vue.config.js configuration item
After the vue-cli3 scaffold is erected, there is no Vue in the project directory config. JS file, which needs to be created manually
Create Vue config. js
vue. config. JS (equivalent to the previous webpack.config.js) is an optional configuration file. If this file exists in the root directory of the project (at the same level as package.json), it will be automatically loaded by @ Vue / cli service. You can also use package The Vue field in JSON, but note that this writing method requires you to write in strict accordance with the format of JSON.
Create vue.com in the root directory config. js
vue.config.js configuration
This file should export an object with options:
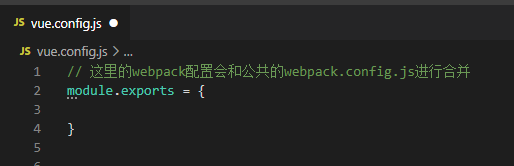
configuration option
publicPath
Type:string
Default:'/'
The basic URL and usage when deploying the application package and the output of the webpack itself Publicpath is consistent.
This value can also be set to an empty string (') or relative path ('. / '), so that all resources will be linked as relative paths, so that the printed packages can be deployed in any path.
// The webpack configuration here will be the same as the public webpack config. JS
module.exports = {
// Execute npm run build unified configuration file path (local access to dist/index.html requires'. / ')
publicPath: './',
}
To set up the development server in the root path, you can use a conditional value:
// The webpack configuration here will be the same as the public webpack config. JS
module.exports = {
// NODE_ENV: Node.js is exposed to system environment variables that execute scripts. It is usually used to determine whether you are in a development or production environment
publicPath: process.env.NODE_ENV === 'production' ? '' : '/',
}
outputDir
Type:string
Default:'dist'
The output file directory is the directory of the production environment build file generated when running Vue cli service build (NPM run build). Note that the target directory will be cleared before construction (pass in – no clean during construction to turn off this behavior).
// The webpack configuration here will be the same as the public webpack config. JS
module.exports = {
// Execute npm run build unified configuration file path (local access to dist/index.html requires'. / ')
// NODE_ENV: Node.js is exposed to system environment variables that execute scripts. It is usually used to determine whether you are in a development or production environment
// publicPath: '/',
publicPath: process.env.NODE_ENV === 'production' ? '' : '/',
outputDir: 'dist', // Output file directory
}
assetsDir
Type:string
Default:''
The directory where the generated static resources (js, css, img, fonts) are placed.
// The webpack configuration here will be the same as the public webpack config. JS
module.exports = {
// Execute npm run build unified configuration file path (local access to dist/index.html requires'. / ')
// NODE_ENV: Node.js is exposed to system environment variables that execute scripts. It is usually used to determine whether you are in a development or production environment
// publicPath: '/',
publicPath: process.env.NODE_ENV === 'production' ? '' : '/',
outputDir: 'dist', // Output file directory
assetsDir: 'static', // Place static resources
}
**Note: * * when overwriting filename or chunkFilename from the generated resource, assetsDir will be ignored.
indexPath
Type:string
Default:'index.html'
Specify the generated index The output path of HTML (relative to outputDir). It can also be an absolute path.
// The webpack configuration here will be the same as the public webpack config. JS
module.exports = {
// Execute npm run build unified configuration file path (local access to dist/index.html requires'. / ')
// NODE_ENV: Node.js is exposed to system environment variables that execute scripts. It is usually used to determine whether you are in a development or production environment
// publicPath: '/',
publicPath: process.env.NODE_ENV === 'production' ? '' : '/',
outputDir: 'dist', // Output file directory
// assetsDir: 'static', / / place static resources
// indexPath: 'index.html ', / / you can leave it unset. Generally, it will default
}
filenameHashing
Type:boolean
Default:true
By default, the generated static resources include a hash in their file names for better cache control. However, this also requires that the HTML of the index is automatically generated by Vue CLI. If you cannot use the index HTML generated by Vue CLI, you can turn off file name hashing by setting this option to false.
// The webpack configuration here will be the same as the public webpack config. JS
module.exports = {
// Execute npm run build unified configuration file path (local access to dist/index.html requires'. / ')
// NODE_ENV: Node.js is exposed to system environment variables that execute scripts. It is usually used to determine whether you are in a development or production environment
// publicPath: '/',
publicPath: process.env.NODE_ENV === 'production' ? '' : '/',
outputDir: 'dist', // Output file directory
// assetsDir: 'static', / / place static resources
// indexPath: 'index.html ', / / you can leave it unset. Generally, it will default
// filenameHashing:true, / / file naming
}
pages
Type:Object
Default:undefined
Build applications in multi page mode. Each "page" should have a corresponding JavaScript entry file.
The value should be an object, the key of the object is the name of the entry, and the value is:
An object that specifies entry,template,filename,title and chunks (all optional except entry);
Or a string specifying its entry.
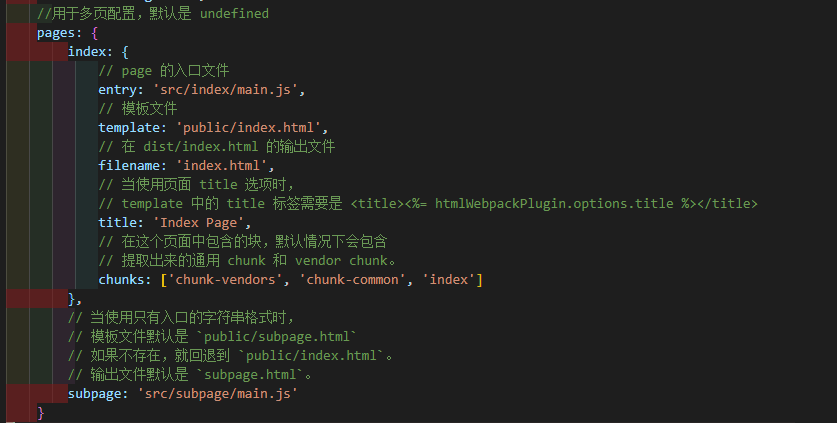
**Note: * * when building in multi page application mode, the webpack configuration will contain different plug-ins (at this time, there will be multiple instances of HTML webpack plugin and preload webpack plugin). If you try to modify the options of these plug-ins, make sure to run vue inspect.
lintOnSave
Type:boolean|'error'
Default:true
Whether to use 'eslint loader' to check when saving. Valid values: ` ture` | `false ` | ` error '` when set to ` ` error', the detected error will trigger compilation failure.
// The webpack configuration here will be the same as the public webpack config. JS
module.exports = {
// Execute npm run build unified configuration file path (local access to dist/index.html requires'. / ')
// NODE_ENV: Node. Expose the JS environment variables of the script execution system. It is usually used to determine whether you are in a development or production environment
// publicPath: '/',
publicPath: process.env.NODE_ENV === 'production' ? '' : '/',
outputDir: 'dist', // Output file directory
// assetsDir: 'static', / / place static resources
// indexPath: 'index.html ', / / you can leave it unset. Generally, it will default
// filenameHashing:true, / / file naming
lintOnSave: false, //Set whether to enable eslint validation every time you save code in the development environment
}
runtimeCompiler
Type:boolean
Default:false
Whether to use the Vue build that contains the runtime compiler. When set to true, you can use the template option in Vue components, but this will add about 10kb to your application.
// The webpack configuration here will be the same as the public webpack config. JS
module.exports = {
// Execute npm run build unified configuration file path (local access to dist/index.html requires'. / ')
// NODE_ENV: Node.js is exposed to system environment variables that execute scripts. It is usually used to determine whether you are in a development or production environment
// publicPath: '/',
publicPath: process.env.NODE_ENV === 'production' ? '' : '/',
outputDir: 'dist', // Output file directory
// assetsDir: 'static', / / place static resources
// indexPath: 'index.html ', / / you can leave it unset. Generally, it will default
// filenameHashing:true, / / file naming
lintOnSave: false, //Set whether to enable eslint validation every time you save code in the development environment
// runtimeCompiler: false, / / whether to use the full build version with in browser compiler
}
transpileDependencies
Type:Array<string | RegExp>
Default:[]
By default, Babel loader ignores all nodes_ Files in modules. If you want to explicitly translate a dependency through Babel, you can list it in this option.
productionSourceMap
Type:boolean
Default:true
If you don't need the source map of the production environment, you can set it to false to speed up the construction of the production environment.
crossorigin
Type:string
Default:undefined
Set generated HTML
integrity
Type:boolean
Default:false
And in the generated HTML
Webpack related configuration
configureWebpack
Type:Object | Function
If this value is an object, it will pass webpack-merge Merge into the final configuration.
If this value is a function, the parsed configuration will be received as a parameter. This function can modify the configuration without returning anything. It can also return a cloned or merged configuration version.
chainWebpack
Type:Function
Is a function that receives a webpack-chain The ChainableConfig instance of. Allows finer grained modifications to the internal webpack configuration.
Css related configuration
css: { // css related configuration
// Whether to extract the CSS in the component into an independent CSS file. It is true in the production environment and false in the development environment
extract: process.env.NODE_ENV === "production",
// Whether to open source map for CSS. Setting to true may affect the performance of the build.
sourceMap: false,
// Enable CSS modules for all CSS / pre processor files (preload)
requireModuleExtension: true,
loaderOptions: {
sass: {
// data: `@import "@/assets/css/variables.scss";`
}
}
},
css.modules(===css.requireModuleExtension)
Type:boolean
Default:false
By default, only * module. The file at the end of [ext] will be regarded as CSS Modules. When set to true, you can remove the in the file name Module and all * (CSS | SCSS | sass | less | style (US)) files are regarded as CSS Modules.
Deprecated from v4, please use [code 010 here] . In v3, this option has the same meaning as CSS Requiremeduleextension
css.extract
Type:boolean | Object
Default: true in production environment and false in development environment
Whether to extract the CSS in the component into a separate CSS file (rather than the inline code dynamically injected into JavaScript).
css.sourceMap
Type:boolean
Default:false
Whether to open source map for CSS. Setting to true may affect the performance of the build.
css.loaderOptions
Type:Object
Default:{}
Pass options to CSS related loader s.
Supported loader s are:
devServer
Type:Object
All? webpack-dev-server? Options for All support. be careful:
Some values such as host, port, and https may be overridden by command line parameters.
Some values like publicPath and historyApiFallback should not be modified because they need to be compatible with the development server publicPath Synchronize to ensure normal operation.
devServer.proxy
Type:string | Object
If your front-end application and back-end API server are not running on the same host, you need to proxy API requests to the API server in the development environment. This problem can be solved through Vue config. Devserver.js Proxy option.
devServer: {
port: 2021, // Set port number
host: '10.32.120.69', // ip local
disableHostCheck: true, //Turn off HOST checking for HTTP requests for DNS rebinding
hotOnly: false, // Hot renewal
https: false, // https:{type:Boolean} configure prefix
open: false, //Configure auto launch browser
proxy: null, //Set agent
// proxy: {/ / the purpose is to solve cross domain. If the test environment does not need cross domain, it does not need to be configured
// '/ api': {/ / intercept url interface starting with / api
// target: 'https://api.taobao.cn/ ', / / target interface domain name
// changeOrigin: true, / / cross domain
// ws: true, / / configure this parameter if you want to proxy websockets
// secure: false, / / this parameter needs to be configured if it is an https interface
// //Identification replacement
// //When the original request address is / api/getData and '/ api' is replaced by '',
// //The request address after proxy is: http://xxx.xxx.xxx/getData
// //If it is replaced with '/ other', the request address after proxy is http://xxx.xxx.xxx/other/getData
// pathRewrite: {/ / identity replacement
// '^ / api': '/' / / rewrite the interface. The background interface points to all interfaces because they are not uniform/
// '^/api': '/api/mock'
// }
// }
// }
},
It is understood here as using '/ api' instead of the address in the target. In the later components, when we drop the interface, we directly use api instead. For example, I want to call ' https://api.taobao.cn/xxx/proxy time=2017-07-07 14:57:22 ', write' / api/xxx directly/ proxy time=2017-07-07 14:57:22 '
import axios from 'axios'
export default {
created() {
// 1. Agent succeeded
// https://api.taobao.cn/users/proxy Convert to http://localhost:2021/api/users/proxy
axios.get('/api/users/proxy').then(res => { // /api cannot be less
console.log(res)
})
}
}
parallel
Type:boolean
Default:require('os').cpus().length > 1
Whether to use thread loader for Babel or TypeScript. This option is automatically enabled when the CPU of the system has more than one kernel and only works on production builds.
pwa study
Type:Object
towards PWA plug-in Transfer options.
The service worker added in this plug-in is only enabled in the production environment (for example, only when you run npmrunbuild or yarnbuild).
Enabling serviceworker in development mode is not recommended because it will result in the use of previously cached assets without including the latest local changes.
pwa: {
// serviceWorker:false,
// Allows you to start with an existing service worker file, create a copy of the file, and inject the "pre cache list" into it.
// workboxPluginMode:'InjectManifest',
// workboxOptions: {
// //swSrc: './app/sw.js', /* Empty file. */
// },
iconPaths: {
favicon32: "favicon.ico",
favicon16: "favicon.ico",
appleTouchIcon: "favicon.ico",
maskIcon: "favicon.ico",
msTileImage: "favicon.ico"
}
}
pluginOptions
Type:Object
This is an object that does not perform any schema validation, so it can be used to pass any third-party plug-in options.
// The webpack configuration here will be the same as the public webpack config. JS
module.exports = {
// Execute npm run build unified configuration file path (local access to dist/index.html requires'. / ')
// NODE_ENV: Node.js is exposed to system environment variables that execute scripts. It is usually used to determine whether you are in a development or production environment
// publicPath: '/',
publicPath: process.env.NODE_ENV === 'production' ? '' : '/',
outputDir: 'dist', // Output file directory
// assetsDir: 'static', / / place static resources
// indexPath: 'index.html ', / / you can leave it unset. Generally, it will default
// filenameHashing:true, / / file naming
lintOnSave: false, //Set whether to enable eslint validation every time you save code in the development environment
// runtimeCompiler: false, / / whether to use the full build version with in browser compiler
configureWebpack: { // Alias configuration
resolve: {
alias: {
//'src ':' @ ', configured by default
'assets': '@/assets',
'common': '@/common',
'components': '@/components',
'api': '@/api',
'views': '@/views',
'plugins': '@/plugins',
'utils': '@/utils',
}
}
// Can be added before use~
},
productionSourceMap: false, //If you don't need the source map of the production environment, you can set it to false to speed up the construction of the production environment
css: { // css related configuration
// Whether to extract the CSS in the component into an independent CSS file. It is true in the production environment and false in the development environment
extract: process.env.NODE_ENV === "production",
// Whether to open source map for CSS. Setting to true may affect the performance of the build.
sourceMap: false,
// Enable CSS modules for all CSS / pre processor files (preload)
requireModuleExtension: true,
loaderOptions: {
sass: {
// data: `@import "@/assets/css/variables.scss";`
}
}
},
devServer: {
port: 2021, // Set port number
host: '10.32.120.69', // ip
disableHostCheck: true, //Turn off HOST checking for HTTP requests for DNS rebinding
hotOnly: false, // Hot renewal
https: false, // https:{type:Boolean} configure prefix
open: false, //Configure auto launch browser
proxy: null, //Set agent
// proxy: {/ / the purpose is to solve cross domain. If the test environment does not need cross domain, it does not need to be configured
// '/ api': {/ / block url interface starting with / api
// target: 'https://api.taobao.cn/ ', / / target interface domain name
// changeOrigin: true, / / cross domain
// ws: true, / / configure this parameter if you want to proxy websockets
// secure: false, / / this parameter needs to be configured if it is an https interface
// //Identification replacement
// //When the original request address is / api/getData and '/ api' is replaced by '',
// //The request address after proxy is: http://xxx.xxx.xxx/getData
// //If it is replaced with '/ other', the request address after proxy is http://xxx.xxx.xxx/other/getData
// pathRewrite: {/ / identity replacement
// '^ / api': '/' / / rewrite the interface. The background interface points to all interfaces because they are not uniform/
// '^/api': '/api/mock'
// }
// }
// }
},
// The service worker added in this plug-in is only enabled in the production environment (for example, only when you run npm run build or yarn build).
// It is not recommended to enable service worker in development mode because it will lead to the use of previously cached assets without including the latest local changes.
pwa: {
// serviceWorker:false,
// Allows you to start with an existing service worker file, create a copy of the file, and inject the "pre cache list" into it.
// workboxPluginMode:'InjectManifest',
// workboxOptions: {
// //swSrc: './app/sw.js', /* Empty file. */
// },
iconPaths: {
favicon32: "favicon.ico",
favicon16: "favicon.ico",
appleTouchIcon: "favicon.ico",
maskIcon: "favicon.ico",
msTileImage: "favicon.ico"
}
}
}