1. What is Shell
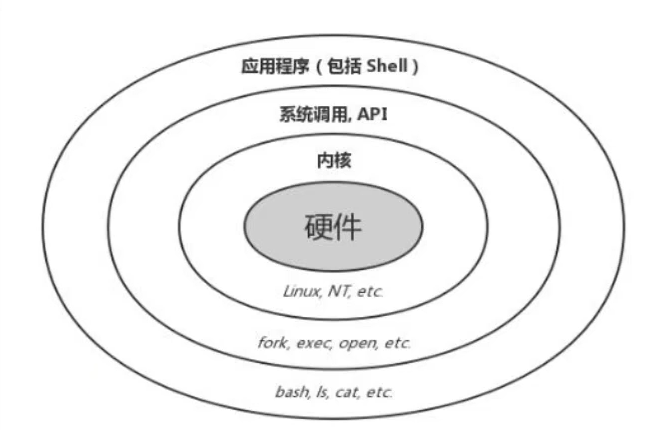
- Externally accept commands entered by users
- Internally, it is passed to the kernel through system calls
- Rendering kernel running results
2. Shell and graphical interface
Graphical interface, mainly mouse operation, easy to learn.
Shell: keyboard operation is the main operation, and various control commands need to be memorized
3. Common commands



Note: the mv command is used to rename files and directories / move files and directories, and the rmdir command can only be used to delete empty directories

be careful:
The touch command is used to create a file
cat commands the user to display the contents of the file
The echo command is used to output a string to the console terminal and reposition the string
[root@iZuf6a7sd2zy3fpen7rmbhZ ~]# Echo 123 > > 123.txt / / append a string to the end of the file [root@iZuf6a7sd2zy3fpen7rmbhZ ~]# ls 123.txt learn serverProject softWare tools [root@iZuf6a7sd2zy3fpen7rmbhZ ~]# cat 123.txt 123 [root@iZuf6a7sd2zy3fpen7rmbhZ ~]# echo hhh >> 123.txt [root@iZuf6a7sd2zy3fpen7rmbhZ ~]# cat 123.txt 123 hhh [root@iZuf6a7sd2zy3fpen7rmbhZ ~]# Echo siglg > 123. TXT / / empty the contents of the file and fill in the contents [root@iZuf6a7sd2zy3fpen7rmbhZ ~]# cat 123.txt siglg
The wc command is used to count the number of lines (- l) words (- w) characters (- c) in a file
The rm command can delete either the directory rm -r or the file
ln command is used to create linked files for files. Linked files can be divided into hard linked files and soft linked files
[root@iZuf6a7sd2zy3fpen7rmbhZ ~]# Ln 123.txt 456 / / used to create a hard link for a file. The so-called hard link means that after the source file 123.txt is deleted, the 456 copy can be output normally [root@iZuf6a7sd2zy3fpen7rmbhZ ~]# ls 123.txt 456 learn serverProject softWare tools [root@iZuf6a7sd2zy3fpen7rmbhZ ~]# ll total 24 -rw-r--r-- 2 root root 6 Nov 29 21:57 123.txt -rw-r--r-- 2 root root 6 Nov 29 21:57 456 drwxr-xr-x 4 root root 4096 Dec 1 09:52 learn drwxr-xr-x 6 root root 4096 Jul 26 19:38 serverProject drwxr-xr-x 2 root root 4096 Nov 8 11:54 softWare drwxr-xr-x 4 root root 4096 Mar 7 2021 tools [root@iZuf6a7sd2zy3fpen7rmbhZ ~]# [root@iZuf6a7sd2zy3fpen7rmbhZ ~]# ln -s 456 789 / / establish a soft connection. The so-called soft connection means that the 789 soft connection is invalid after the source file 456 is deleted [root@iZuf6a7sd2zy3fpen7rmbhZ ~]# [root@iZuf6a7sd2zy3fpen7rmbhZ ~]# ll total 20 -rw-r--r-- 1 root root 6 Nov 29 21:57 456 lrwxrwxrwx 1 root root 3 Dec 1 11:37 789 -> 456 drwxr-xr-x 4 root root 4096 Dec 1 09:52 learn drwxr-xr-x 6 root root 4096 Jul 26 19:38 serverProject drwxr-xr-x 2 root root 4096 Nov 8 11:54 softWare drwxr-xr-x 4 root root 4096 Mar 7 2021 tools [root@iZuf6a7sd2zy3fpen7rmbhZ ~]# rm -f 456 [root@iZuf6a7sd2zy3fpen7rmbhZ ~]# ll total 16 lrwxrwxrwx 1 root root 3 Dec 1 11:37 789 -> 456 drwxr-xr-x 4 root root 4096 Dec 1 09:52 learn drwxr-xr-x 6 root root 4096 Jul 26 19:38 serverProject drwxr-xr-x 2 root root 4096 Nov 8 11:54 softWare drwxr-xr-x 4 root root 4096 Mar 7 2021 tools [root@iZuf6a7sd2zy3fpen7rmbhZ ~]# cat 789 cat: 789: No such file or directory
The cp command is used to copy files. cp -r can copy folders
The tar command is used to package and unpack, and is not responsible for compression
tar -cvf file name => Packed File tar -xvf file name => Unzip file tar -tvf file name => List archived documents in detail
The find command can quickly find the file path of the file we need
[root@iZuf6a7sd2zy3fpen7rmbhZ ~]# find / -name learn /root/learn [root@iZuf6a7sd2zy3fpen7rmbhZ ~]# ls learn serverProject softWare tools
The grep command can help us find the string we need from the text
[root@iZuf6a7sd2zy3fpen7rmbhZ ~]# grep "Linux" 123.txt I love Linux [root@iZuf6a7sd2zy3fpen7rmbhZ ~]# grep "Linux" 123.txt -n // -n stands for the positioning line number 1:I love Linux
The sudo command helps ordinary users gain root privileges briefly
su command can realize user switching
The useradd command only creates the simplest and most basic user, and some user related configuration information is not initialized (password and home directory are not set).
The adduser command will guide you through user configuration during creation. After testing, it is found that the two user creation commands are the same in some Linux systems.
Modify GID with usermod command
[root@iZuf6a7sd2zy3fpen7rmbhZ ~]# cat /etc/passwd xiaoming:x:1004:1004::/home/xiaoming:/bin/bash xiaowu:x:1005:1005::/home/xiaowu:/bin/bash [root@iZuf6a7sd2zy3fpen7rmbhZ ~]# usermod -g 1004 xiaowu [root@iZuf6a7sd2zy3fpen7rmbhZ ~]# cat /etc/passwd xiaoming:x:1004:1004::/home/xiaoming:/bin/bash xiaowu:x:1005:1004::/home/xiaowu:/bin/bash
The deluser command is used to delete a user
The passwd command is used to change the user password
[root@iZuf6a7sd2zy3fpen7rmbhZ ~]# passwd xiaoming Changing password for user xiaoming. New password: BAD PASSWORD: The password is shorter than 8 characters Retype new password: passwd: all authentication tokens updated successfully.
The groupadd command is used to add user groups. The added user groups can be viewed in / etc/group
[root@iZuf6a7sd2zy3fpen7rmbhZ ~]# groupadd test [root@iZuf6a7sd2zy3fpen7rmbhZ ~]# cat /etc/group test:x:1006:
The groupdel command is used to delete user groups
[root@iZuf6a7sd2zy3fpen7rmbhZ ~]# cat /etc/group root:x:0: bin:x:1: daemon:x:2: sys:x:3: adm:x:4: tty:x:5: disk:x:6: lp:x:7: mem:x:8: kmem:x:9: wheel:x:10: cdrom:x:11: mail:x:12:postfix man:x:15: dialout:x:18: floppy:x:19: games:x:20: tape:x:33: video:x:39: ftp:x:50: lock:x:54: audio:x:63: nobody:x:99: users:x:100: utmp:x:22: utempter:x:35: input:x:999: systemd-journal:x:190: systemd-network:x:192: dbus:x:81: polkitd:x:998: ssh_keys:x:997: sshd:x:74: postdrop:x:90: postfix:x:89: chrony:x:996: ntp:x:38: tcpdump:x:72: nscd:x:28: yiwen:x:1000: yiwen3:x:1002: yiqi:x:1003: xiaoming:x:1004: xiaowu:x:1005:

[root@iZuf6a7sd2zy3fpen7rmbhZ ~]# ll total 20 -rw-r--r-- 1 root root 13 Dec 1 11:54 123.txt -: Ordinary file rw-: Represents the readable and writable binary correspondence 110 of personal user rights => Decimal correspondence 6 r--: Indicates user group permissions r--: Indicates other user permissions
chmod modify file permissions
[root@iZuf6a7sd2zy3fpen7rmbhZ ~]# ll total 20 -rw-r--r-- 1 root root 13 Dec 1 11:54 123.txt drwxr-xr-x 4 root root 4096 Dec 1 09:52 learn drwxr-xr-x 6 root root 4096 Jul 26 19:38 serverProject drwxr-xr-x 2 root root 4096 Nov 8 11:54 softWare drwxr-xr-x 4 root root 4096 Mar 7 2021 tools [root@iZuf6a7sd2zy3fpen7rmbhZ ~]# chmod 777 123.txt [root@iZuf6a7sd2zy3fpen7rmbhZ ~]# ll total 20 -rwxrwxrwx 1 root root 13 Dec 1 11:54 123.txt drwxr-xr-x 4 root root 4096 Dec 1 09:52 learn drwxr-xr-x 6 root root 4096 Jul 26 19:38 serverProject drwxr-xr-x 2 root root 4096 Nov 8 11:54 softWare drwxr-xr-x 4 root root 4096 Mar 7 2021 tools [root@iZuf6a7sd2zy3fpen7rmbhZ ~]#
The chown command modifies the file owner
[root@iZuf6a7sd2zy3fpen7rmbhZ ~]# ll total 20 -rwxrwxrwx 1 root root 13 Dec 1 11:54 123.txt drwxr-xr-x 4 root root 4096 Dec 1 09:52 learn drwxr-xr-x 6 root root 4096 Jul 26 19:38 serverProject drwxr-xr-x 2 root root 4096 Nov 8 11:54 softWare drwxr-xr-x 4 root root 4096 Mar 7 2021 tools [root@iZuf6a7sd2zy3fpen7rmbhZ ~]# chown yiqi 123.txt [root@iZuf6a7sd2zy3fpen7rmbhZ ~]# ll total 20 -rwxrwxrwx 1 yiqi root 13 Dec 1 11:54 123.txt drwxr-xr-x 4 root root 4096 Dec 1 09:52 learn drwxr-xr-x 6 root root 4096 Jul 26 19:38 serverProject drwxr-xr-x 2 root root 4096 Nov 8 11:54 softWare drwxr-xr-x 4 root root 4096 Mar 7 2021 tools
The chgrp command is used to modify the user group to which the file belongs
[root@iZuf6a7sd2zy3fpen7rmbhZ ~]# ll total 20 -rwxrwxrwx 1 yiqi root 13 Dec 1 11:54 123.txt drwxr-xr-x 4 root root 4096 Dec 1 09:52 learn drwxr-xr-x 6 root root 4096 Jul 26 19:38 serverProject drwxr-xr-x 2 root root 4096 Nov 8 11:54 softWare drwxr-xr-x 4 root root 4096 Mar 7 2021 tools [root@iZuf6a7sd2zy3fpen7rmbhZ ~]# chgrp yiqi 123.txt [root@iZuf6a7sd2zy3fpen7rmbhZ ~]# ll total 20 -rwxrwxrwx 1 yiqi yiqi 13 Dec 1 11:54 123.txt drwxr-xr-x 4 root root 4096 Dec 1 09:52 learn drwxr-xr-x 6 root root 4096 Jul 26 19:38 serverProject drwxr-xr-x 2 root root 4096 Nov 8 11:54 softWare drwxr-xr-x 4 root root 4096 Mar 7 2021 tools

The df command is used to display information about the file system
[root@iZuf6a7sd2zy3fpen7rmbhZ ~]# df Filesystem 1K-blocks Used Available Use% Mounted on /dev/vda1 41147472 4998956 34245024 13% / devtmpfs 877748 0 877748 0% /dev tmpfs 888200 0 888200 0% /dev/shm tmpfs 888200 476 887724 1% /run tmpfs 888200 0 888200 0% /sys/fs/cgroup tmpfs 177644 0 177644 0% /run/user/0 [root@iZuf6a7sd2zy3fpen7rmbhZ ~]# df -h Filesystem Size Used Avail Use% Mounted on /dev/vda1 40G 4.8G 33G 13% / devtmpfs 858M 0 858M 0% /dev tmpfs 868M 0 868M 0% /dev/shm tmpfs 868M 476K 867M 1% /run tmpfs 868M 0 868M 0% /sys/fs/cgroup tmpfs 174M 0 174M 0% /run/user/0
The du command summarizes disk information
[root@iZuf6a7sd2zy3fpen7rmbhZ ~]# du -sh // -s means that only the current folder is displayed, not to the file - h means that the size is displayed in the way that humans are used to 1.7G .
The mount command is mainly used to mount some hardware devices / network devices under the specified directory of the system. After mounting, you can access the hardware devices or network devices through the specified directory
Usage: mount [-lhV] mount -a [options] mount [options] [--source] <source> | [--target] <directory> mount [options] <source> <directory> mount <operation> <mountpoint> [<target>]
The umount command is used to unmount
Usage: umount [-hV] umount -a [options] umount [options] <source> | <directory>

ifconfig //View device network information ifconfig Network card name IP address //Replace the network card IP address ifconfig Network card name down //Stop network card ifconfig Network card name up //boot adapter
