshot_as_file(fp) # Screenshots,Here is the screenshot. It's a complete picture of the web page. You can interrupt and take a look at the picture img = Image.open(fp=fp) img2 = img.crop((el.location["x"], 0, el.size["width"] + el.location["x"], sc_hight)) # Cut pictures img2.save(fp) # Save the picture and cover the complete picture of the web page img_path.append(fp) # Add picture path time.sleep(0.5) print(js) else: js = "scrollTo(0,%s)" % last_px # Scroll to the last position b.execute_script(js) fp = r"C:\Users\wdj\Desktop\last.png" b.get_screenshot_as_file(fp) img = Image.open(fp=fp) print((el.location["x"], sc_hight - surplus_px, el.size["width"] + el.location["x"], sc_hight)) img2 = img.crop((el.location["x"], sc_hight - surplus_px, el.size["width"] + el.location["x"], sc_hight)) img2.save(fp) img_path.append(fp) print(js) new_img = Image.new("RGB", (el.size["width"], el.size["height"])) # Create a new picture,Size is the size of the element k = 0 for i in img_path: tem_img = Image.open(i) new_img.paste(tem_img, (0, sc_hight * k)) # Put the picture on it,Distance between screenshots k += 1 else: new_img.save(r"C:\Users\wdj\Desktop\test.png") # Preservation b=webdriver.Chrome(executable_path=r"C:\Users\wdj\Desktop\chromedriver.exe")#Specify driver b.get("https://www.w3school.com.cn/html/html_links.asp") b.maximize_window()#maximize window # b.get_screenshot_as_file(fp) sc_hight=614#The default size of your screenshot. You can take a screenshot and draw it to see how many pixels it is. Here is 614 pixels # b.switch_to.frame(b.find_element_by_xpath('//*[@id="intro"]/iframe')) el=b.find_element_by_id("maincontent")#Find elements if el.size["height"]>sc_hight: long_sc(el,b) else: short_sc(el,b)
from selenium import webdriver from PIL import Image import time def short_sc(el,b): start_higth = el.location["y"] js = "scrollTo(0,%s)" % (start_higth) b.execute_script(js) # implement js time.sleep(0.5) fp = r"C:\Users\wdj\Desktop\test.png" # Picture address, if running, change it b.get_screenshot_as_file(fp) img = Image.open(fp=fp) img2 = img.crop((el.location["x"], 0, el.size["width"] + el.location["x"], el.size["height"])) # Cut pictures img2.save(fp) def long_sc(el,b): count = int(el.size["height"] / sc_hight) # The height of the element divided by the number of times you cut each time start_higth = el.location["y"] # Initial height of element max_px = start_higth + (count - 1) * sc_hight # for The largest in the cycle px last_px = el.size["height"] + start_higth - sc_hight # The lowest position of an element surplus_px = last_px - max_px # Height of remaining edges img_path = [] # Used to store image address for i in range(0, count): js = "scrollTo(0,%s)" % (start_higth + i * sc_hight) # For moving the pulley, each time 614 px,The initial value is the initial height of the element b.execute_script(js) # implement js time.sleep(0.5) fp = r"C:\Users\wdj\Desktop\%s.png" % i # Picture address, if running, change it b.get_screenshot_as_file(fp) # Screenshots,Here is the screenshot. It's a complete picture of the web page. You can interrupt and take a look at the picture img = Image.open(fp=fp) img2 = img.crop((el.location["x"], 0, el.size["width"] + el.location["x"], sc_hight)) # Cut pictures img2.save(fp) # Save the picture and cover the complete picture of the web page img_path.append(fp) # Add picture path time.sleep(0.5) print(js) else: js = "scrollTo(0,%s)" % last_px # Scroll to the last position b.execute_script(js) fp = r"C:\Users\wdj\Desktop\last.png" b.get_screenshot_as_file(fp) img = Image.open(fp=fp) print((el.location["x"], sc_hight - surplus_px, el.size["width"] + el.location["x"], sc_hight)) img2 = img.crop((el.location["x"], sc_hight - surplus_px, el.size["width"] + el.location["x"], sc_hight)) img2.save(fp) img_path.append(fp) print(js) new_img = Image.new("RGB", (el.size["width"], el.size["height"])) # Create a new picture,Size is the size of the element k = 0 for i in img_path: tem_img = Image.open(i) new_img.paste(tem_img, (0, sc_hight * k)) # Put the picture on it,Distance between screenshots k += 1 else: new_img.save(r"C:\Users\wdj\Desktop\test.png") # Preservation b=webdriver.Chrome(executable_path=r"C:\Users\wdj\Desktop\chromedriver.exe")#Specify driver b.get("https://www.w3school.com.cn/html/html_links.asp") b.maximize_window()#maximize window # b.get_screenshot_as_file(fp) sc_hight=614#The default size of your screenshot. You can take a screenshot and draw it to see how many pixels it is. Here is 614 pixels # b.switch_to.frame(b.find_element_by_xpath('//*[@id="intro"]/iframe')) el=b.find_element_by_id("maincontent")#Find elements if el.size["height"]>sc_hight: long_sc(el,b) else: short_sc(el,b)