Here we introduce some geometry provided by threejs:
- Planegeometry (plane)
- CircleGeometry (circle)
- Shapeometry (shaping)
- Cube geometry
- Sphereometry (sphere)
- Cylinder geometry
- Torusgeometry (torusgeometry)
- Torus knot geometry
- Polyhedron geometry
- Icosahedrongeometry (more than 20 sides)
- Octahedron geometry
- Tetrahedron geometry
2D geometry
PlaneGeometry
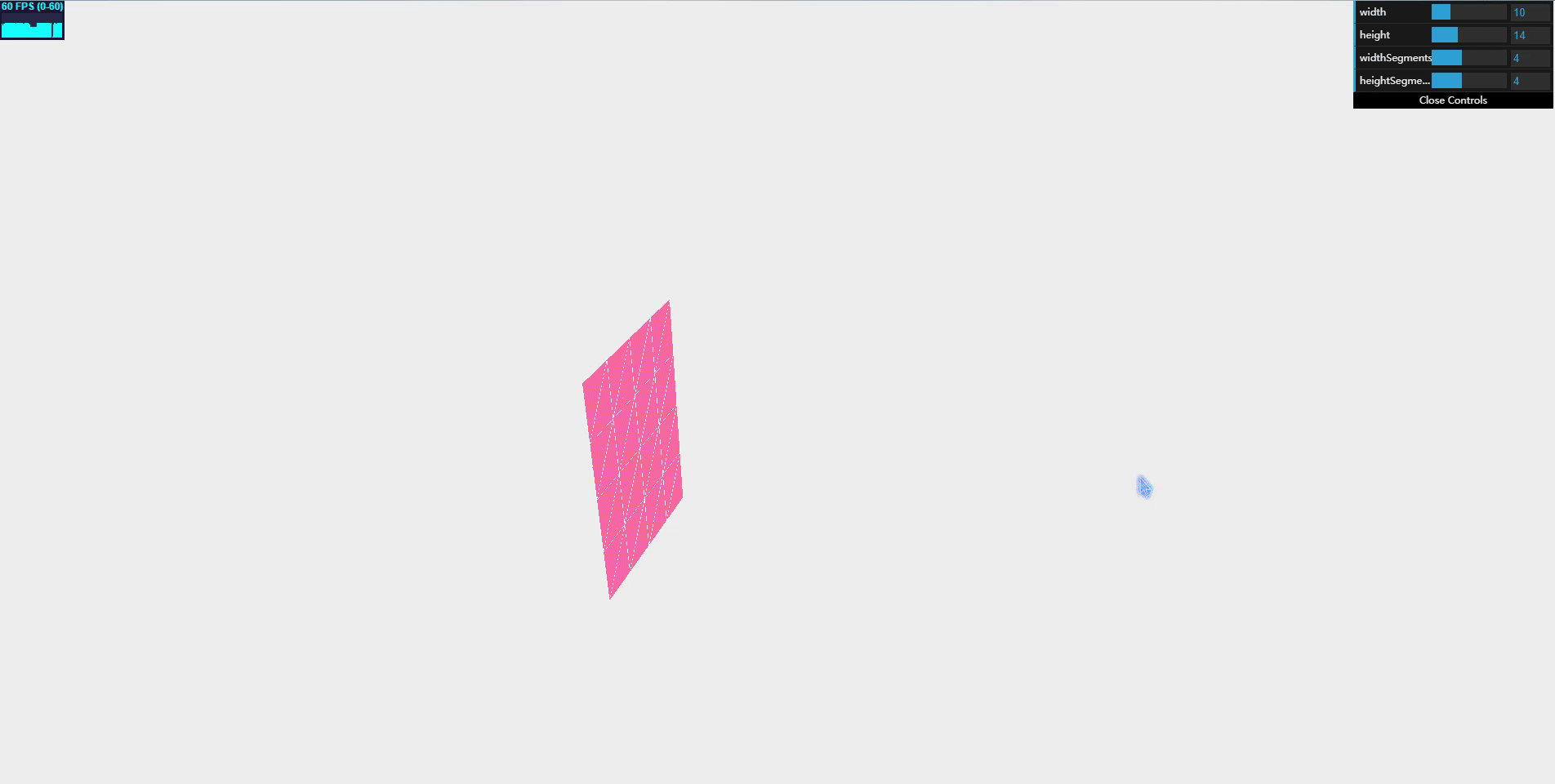
PlaneGeometry can be used to create very simple 2D rectangles.
Its construction method prototype is:
new THREE.PlaneGeometry(width, height, widthSegments, heightSegments)
The meaning of each parameter is as follows:
| attribute | Required or not | describe |
|---|---|---|
| Width | yes | Specifies the width of the rectangle |
| Height | yes | Specifies the height of the rectangle |
| Widthsegments | no | Specifies that the width of the rectangle should be divided into segments |
| Height segments | no | Specifies that the height of the rectangle should be divided into segments |
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<title>chapter 5-1</title>
<script type="text/javascript" src="../libs/three.js"></script>
<script type="text/javascript" src="../libs/stats.js"></script>
<script type="text/javascript" src="../libs/dat.gui.js"></script>
<style>
body {
margin: 0;
overflow: hidden;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div id="Stats-output"></div>
<div id="threejs-example"></div>
<script type="text/javascript">
function init() {
var stats = initStats();
var scene = new THREE.Scene();
var camera = new THREE.PerspectiveCamera(45, window.innerWidth / window.innerHeight, 0.1, 1000);
var webGLRenderer = new THREE.WebGLRenderer();
webGLRenderer.setClearColor(new THREE.Color(0xEEEEEE, 1.0));
webGLRenderer.setSize(window.innerWidth, window.innerHeight);
webGLRenderer.shadowMapEnabled = true;
// First, add an initial plane to the scene
var plane = createMesh(new THREE.PlaneGeometry(10, 14, 4, 4));
scene.add(plane);
camera.position.x = -20;
camera.position.y = 30;
camera.position.z = 40;
camera.lookAt(new THREE.Vector3(10, 0, 0));
var spotLight = new THREE.SpotLight(0xffffff);
spotLight.position.set(-40, 60, -10);
scene.add(spotLight);
document.getElementById("threejs-example").appendChild(webGLRenderer.domElement);
var controls = new function () {
// Initialize controls with several basic attribute values of plane
this.width = plane.children[0].geometry.parameters.width;
this.height = plane.children[0].geometry.parameters.height;
// The width and height of the geometry line
this.widthSegments = plane.children[0].geometry.parameters.widthSegments;
this.heightSegments = plane.children[0].geometry.parameters.heightSegments;
this.redraw = function () {
scene.remove(plane); // Delete the original plane object
// Construct a new plane object with several current attribute values of controls
plane = createMesh(new THREE.PlaneGeometry(controls.width, controls.height, Math.round(controls.widthSegments), Math.round(controls.heightSegments)));
scene.add(plane);
};
};
var gui = new dat.GUI();
// When the value of [width slider] changes, assign the value of the current slider to controls.width, and call the controls.redraw() function to redraw the plane
gui.add(controls, 'width', 0, 40).onChange(controls.redraw);
gui.add(controls, 'height', 0, 40).onChange(controls.redraw);
gui.add(controls, 'widthSegments', 0, 10).onChange(controls.redraw);
gui.add(controls, 'heightSegments', 0, 10).onChange(controls.redraw);
function createMesh(geom) {
var meshMaterial = new THREE.MeshNormalMaterial();
meshMaterial.side = THREE.DoubleSide; // To keep the plane visible during rotation (both sides are colored)
var wireFrameMat = new THREE.MeshBasicMaterial();
wireFrameMat.wireframe = true; // Displays the line frame of the plane
// The geometry represented by geom and two materials are assembled into a new plane object
var plane = THREE.SceneUtils.createMultiMaterialObject(geom, [meshMaterial, wireFrameMat]);
return plane;
}
var step = 0;
renderScene();
function renderScene() {
stats.update();
plane.rotation.y = step += 0.01;
requestAnimationFrame(renderScene);
webGLRenderer.render(scene, camera);
}
function initStats() {
var stats = new Stats();
stats.setMode(0);
stats.domElement.style.position = 'absolute';
stats.domElement.style.left = '0px';
stats.domElement.style.top = '0px';
document.getElementById("Stats-output").appendChild(stats.domElement);
return stats;
}
}
window.onload = init;
</script>
</body>
</html>
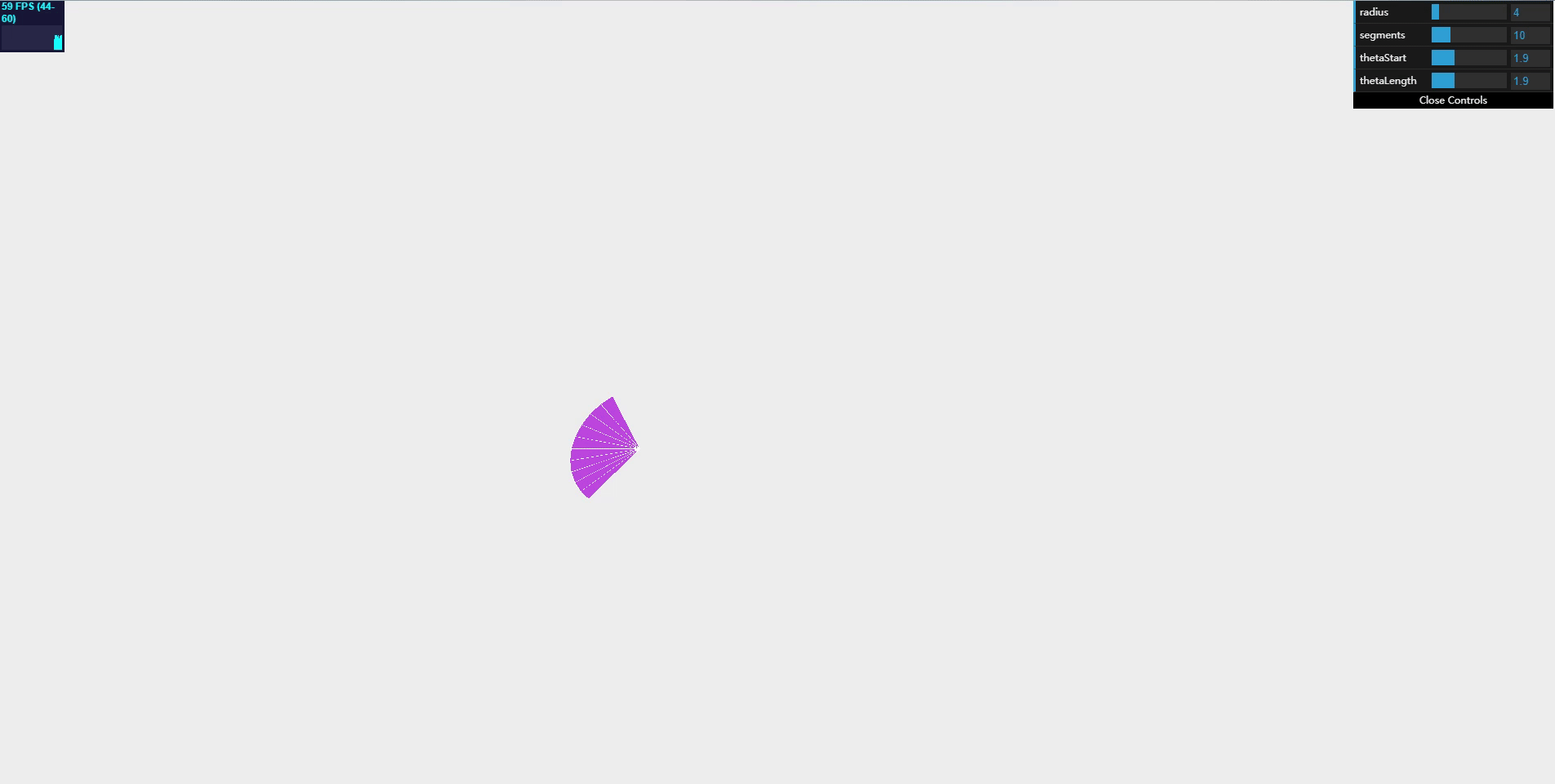
CircleGeometry
With circular geometry, you can build a simple two-dimensional circle.
When creating a CircleGeometry object, you can specify several properties:
| attribute | Is it necessary | describe |
|---|---|---|
| Radius | yes | This attribute defines the radius of the circle, which determines the size of the circle |
| Segment | no | This attribute defines the number of faces used to create the circle. At least 3, if not specified, the default is 8. The higher the value, the smoother the circle is created |
| Thetastart (arc start angle) | no | This attribute defines where to draw a circle from, and the value range is 0~2*PI |
| Thetalongth (angle of arc opening) | This attribute defines how big the circle should be drawn. Combined with thetaStart attribute and this attribute, you can define the shape of the circle. If not specified, it defaults to 2 * PI (full circle). |
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<title>chapter 5-2</title>
<script type="text/javascript" src="../libs/three.js"></script>
<script type="text/javascript" src="../libs/stats.js"></script>
<script type="text/javascript" src="../libs/dat.gui.js"></script>
<style>
body {
margin: 0;
overflow: hidden;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div id="Stats-output"></div>
<div id="threejs-example"></div>
<script type="text/javascript">
function init() {
var stats = initStats();
var scene = new THREE.Scene();
var camera = new THREE.PerspectiveCamera(45, window.innerWidth / window.innerHeight, 0.1, 1000);
var webGLRenderer = new THREE.WebGLRenderer();
webGLRenderer.setClearColor(new THREE.Color(0xEEEEEE, 1.0));
webGLRenderer.setSize(window.innerWidth, window.innerHeight);
webGLRenderer.shadowMapEnabled = true;
// First, use CircleGeometry to add a circle to the scene
var circle = createMesh(new THREE.CircleGeometry(4, 10, 0.3 * Math.PI * 2, 0.3 * Math.PI * 2));
scene.add(circle);
camera.position.x = -20;
camera.position.y = 30;
camera.position.z = 40;
camera.lookAt(new THREE.Vector3(10, 0, 0));
var spotLight = new THREE.SpotLight(0xffffff);
spotLight.position.set(-40, 60, -10);
scene.add(spotLight);
document.getElementById("threejs-example").appendChild(webGLRenderer.domElement);
var controls = new function () {
this.radius = 4;
this.thetaStart = 0.3 * Math.PI * 2;
this.thetaLength = 0.3 * Math.PI * 2;
this.segments = 10;
this.redraw = function () {
// Delete original circle
scene.remove(circle);
// Add a new circle to the scene
circle = createMesh(new THREE.CircleGeometry(controls.radius, controls.segments, controls.thetaStart, controls.thetaLength));
scene.add(circle);
};
};
var gui = new dat.GUI();
gui.add(controls, 'radius', 0, 40).onChange(controls.redraw);
gui.add(controls, 'segments', 0, 40).onChange(controls.redraw);
gui.add(controls, 'thetaStart', 0, 2 * Math.PI).onChange(controls.redraw);
gui.add(controls, 'thetaLength', 0, 2 * Math.PI).onChange(controls.redraw);
function createMesh(geom) {
//Define two materials
var meshMaterial = new THREE.MeshNormalMaterial();
meshMaterial.side = THREE.DoubleSide;
var wireFrameMat = new THREE.MeshBasicMaterial();
wireFrameMat.wireframe = true;
// Use the createMultiMaterialObject() scene to create mesh objects that contain multiple materials
var mesh = THREE.SceneUtils.createMultiMaterialObject(geom, [meshMaterial, wireFrameMat]);
return mesh;
}
var step = 0;
renderScene();
function renderScene() {
stats.update();
// Rotate 2D circle
circle.rotation.y = step += 0.01;
requestAnimationFrame(renderScene);
webGLRenderer.render(scene, camera);
}
function initStats() {
var stats = new Stats();
stats.setMode(0);
stats.domElement.style.position = 'absolute';
stats.domElement.style.left = '0px';
stats.domElement.style.top = '0px';
document.getElementById("Stats-output").appendChild(stats.domElement);
return stats;
}
}
window.onload = init;
</script>
</body>
</html>
threejs only uses the x-axis and y-axis when creating two-dimensional graphics (PlaneGeometry,CircleGeometry and shapeometry), so these two-dimensional graphics are upright in the viewer. To create a 2D object placed horizontally rather than vertically, rotate the mesh object back a quarter of a turn along the X axis:
mesh.rotation.x = -Math.PI/2;
ShapeGeometry
PlaneGeometry and CircleGeometry have only limited ways to customize their appearance. If you want to create a two-dimensional shape that can customize the shape, you can use shapeometry.
with shapeometry, you can call several functions to create your own graphics. You can compare this function with the path function in html canvas and svg.
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<title>chapter 5-3</title>
<script type="text/javascript" src="../libs/three.js"></script>
<script type="text/javascript" src="../libs/stats.js"></script>
<script type="text/javascript" src="../libs/dat.gui.js"></script>
<style>
body {
margin: 0;
overflow: hidden;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div id="Stats-output"></div>
<div id="threejs-example"></div>
<script type="text/javascript">
function init() {
var stats = initStats();
var scene = new THREE.Scene();
var camera = new THREE.PerspectiveCamera(45, window.innerWidth / window.innerHeight, 0.1, 1000);
var webGLRenderer = new THREE.WebGLRenderer();
webGLRenderer.setClearColor(new THREE.Color(0xEEEEEE, 1.0));
webGLRenderer.setSize(window.innerWidth, window.innerHeight);
webGLRenderer.shadowMapEnabled = true;
// First add the drawn shape to the picture
var shape = createMesh(new THREE.ShapeGeometry(drawShape()));
scene.add(shape);
camera.position.x = -30;
camera.position.y = 70;
camera.position.z = 70;
camera.lookAt(new THREE.Vector3(10, 0, 0));
var spotLight = new THREE.SpotLight(0xffffff);
spotLight.position.set(-40, 60, -10);
scene.add(spotLight);
document.getElementById("threejs-example").appendChild(webGLRenderer.domElement);
var controls = new function () {
this.asGeom = function () {
scene.remove(shape); // Remove the original shape
shape = createMesh(new THREE.ShapeGeometry(drawShape())); // Create a new shape object, three Shapeometry (three. Shape geometry object))
scene.add(shape);
};
this.asPoints = function () {
scene.remove(shape);
shape = createLine(drawShape());
scene.add(shape);
};
};
var gui = new dat.GUI();
gui.add(controls, 'asGeom');
gui.add(controls, 'asPoints');
// Through three Some methods of the shape class draw the shape of the shape
function drawShape() {
var shape = new THREE.Shape();
// Draw a straight line
shape.moveTo(10, 10);
shape.lineTo(10, 40);
// Draw a curve
shape.bezierCurveTo(15, 25, 25, 25, 30, 40);
// Draw a smooth curve along the current coordinates of the path
shape.splineThru([
new THREE.Vector2(32, 30),
new THREE.Vector2(28, 20),
new THREE.Vector2(30, 10),
]);
// The curve below
shape.quadraticCurveTo(20, 15, 10, 10);
// Use three The absellipse() method of the path class instance object draws a hole in the shape
// Draw left eye hole
var hole1 = new THREE.Path();
hole1.absellipse(16, 24, 2, 3, 0, Math.PI * 2, true);
shape.holes.push(hole1);
// Draw the right eye hole
var hole2 = new THREE.Path();
hole2.absellipse(23, 24, 2, 3, 0, Math.PI * 2, true);
shape.holes.push(hole2);
// Draw mouth
var hole3 = new THREE.Path();
hole3.absarc(20, 16, 2, 0, Math.PI, true);
shape.holes.push(hole3);
return shape;
}
function createLine(shape) {
console.log(shape);
var mesh = new THREE.Line(shape.createPointsGeometry(10), new THREE.LineBasicMaterial({
color: 0xff3333,
linewidth: 2
}));
return mesh;
}
function createMesh(geom) {
// Define two material objects
var meshMaterial = new THREE.MeshNormalMaterial();
meshMaterial.side = THREE.DoubleSide;
var wireFrameMat = new THREE.MeshBasicMaterial();
wireFrameMat.wireframe = true;
// Create a mesh object using two materials
var mesh = THREE.SceneUtils.createMultiMaterialObject(geom, [meshMaterial, wireFrameMat]);
return mesh;
}
var step = 0;
renderScene();
function renderScene() {
stats.update();
// Custom shapes rotate about the y axis
shape.rotation.y = step += 0.01;
requestAnimationFrame(renderScene);
webGLRenderer.render(scene, camera);
}
function initStats() {
var stats = new Stats();
stats.setMode(0);
stats.domElement.style.position = 'absolute';
stats.domElement.style.left = '0px';
stats.domElement.style.top = '0px';
document.getElementById("Stats-output").appendChild(stats.domElement);
return stats;
}
}
window.onload = init;
</script>
</body>
</html>
in the above example, we use line, curve and spline to create the outline of the figure. Then use three The holes attribute of the shape class makes several "holes" in the shape.
shapeometry class has no other options to customize graphics, so we'll take a look at three The shape class uses various functions to draw graphics:
the last thing to note is that the shape object attribute is the holes attribute. Add three to this attribute Shape object, you can make several holes in the shape.
in the above example, we use three The shapeometry (drawshape()) function creates a shapeometry from the Shape object. The Shape object itself has several auxiliary functions that you can use to create geometry.

You can use the createPointsGeometry function to create a set of points, and then you can use these points to create segments:
new THREE.Line(shape.createPointsGeometry(10), new THREE.LineBasicMaterial({color: 0xff3333, linewidth: 2}));

3D geometry
RingGeometry
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<title>chapter 5-4</title>
<script type="text/javascript" src="../libs/three.js"></script>
<script type="text/javascript" src="../libs/stats.js"></script>
<script type="text/javascript" src="../libs/dat.gui.js"></script>
<style>
body {
margin: 0;
overflow: hidden;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div id="Stats-output"></div>
<div id="threejs-example"></div>
<script type="text/javascript">
function init() {
var stats = initStats();
var scene = new THREE.Scene();
var camera = new THREE.PerspectiveCamera(45, window.innerWidth / window.innerHeight, 0.1, 1000);
var webGLRenderer = new THREE.WebGLRenderer();
webGLRenderer.setClearColor(new THREE.Color(0xEEEEEE, 1.0));
webGLRenderer.setSize(window.innerWidth, window.innerHeight);
webGLRenderer.shadowMapEnabled = true;
// First add a ring to the scene
var ring = createMesh(new THREE.RingGeometry());
scene.add(ring);
camera.position.x = -30;
camera.position.y = 40;
camera.position.z = 50;
camera.lookAt(new THREE.Vector3(10, 0, 0));
document.getElementById("threejs-example").appendChild(webGLRenderer.domElement);
var controls = new function () {
this.innerRadius = 0;
this.outerRadius = 50;
this.thetaSegments = 8;
this.phiSegments = 8;
this.thetaStart = 0;
this.thetaLength = Math.PI * 2;
this.redraw = function () {
scene.remove(ring);
ring = createMesh(new THREE.RingGeometry(
controls.innerRadius,
controls.outerRadius,
controls.thetaSegments,
controls.phiSegments,
controls.thetaStart,
controls.thetaLength)
);
scene.add(ring);
};
};
var gui = new dat.GUI();
gui.add(controls, 'innerRadius', 0, 40).onChange(controls.redraw);
gui.add(controls, 'outerRadius', 0, 100).onChange(controls.redraw);
gui.add(controls, 'thetaSegments', 1, 40).step(1).onChange(controls.redraw);
gui.add(controls, 'phiSegments', 1, 20).step(1).onChange(controls.redraw);
gui.add(controls, 'thetaStart', 0, Math.PI * 2).onChange(controls.redraw);
gui.add(controls, 'thetaLength', 0, Math.PI * 2).onChange(controls.redraw);
function createMesh(geom) {
// Building objects with two materials
var meshMaterial = new THREE.MeshNormalMaterial();
meshMaterial.side = THREE.DoubleSide;
var wireFrameMat = new THREE.MeshBasicMaterial();
wireFrameMat.wireframe = true;
var mesh = THREE.SceneUtils.createMultiMaterialObject(geom, [meshMaterial, wireFrameMat]);
return mesh;
}
var step = 0;
renderScene();
function renderScene() {
stats.update();
// rotating ring
ring.rotation.y = step += 0.01;
requestAnimationFrame(renderScene);
webGLRenderer.render(scene, camera);
}
function initStats() {
var stats = new Stats();
stats.setMode(0);
stats.domElement.style.position = 'absolute';
stats.domElement.style.left = '0px';
stats.domElement.style.top = '0px';
document.getElementById("Stats-output").appendChild(stats.domElement);
return stats;
}
}
window.onload = init;
</script>
</body>
</html>

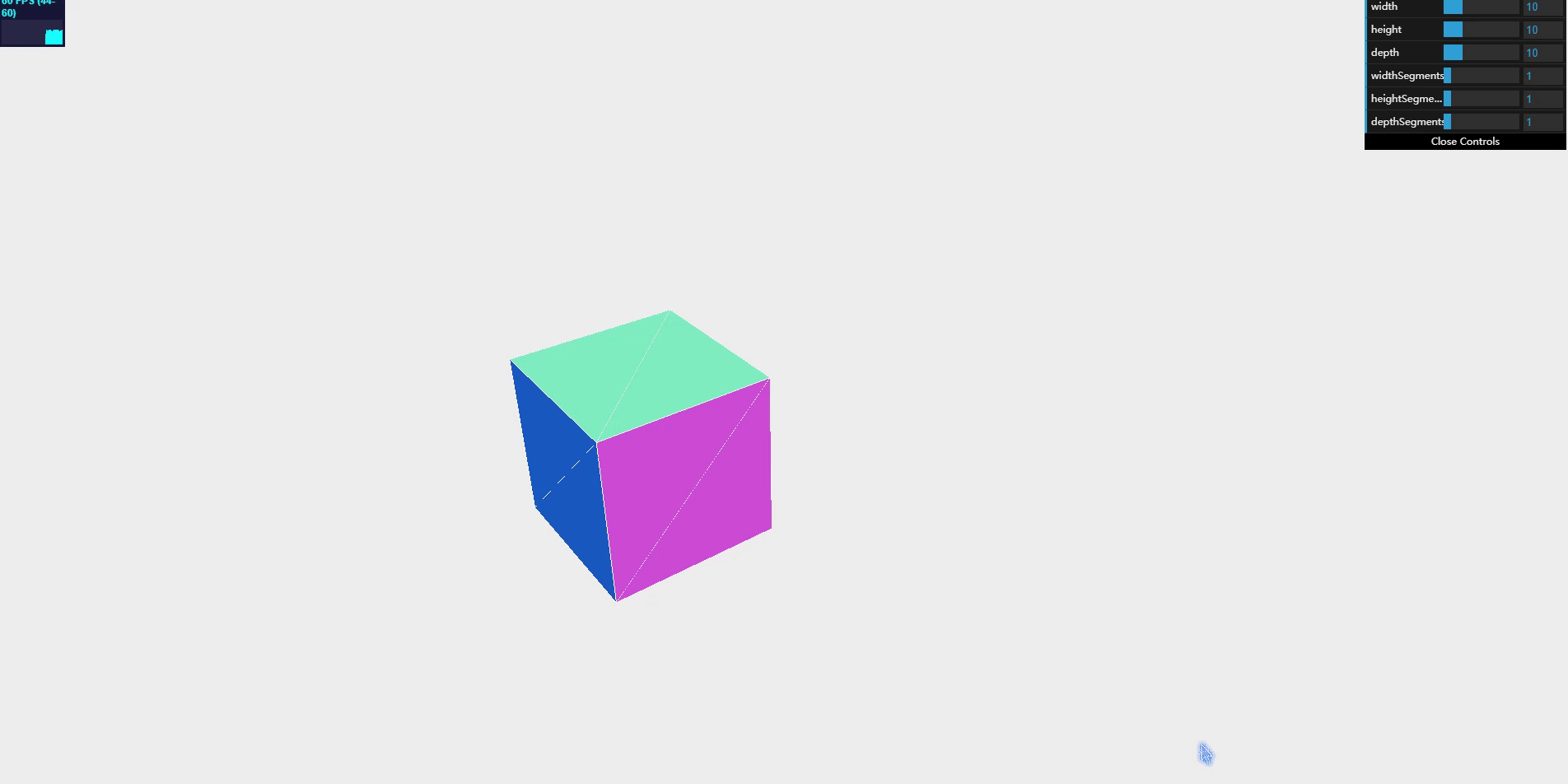
CubeGeometry
cube geometry is a very simple three-dimensional geometry. You can create a square by specifying the width, height and depth.
you can control the size of the mesh by changing the width, height and depth of the CubeGeometry object. Of course, these three attributes must also be provided to the constructor when creating a block.
by adding the attribute of each segment, you can divide the six large faces of the box into many small faces, which is useful when using MeshFaceMaterial material to assign different materials to different parts of the box.
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<title>chapter 5-5</title>
<script type="text/javascript" src="../libs/three.js"></script>
<script type="text/javascript" src="../libs/stats.js"></script>
<script type="text/javascript" src="../libs/dat.gui.js"></script>
<style>
body {
margin: 0;
overflow: hidden;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div id="Stats-output"></div>
<div id="threejs-example"></div>
<script type="text/javascript">
function init() {
var stats = initStats();
var scene = new THREE.Scene();
var camera = new THREE.PerspectiveCamera(45, window.innerWidth / window.innerHeight, 0.1, 1000);
var webGLRenderer = new THREE.WebGLRenderer();
webGLRenderer.setClearColor(new THREE.Color(0xEEEEEE, 1.0));
webGLRenderer.setSize(window.innerWidth, window.innerHeight);
webGLRenderer.shadowMapEnabled = true;
var cube = createMesh(new THREE.CubeGeometry(10, 10, 10, 1, 1, 1));
scene.add(cube);
camera.position.x = -20;
camera.position.y = 30;
camera.position.z = 40;
camera.lookAt(new THREE.Vector3(10, 0, 0));
var spotLight = new THREE.SpotLight(0xffffff);
spotLight.position.set(-40, 60, -10);
scene.add(spotLight);
document.getElementById("threejs-example").appendChild(webGLRenderer.domElement);
var controls = new function () {
// cube.children[0] explained that the attribute of the child cube object covered with eshNormalMaterial material should be changed
this.width = cube.children[0].geometry.parameters.width;
this.height = cube.children[0].geometry.parameters.height;
this.depth = cube.children[0].geometry.parameters.depth;
this.widthSegments = cube.children[0].geometry.parameters.widthSegments;
this.heightSegments = cube.children[0].geometry.parameters.heightSegments;
this.depthSegments = cube.children[0].geometry.parameters.depthSegments;
this.redraw = function () {
scene.remove(cube); // Remove the original cube
cube = createMesh(new THREE.CubeGeometry(controls.width, controls.height, controls.depth, Math.round(controls.widthSegments), Math.round(controls.heightSegments), Math.round(controls.depthSegments)));
scene.add(cube); // Add a new cube
};
};
var gui = new dat.GUI(); // Controls various attributes of CubeGeometry geometry
gui.add(controls, 'width', 0, 40).onChange(controls.redraw);
gui.add(controls, 'height', 0, 40).onChange(controls.redraw);
gui.add(controls, 'depth', 0, 40).onChange(controls.redraw);
gui.add(controls, 'widthSegments', 0, 10).onChange(controls.redraw);
gui.add(controls, 'heightSegments', 0, 10).onChange(controls.redraw);
gui.add(controls, 'depthSegments', 0, 10).onChange(controls.redraw);
function createMesh(geom) {
// Use two materials to create cube squares
var meshMaterial = new THREE.MeshNormalMaterial();
meshMaterial.side = THREE.DoubleSide;
var wireFrameMat = new THREE.MeshBasicMaterial();
wireFrameMat.wireframe = true;
var mesh = THREE.SceneUtils.createMultiMaterialObject(geom, [meshMaterial, wireFrameMat]);
return mesh;
}
var step = 0;
renderScene();
function renderScene() {
stats.update();
// Cube Craze
cube.rotation.y = step += 0.01;
requestAnimationFrame(renderScene);
webGLRenderer.render(scene, camera);
}
function initStats() {
var stats = new Stats();
stats.setMode(0);
stats.domElement.style.position = 'absolute';
stats.domElement.style.left = '0px';
stats.domElement.style.top = '0px';
document.getElementById("Stats-output").appendChild(stats.domElement);
return stats;
}
}
window.onload = init;
</script>
</body>
</html>
In fact, cube geometry has another equivalent expression, BoxGeometry.
SphereGeometry
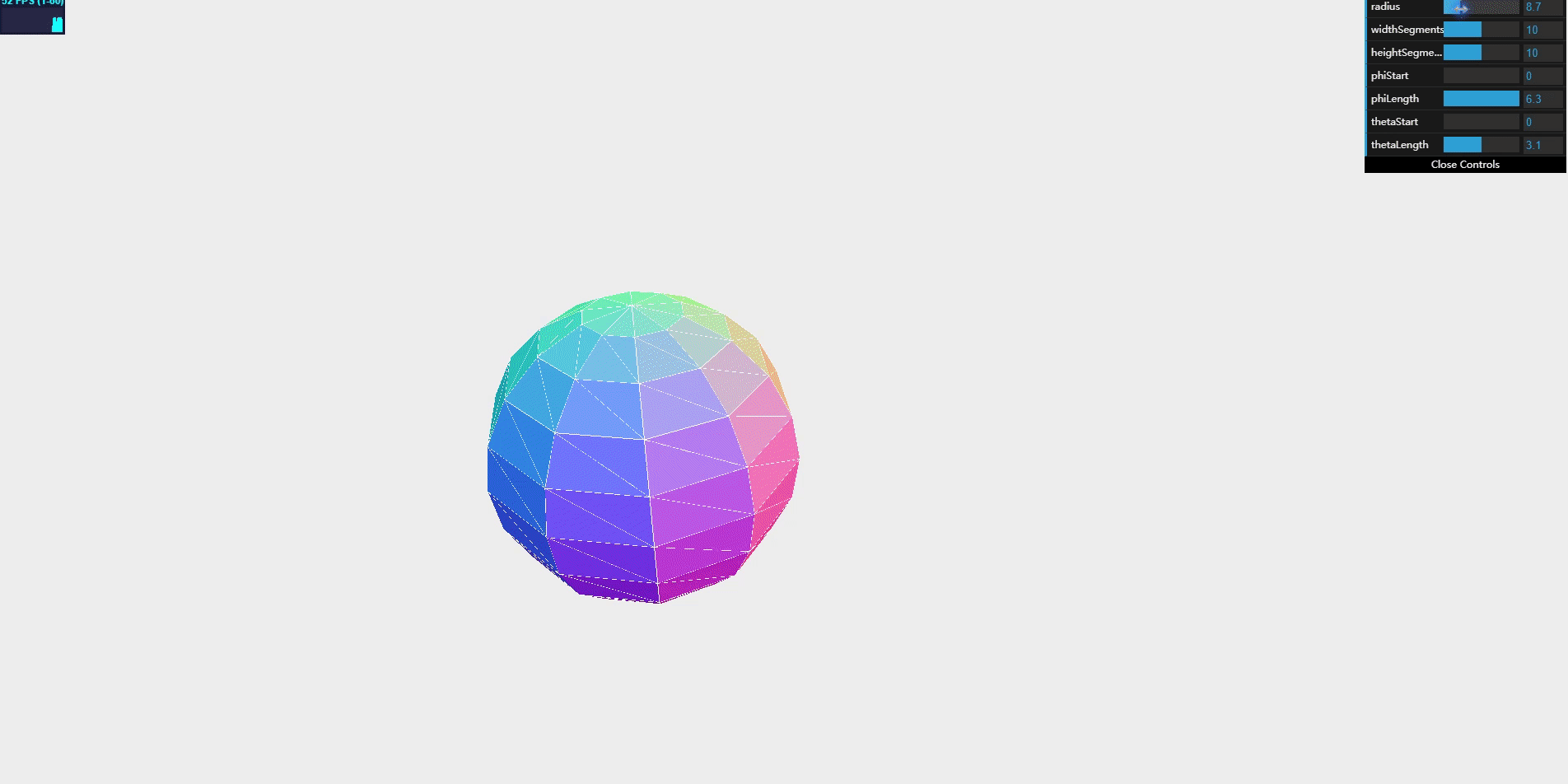
Sphere geometry lets you create a three-dimensional sphere.
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<title>chapter 5-6</title>
<script type="text/javascript" src="../libs/three.js"></script>
<script type="text/javascript" src="../libs/stats.js"></script>
<script type="text/javascript" src="../libs/dat.gui.js"></script>
<style>
body {
margin: 0;
overflow: hidden;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div id="Stats-output"></div>
<div id="threejs-example"></div>
<script type="text/javascript">
function init() {
var stats = initStats();
var scene = new THREE.Scene();
var camera = new THREE.PerspectiveCamera(45, window.innerWidth / window.innerHeight, 0.1, 1000);
var webGLRenderer = new THREE.WebGLRenderer();
webGLRenderer.setClearColor(new THREE.Color(0xEEEEEE, 1.0));
webGLRenderer.setSize(window.innerWidth, window.innerHeight);
webGLRenderer.shadowMapEnabled = true;
var sphere = createMesh(new THREE.SphereGeometry(4, 10, 10));
scene.add(sphere);
camera.position.x = -20;
camera.position.y = 30;
camera.position.z = 40;
camera.lookAt(new THREE.Vector3(10, 0, 0));
document.getElementById("threejs-example").appendChild(webGLRenderer.domElement);
var controls = new function () {
this.radius = sphere.children[0].geometry.parameters.radius;
this.widthSegments = sphere.children[0].geometry.parameters.widthSegments;
this.heightSegments = sphere.children[0].geometry.parameters.heightSegments;
this.phiStart = 0;
this.phiLength = Math.PI * 2;
this.thetaStart = 0;
this.thetaLength = Math.PI;
this.redraw = function () {
scene.remove(sphere);
sphere = createMesh(new THREE.SphereGeometry(
controls.radius,
controls.widthSegments,
controls.heightSegments,
controls.phiStart,
controls.phiLength,
controls.thetaStart,
controls.thetaLength
));
scene.add(sphere);
};
};
// Test various properties of sphereometry
var gui = new dat.GUI();
gui.add(controls, 'radius', 0, 40).onChange(controls.redraw);
gui.add(controls, 'widthSegments', 0, 20).onChange(controls.redraw);
gui.add(controls, 'heightSegments', 0, 20).onChange(controls.redraw);
gui.add(controls, 'phiStart', 0, 2 * Math.PI).onChange(controls.redraw);
gui.add(controls, 'phiLength', 0, 2 * Math.PI).onChange(controls.redraw);
gui.add(controls, 'thetaStart', 0, 2 * Math.PI).onChange(controls.redraw);
gui.add(controls, 'thetaLength', 0, 2 * Math.PI).onChange(controls.redraw);
function createMesh(geom) {
var meshMaterial = new THREE.MeshNormalMaterial();
meshMaterial.side = THREE.DoubleSide;
var wireFrameMat = new THREE.MeshBasicMaterial();
wireFrameMat.wireframe = true;
var mesh = THREE.SceneUtils.createMultiMaterialObject(geom, [meshMaterial, wireFrameMat]);
return mesh;
}
var step = 0;
renderScene();
function renderScene() {
stats.update();
sphere.rotation.y = step += 0.01;
requestAnimationFrame(renderScene);
webGLRenderer.render(scene, camera);
}
function initStats() {
var stats = new Stats();
stats.setMode(0);
stats.domElement.style.position = 'absolute';
stats.domElement.style.left = '0px';
stats.domElement.style.top = '0px';
document.getElementById("Stats-output").appendChild(stats.domElement);
return stats;
}
}
window.onload = init;
</script>
</body>
</html>
The various properties of sphereometry are as follows:
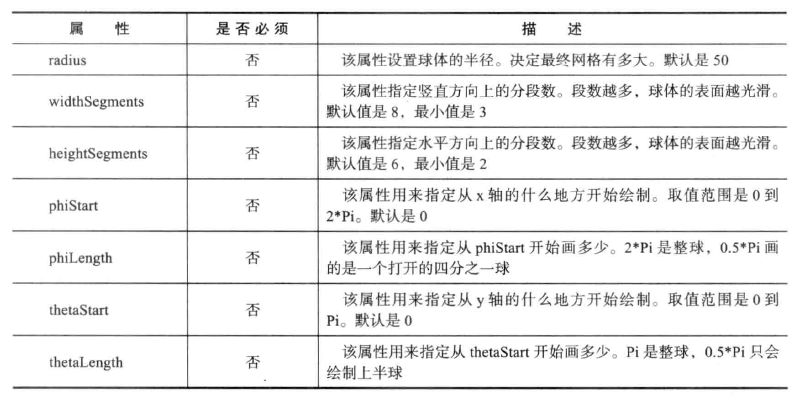
Through these attributes, you can control the shape and style of the object.

CylinderGeometry
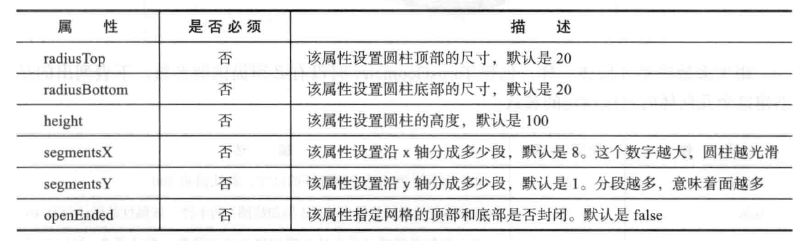
with CylinderGeometry geometry, we can create cylinders and cylinder like objects.
when creating CylinderGeometry, there are no parameters that must be provided to the constructor, so you just call new three CylinderGeometry() creates a cylinder. Of course, providing the following parameters can also make the appearance of the cylinder more personalized.
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<title>chapter 5-7</title>
<script type="text/javascript" src="../libs/three.js"></script>
<script type="text/javascript" src="../libs/stats.js"></script>
<script type="text/javascript" src="../libs/dat.gui.js"></script>
<style>
body {
margin: 0;
overflow: hidden;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div id="Stats-output"></div>
<div id="threejs-example"></div>
<script type="text/javascript">
function init() {
var stats = initStats();
var scene = new THREE.Scene();
var camera = new THREE.PerspectiveCamera(45, window.innerWidth / window.innerHeight, 0.1, 1000);
var webGLRenderer = new THREE.WebGLRenderer();
webGLRenderer.setClearColor(new THREE.Color(0xEEEEEE, 1.0));
webGLRenderer.setSize(window.innerWidth, window.innerHeight);
webGLRenderer.shadowMapEnabled = true;
// First add a cylinder to the scene
var cylinder = createMesh(new THREE.CylinderGeometry(20, 20, 20));
scene.add(cylinder);
camera.position.x = -30;
camera.position.y = 40;
camera.position.z = 50;
camera.lookAt(new THREE.Vector3(10, 0, 0));
document.getElementById("threejs-example").appendChild(webGLRenderer.domElement);
var controls = new function () {
this.radiusTop = 20;
this.radiusBottom = 20;
this.height = 20;
this.radialSegments = 8;
this.heightSegments = 8;
this.openEnded = false;
this.redraw = function () {
scene.remove(cylinder); // Remove the original cylinder
// Use three Cylindergeometry constructs a cylinder
cylinder = createMesh(new THREE.CylinderGeometry(
controls.radiusTop,
controls.radiusBottom,
controls.height,
controls.radialSegments,
controls.heightSegments,
controls.openEnded)
);
scene.add(cylinder); // Add a new cylinder
};
};
var gui = new dat.GUI();
gui.add(controls, 'radiusTop', -40, 40).onChange(controls.redraw);
gui.add(controls, 'radiusBottom', -40, 40).onChange(controls.redraw);
gui.add(controls, 'height', 0, 40).onChange(controls.redraw);
gui.add(controls, 'radialSegments', 1, 20).step(1).onChange(controls.redraw);
gui.add(controls, 'heightSegments', 1, 20).step(1).onChange(controls.redraw);
gui.add(controls, 'openEnded').onChange(controls.redraw);
function createMesh(geom) {
// Use multiple materials when creating cylinders
var meshMaterial = new THREE.MeshNormalMaterial();
meshMaterial.side = THREE.DoubleSide;
var wireFrameMat = new THREE.MeshBasicMaterial();
wireFrameMat.wireframe = true;
var mesh = THREE.SceneUtils.createMultiMaterialObject(geom, [meshMaterial, wireFrameMat]);
return mesh;
}
var step = 0;
renderScene();
function renderScene() {
stats.update();
// Rotating cylinder
cylinder.rotation.y = step += 0.01;
requestAnimationFrame(renderScene);
webGLRenderer.render(scene, camera);
}
function initStats() {
var stats = new Stats();
stats.setMode(0);
stats.domElement.style.position = 'absolute';
stats.domElement.style.left = '0px';
stats.domElement.style.top = '0px';
document.getElementById("Stats-output").appendChild(stats.domElement);
return stats;
}
}
window.onload = init;
</script>
</body>
</html>
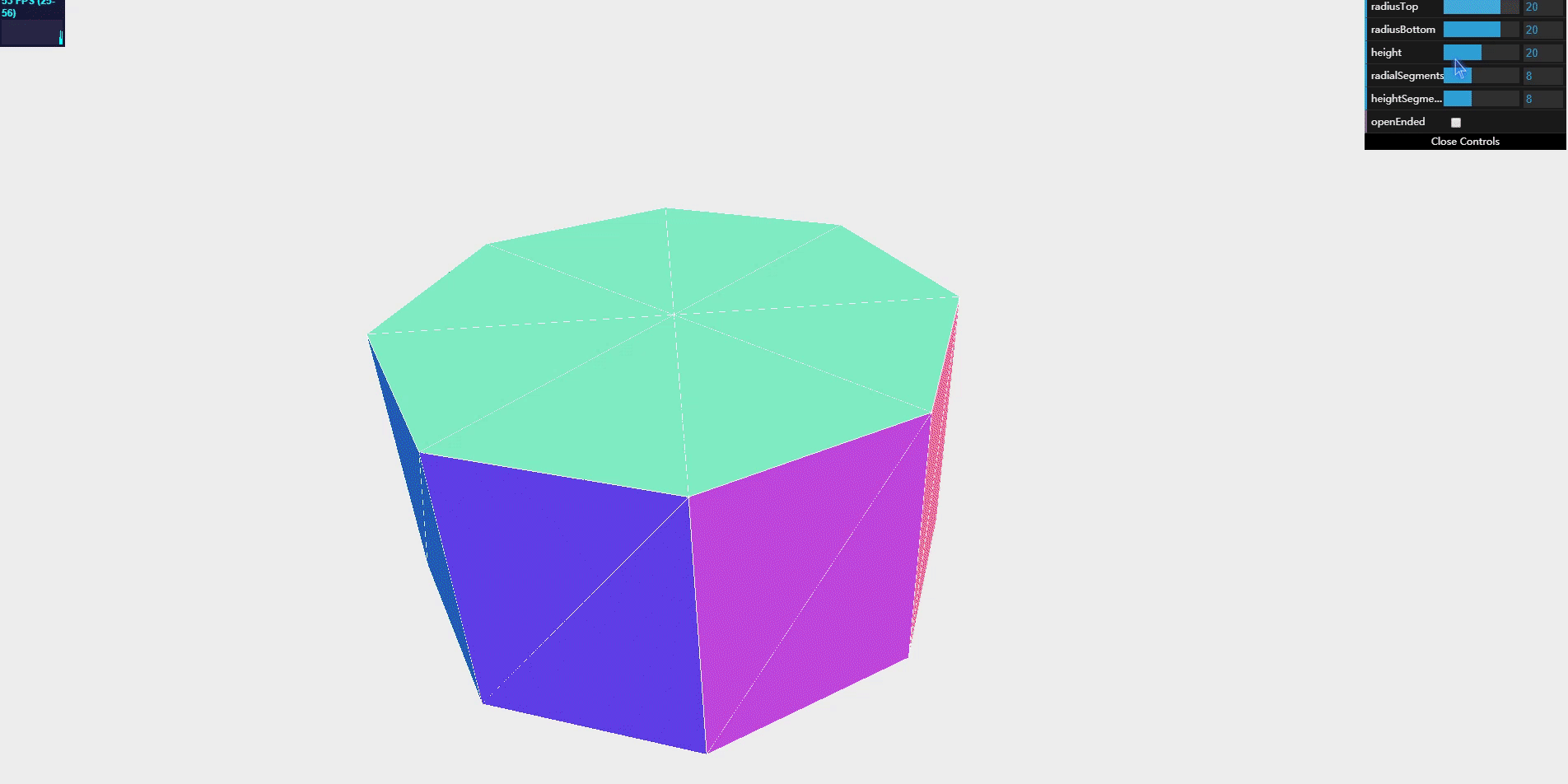
TorusGeometry
Torus is a simple figure that looks like a doughnut.
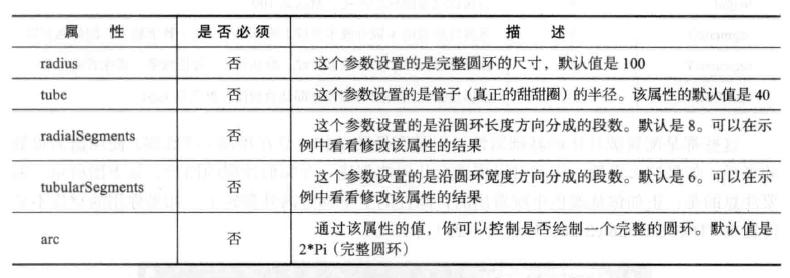
like most simple geometry creation, there are no parameters that must be provided when creating TorusGeometry. The following table lists the parameters that can be specified when creating this geometry:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<title>chapter 5-8</title>
<script type="text/javascript" src="../libs/three.js"></script>
<script type="text/javascript" src="../libs/stats.js"></script>
<script type="text/javascript" src="../libs/dat.gui.js"></script>
<style>
body {
margin: 0;
overflow: hidden;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div id="Stats-output"></div>
<div id="threejs-example"></div>
<script type="text/javascript">
function init() {
var stats = initStats();
var scene = new THREE.Scene();
var camera = new THREE.PerspectiveCamera(45, window.innerWidth / window.innerHeight, 0.1, 1000);
var webGLRenderer = new THREE.WebGLRenderer();
webGLRenderer.setClearColor(new THREE.Color(0xEEEEEE, 1.0));
webGLRenderer.setSize(window.innerWidth, window.innerHeight);
webGLRenderer.shadowMapEnabled = true;
// Add one to the scene first
var torus = createMesh(new THREE.TorusGeometry(10, 10, 8, 6, Math.PI * 2));
scene.add(torus);
camera.position.x = -30;
camera.position.y = 40;
camera.position.z = 50;
camera.lookAt(new THREE.Vector3(10, 0, 0));
document.getElementById("threejs-example").appendChild(webGLRenderer.domElement);
var controls = new function () {
// Change some TorusGeometry geometry properties of the object covered with MeshNormalMaterial material
this.radius = torus.children[0].geometry.parameters.radius;
this.tube = torus.children[0].geometry.parameters.tube;
this.radialSegments = torus.children[0].geometry.parameters.radialSegments;
this.tubularSegments = torus.children[0].geometry.parameters.tubularSegments;
this.arc = torus.children[0].geometry.parameters.arc;
this.redraw = function () {
scene.remove(torus); // Remove the original torus in the scene
torus = createMesh(new THREE.TorusGeometry(
controls.radius,
controls.tube, Math.round(controls.radialSegments),
Math.round(controls.tubularSegments),
controls.arc)
);
scene.add(torus); // Add torus to the scene
};
};
var gui = new dat.GUI();
gui.add(controls, 'radius', 0, 40).onChange(controls.redraw);
gui.add(controls, 'tube', 0, 40).onChange(controls.redraw);
gui.add(controls, 'radialSegments', 0, 40).onChange(controls.redraw);
gui.add(controls, 'tubularSegments', 1, 20).onChange(controls.redraw);
gui.add(controls, 'arc', 0, Math.PI * 2).onChange(controls.redraw);
function createMesh(geom) {
// Building torus objects with two materials
var meshMaterial = new THREE.MeshNormalMaterial();
meshMaterial.side = THREE.DoubleSide;
var wireFrameMat = new THREE.MeshBasicMaterial();
wireFrameMat.wireframe = true;
var mesh = THREE.SceneUtils.createMultiMaterialObject(geom, [meshMaterial, wireFrameMat]);
return mesh;
}
var step = 0;
renderScene();
function renderScene() {
stats.update();
// Rotating disc
torus.rotation.y = step += 0.01;
requestAnimationFrame(renderScene);
webGLRenderer.render(scene, camera);
}
function initStats() {
var stats = new Stats();
stats.setMode(0);
stats.domElement.style.position = 'absolute';
stats.domElement.style.left = '0px';
stats.domElement.style.top = '0px';
document.getElementById("Stats-output").appendChild(stats.domElement);
return stats;
}
}
window.onload = init;
</script>
</body>
</html>
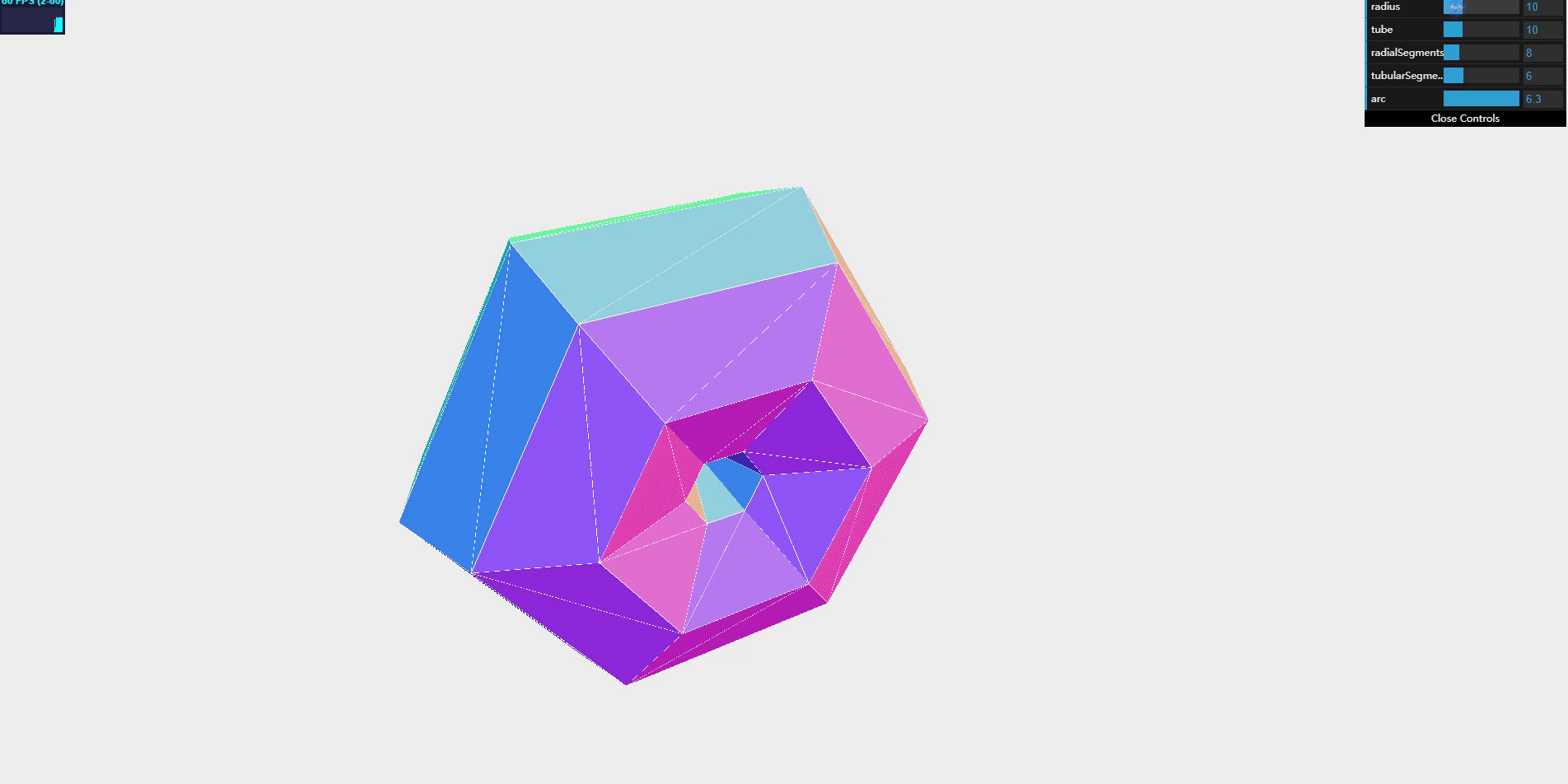
TorusKnotGeometry
through torus knotgeometry, you can create a torus knot. Torus knot is a special knot. It looks like a tube has turned around itself for several times.
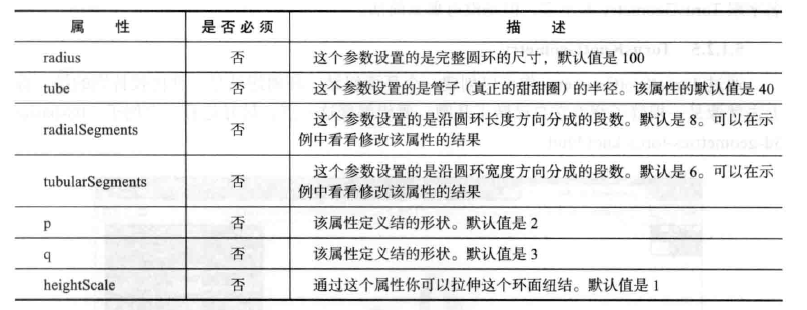
by modifying attributes p and q, you can create a variety of beautiful geometry. The p attribute defines how often the knot rotates around its axis, and the q attribute defines how many times the knot rotates around its interior. If it sounds empty, you don't have to worry.
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<title>chapter 5-9</title>
<script type="text/javascript" src="../libs/three.js"></script>
<script type="text/javascript" src="../libs/stats.js"></script>
<script type="text/javascript" src="../libs/dat.gui.js"></script>
<style>
body {
margin: 0;
overflow: hidden;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div id="Stats-output"></div>
<div id="threejs-example"></div>
<script type="text/javascript">
function init() {
var stats = initStats();
var scene = new THREE.Scene();
var camera = new THREE.PerspectiveCamera(45, window.innerWidth / window.innerHeight, 0.1, 1000);
var webGLRenderer = new THREE.WebGLRenderer();
webGLRenderer.setClearColor(new THREE.Color(0xEEEEEE, 1.0));
webGLRenderer.setSize(window.innerWidth, window.innerHeight);
webGLRenderer.shadowMapEnabled = true;
// First, add a kont object to the scene
var knot = createMesh(new THREE.TorusKnotGeometry(10, 1, 64, 8, 2, 3, 1));
scene.add(knot);
camera.position.x = -30;
camera.position.y = 40;
camera.position.z = 50;
camera.lookAt(new THREE.Vector3(10, 0, 0));
document.getElementById("threejs-example").appendChild(webGLRenderer.domElement);
var controls = new function () {
this.radius = knot.children[0].geometry.parameters.radius;
this.tube = 0.3;
this.radialSegments = knot.children[0].geometry.parameters.radialSegments;
this.tubularSegments = knot.children[0].geometry.parameters.tubularSegments;
this.p = knot.children[0].geometry.parameters.p;
this.q = knot.children[0].geometry.parameters.q;
this.heightScale = knot.children[0].geometry.parameters.heightScale;
this.redraw = function () {
scene.remove(knot); // Remove the original knot
knot = createMesh(new THREE.TorusKnotGeometry(
controls.radius,
controls.tube, Math.round(controls.radialSegments),
Math.round(controls.tubularSegments),
Math.round(controls.p),
Math.round(controls.q),
controls.heightScale)
);
scene.add(knot); // Add a new knot object
};
};
var gui = new dat.GUI();
gui.add(controls, 'radius', 0, 40).onChange(controls.redraw);
gui.add(controls, 'tube', 0, 40).onChange(controls.redraw);
gui.add(controls, 'radialSegments', 0, 400).step(1).onChange(controls.redraw);
gui.add(controls, 'tubularSegments', 1, 20).step(1).onChange(controls.redraw);
gui.add(controls, 'p', 1, 10).step(1).onChange(controls.redraw);
gui.add(controls, 'q', 1, 15).step(1).onChange(controls.redraw);
gui.add(controls, 'heightScale', 0, 5).onChange(controls.redraw);
function createMesh(geom) {
// Create an object using the MeshNormalMaterial material
var meshMaterial = new THREE.MeshNormalMaterial({});
meshMaterial.side = THREE.DoubleSide;
var mesh = THREE.SceneUtils.createMultiMaterialObject(geom, [meshMaterial]);
return mesh;
}
var step = 0;
renderScene();
function renderScene() {
stats.update();
// Rotating knot
knot.rotation.y = step += 0.01;
requestAnimationFrame(renderScene);
webGLRenderer.render(scene, camera);
}
function initStats() {
var stats = new Stats();
stats.setMode(0);
stats.domElement.style.position = 'absolute';
stats.domElement.style.left = '0px';
stats.domElement.style.top = '0px';
document.getElementById("Stats-output").appendChild(stats.domElement);
return stats;
}
}
window.onload = init;
</script>
</body>
</html>

PolyhedronGeometry
with this geometry, you can easily create a polyhedron. The so-called polyhedron refers to the geometry with only plane and straight edges. But in most cases, you won't use this geometry directly. Threejs has provided several specific polyhedrons, which can be used directly without directly setting the fixed points and faces of polyhedron geometry.
When you create a polyhedron, you can pass in the following four attributes:

<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<title>chapter 5-10</title>
<script type="text/javascript" src="../libs/three.js"></script>
<script type="text/javascript" src="../libs/stats.js"></script>
<script type="text/javascript" src="../libs/dat.gui.js"></script>
<style>
body {
margin: 0;
overflow: hidden;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div id="Stats-output"></div>
<div id="threejs-example"></div>
<script type="text/javascript">
function init() {
var stats = initStats();
var scene = new THREE.Scene();
var camera = new THREE.PerspectiveCamera(45, window.innerWidth / window.innerHeight, 0.1, 1000);
var webGLRenderer = new THREE.WebGLRenderer();
webGLRenderer.setClearColor(new THREE.Color(0xEEEEEE, 1.0));
webGLRenderer.setSize(window.innerWidth, window.innerHeight);
webGLRenderer.shadowMapEnabled = true;
// First, add an IcosahedronGeometry geometry to the scene
var polyhedron = createMesh(new THREE.IcosahedronGeometry(10, 0));
scene.add(polyhedron);
camera.position.x = -30;
camera.position.y = 40;
camera.position.z = 50;
camera.lookAt(new THREE.Vector3(10, 0, 0));
document.getElementById("threejs-example").appendChild(webGLRenderer.domElement);
var controls = new function () {
this.radius = 10;
this.detail = 0;
this.type = 'Icosahedron';
this.redraw = function () {
scene.remove(polyhedron);
switch (controls.type) {
// The following four are threejs predefined polyhedrons
// Regular 20 polygon (polyhedron with 20 identical triangular faces, which are created from 12 vertices. When using, you only need to specify radius and detail)
case 'Icosahedron': polyhedron = createMesh(new THREE.IcosahedronGeometry(controls.radius, controls.detail));
break;
// Regular tetrahedron (with 4 triangular faces created by 4 vertices)
case 'Tetrahedron': polyhedron = createMesh(new THREE.TetrahedronGeometry(controls.radius, controls.detail));
break;
// Regular octahedron
case 'Octahedron': polyhedron = createMesh(new THREE.OctahedronGeometry(controls.radius, controls.detail));
break;
case 'Dodecahedron':polyhedron = createMesh(new THREE.DodecahedronGeometry(controls.radius, controls.detail));
break;
case 'Custom': // Custom polyhedron (required)
var vertices = [
1, 1, 1, // The relative 3D coordinates of the first vertex
-1, -1, 1,
-1, 1, -1,
1, -1, -1
];
var faces = [
2, 1, 0, // In the vertex array vertices, vertices with indexes of 2, 1, 0 form a face
0, 3, 2,
1, 3, 0,
2, 3, 1
];
polyhedron = createMesh(new THREE.PolyhedronGeometry(
vertices,
faces,
controls.radius,
controls.detail)
);
break;
}
scene.add(polyhedron);
};
};
var gui = new dat.GUI();
gui.add(controls, 'radius', 0, 40).step(1).onChange(controls.redraw);
gui.add(controls, 'detail', 0, 3).step(1).onChange(controls.redraw);
gui.add(controls, 'type', ['Icosahedron', 'Tetrahedron', 'Octahedron', 'Dodecahedron', 'Custom']).onChange(controls.redraw);
function createMesh(geom) {
// Create an object using two materials
var meshMaterial = new THREE.MeshNormalMaterial();
meshMaterial.side = THREE.DoubleSide;
var wireFrameMat = new THREE.MeshBasicMaterial();
wireFrameMat.wireframe = true;
var mesh = THREE.SceneUtils.createMultiMaterialObject(geom, [meshMaterial, wireFrameMat]);
return mesh;
}
var step = 0;
renderScene();
function renderScene() {
stats.update();
// Rotating polyhedron
polyhedron.rotation.y = step += 0.01;
requestAnimationFrame(renderScene);
webGLRenderer.render(scene, camera);
}
function initStats() {
var stats = new Stats();
stats.setMode(0);
stats.domElement.style.position = 'absolute';
stats.domElement.style.left = '0px';
stats.domElement.style.top = '0px';
document.getElementById("Stats-output").appendChild(stats.domElement);
return stats;
}
}
window.onload = init;
</script>
</body>
</html>
