Vue2.x / Vue3.0 source code analysis
I
1. Data driven (Vue's biggest feature)
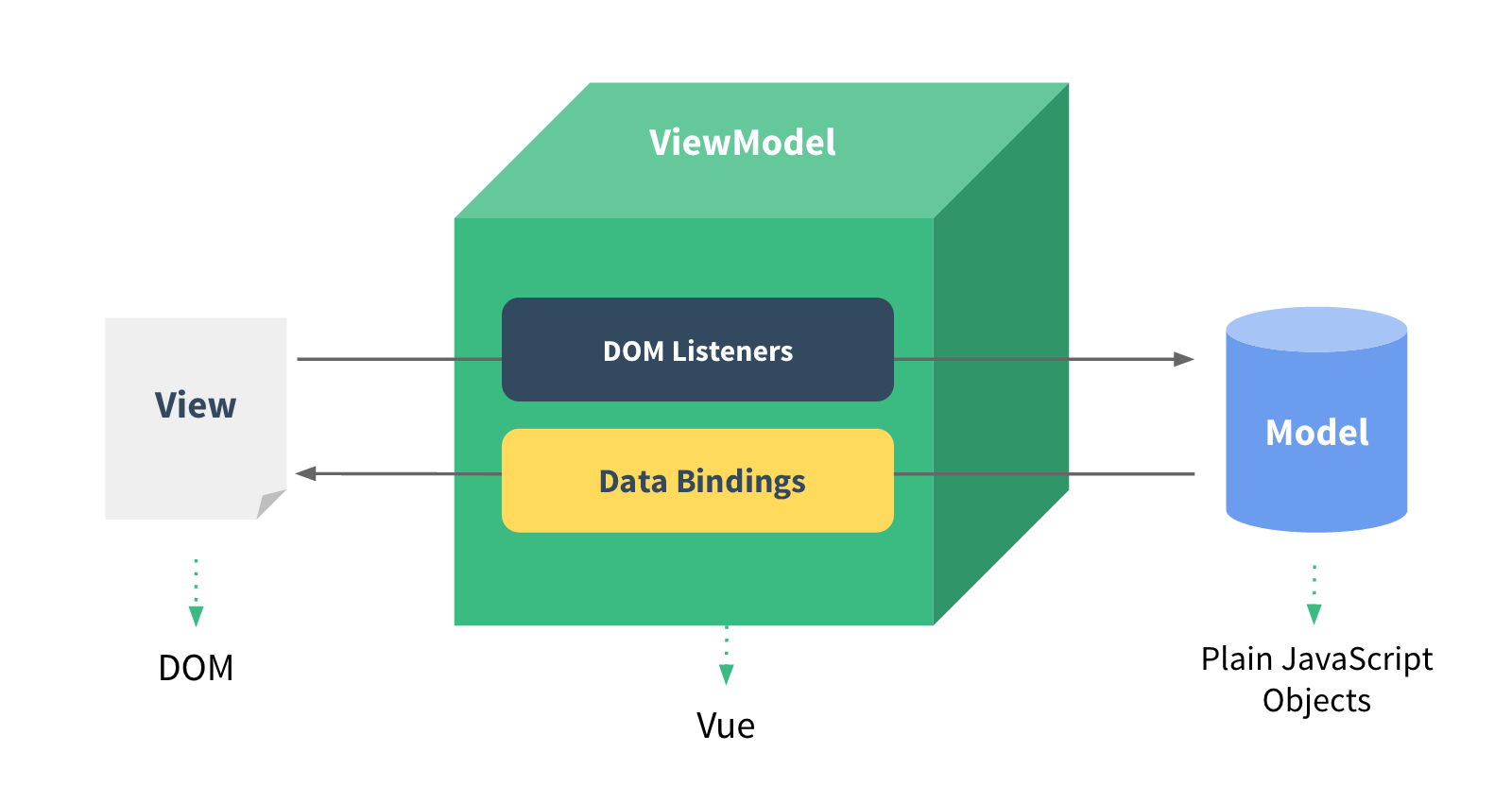
I MVVM (data driven view): model view ViewModel
Traditional data driven approach
Use DOM operations to update the view
Updated method: vm=new Vue() is used for data initialization and view update. DOM operation is still used, but it is encapsulated in vm=new Vue(). We do not need to apply it ourselves. It is an internal application
2. Data hijacking (an important principle for realizing bidirectional data binding)
Hijack the data in a simulated Vue object. Once the data changes, it will be intercepted without direct change
Using object The defineproperty (target object, property, description) function is used for data hijacking
It mainly depends on the two methods get() and set() encapsulated in this function
get() {
console.log("get", data.msg);
}
set(newValue) {
console.log("set", newValue);
if (newValue === data.msg) {
return;
}
data.msg = newValue;
}
3. Multi attribute data hijacking
By encapsulating a data hijacking function, the function includes traversing the attribute values of the whole object, data hijacking, data update, and data-driven view operations
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="IE=edge">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<title>Document</title>
<div id="app">
</div>
</head>
<body>
<script src="js/vue.js"></script>
<script>
const data={
name:"aa",
age:18
};
let vm={}
function handleData(data){
Object.keys(data).forEach((key)=> {
Object.defineProperty(vm,key,{
get(){
console.log('get',data[key]);
},
set(newValue){
console.log('set',newValue);
if(newValue===data[key])
{
return
}
data[key]=newValue;//Data update
//Data driven view
document.querySelector("#app").textContent=document.querySelector("#app").textContent+" "+data[key];
}
})
});
}
handleData(data)
console.log(vm.name);//get
vm.name="bb";//set
console.log(vm.age);//get
vm.age=100;
</script>
</body>
</html>
4. There is data hijacking of the object in the attribute
For example:
const data = {
name: "aa",
age: 18,
friend: {
gender: 0,
name1: "bb",
},
};//friend is an object
Methods: define responsive data, hijack each attribute, and use recursion and traversal to realize the operation of data hijacking
5. Optimization scheme of data hijacking: Proxy proxy object
Vue3. Version 0 further optimizes the scheme of data hijacking:
Instead of thinking about internal attributes, you can directly represent the whole object
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8" />
<meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="IE=edge" />
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0" />
<title>Document</title>
<div id="app">{{msg}}</div>
</head>
<body>
<script src="js/vue.js"></script>
<script>
const data = {
name:'aaa',
age:18,
friend:{
gender:"female",
name:'bbb'
}
};
let vm = new Proxy(data,{
get(target,key){ //Target represents the target object and cannot be a concrete object
console.log('get',target[key]);
return target[key]
},
set(target,key,value){
console.log('set',value);
if(value===target[key])
{
return
}
target[key]=value;
}
})
console.log(vm.name);
vm.age=100;
</script>
</body>
</html>
II
1. Publish and subscribe
utilize o n and on and on and emit to register events and trigger events, respectively.
e m i t use come touch hair , and emit is used to trigger, and emit is used to trigger and on is used to subscribe
let vm=new Vue();//They are all the same and cannot be split into three roles
//Registration event
//Parameters: event type, event handler
vm.$on('change',()=>{
console.log('event1');
})
vm.$on('change',()=>{
console.log('event2');
})
vm.$emit('change')//Event type, event handling
2. Publish and subscribe source code
Idea:
Release( e m i t ) person transfer use matter piece in heart ( touch hair matter piece ) , however after book Read ( Emitters call the event center (trigger events) and subscribe( The "emit" user calls the event center (trigger event), and then the "on" user registers the task in the event center to subscribe (register event) [the external chain picture transfer fails, and the source station may have an anti-theft chain mechanism. It is recommended to save the picture and upload it directly (img-rVHNMUnD-1627296233557)(Vue2.x Vue3.0 source code analysis. assets/image-20210716182850218.png)]
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8" />
<meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="IE=edge" />
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0" />
<title>Document</title>
<div id="app"></div>
</head>
<body>
<script src="js/vue.js"></script>
<script>
//You can have multiple handler functions for the same event type
class Vue1{
constructor(){
this.subs=Object.create(null)//Than this Sub = {} is better. It means there is no attribute. It is empty
//The container is used to store the relationship between eventType and handler
//{eventType1:[fun1,fun2..],eventType2:[],}
}
$on(eventType,handler){//Register events, subscribe, and register data with the handler
this.subs[eventType]=this.subs[eventType]||[]
this.subs[eventType].push(handler)
}
$emit(eventType){//Trigger events are not registered events. They cannot be initialized as above, but should be judged
if(this.subs[eventType])
{
this.subs[eventType].forEach(fun => {
fun()//Each eventType corresponds to more than one function. When this event is triggered, all the functions it includes will be triggered at the same time
});
}
}
}
let vm=new Vue1();
//Registration event
//Parameters: event type, event handler
vm.$on('change',()=>{
console.log('event1');
})
vm.$on('change',()=>{
console.log('event2');
})
vm.$emit('change')//Event type, event handling
</script>
</body>
</html>
3. Observer mode
Compared with the publish subscribe model, the publisher is more closely related to the subscriber (observer), and there is no separate event center.
[the external chain picture transfer fails. The source station may have an anti-theft chain mechanism. It is recommended to save the picture and upload it directly (img-X6plTuJN-1627296233559)(Vue2.x Vue3.0 source code analysis. assets/image-20210716183445822.png)]
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8" />
<meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="IE=edge" />
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0" />
<title>Document</title>
</head>
<body>
<script src="js/vue.js"></script>
<script>
class Publisher{
constructor(){
this.subs=[]
}
//Add subscriber
addSub(sub){
if(sub&&sub.update()){
this.subs.push(sub)
}
}
//Notify subscribers
notify(){
this.subs.forEach(w=>{
w.update()
})
}
}
class Watcher{
//Get publisher's notification information
update(){
console.log('update');
}
}
const p=new Publisher()
const w1=new Watcher()
const w2=new Watcher()
p.addSub(w1)
p.addSub(w2)
</script>
</body>
</html>
4. Vue source code
Vue source code is compiled by means of data hijacking and template compilation
//compiler.js
// Template related operations
// dom :el
// data
class Compiler{
constructor(vm){
this.el = vm.$el
this.data = vm.$data
this.compile(this.el)
}
// compile
compile(el){
let childNodes = el.childNodes
// Traversal and recursion
Array.from(childNodes).forEach(node=>{
// Code segmentation
console.log('this');
if(this.isTextNode(node)){ // text processing
console.log(this);
compileText(node)
}else if(this.isElementNode(node)){ //Element processing
this.compileElement(node)
}
if(node.childNodes){
this.compile(node) // recursion
}
})
}
// Compile text interpolation type processing {{msg}}: for example, hello world {{msg} = > Hello World Vue
compileText(node){
console.log(this);
let value = node.textContent //content
let reg = /\{\{(.+?)\}\}/ // Regular rules
if(reg.test(value)){
// Get: variable name of interpolation expression
let k = RegExp.$1.trim()
console.log(k);
// replace
node.textContent = value.replace(reg,this.data[k])
//Data change - Notification subscription - Update - CB - compiler DOM operation
new Watcher(this.data,k,(newVlaue)=>{
console.log('compiler--callback');
node.textContent = newVlaue
console.log('view update');
})
}
}
// Compile element
compileElement(node){
// get attribute
let attributes = node.attributes
// Traverse all attributes
Array.from(attributes).forEach(attr=>{
// V -: V text - > text get vue instruction
console.log(attr);
let attrName = attr.name // Attribute name
// Is it instruction v-
if(this.isDirective(attrName)){
// Get the part v- after the attribute name -- instruction name
attrName = attrName.substr(2)
console.log(attrName);
// Attribute value - data (key)
let key = attr.value
// text - mapping method. Different instructions and different processing methods are different functions
this.update(node,attrName,key)
}
})
}
// Call the instruction function to update the dom content
update(node,attrname,key){
// if(attrname=='text'){
// this.textUpdate(node,attrname,key)
// }
// if(attrname=='model'){
// this.modelUpdate(node,attrname,key)
// }
let fn = this[attrname + 'Update']
fn && fn.call(this,node,attrname,key)
}
// Code segmentation
textUpdate(node,attrname,key){
node.textContent = this.data[key]
//Data change - Notification subscription - Update - CB - compiler DOM operation
new Watcher(this.data,key,(newVlaue)=>{
node.textContent = newVlaue
})
}
modelUpdate(node,attrname,key){
// Note value
node.value =this.data[key]
new Watcher(this.data,key,(newVlaue)=>{
node.value = newVlaue
})
node.addEventListener('input',()=>{
this.data[key] =node.value
})
}
// Node judgment correlation
isTextNode(node){
return node.nodeType === 3
}
isElementNode(node){
return node.nodeType === 1
}
isAttrNode(node){
return node.nodeType === 2
}
isDirective(attrName){
return attrName.startsWith('v-')
}
// js dom
// jquery dom
// template view data has no status tracking
// MVVM: view data state synchronization, high data driving efficiency; Virtual DOM js {1} {2}
}
//Vue.js
class Vue{
constructor(options){
this.$options = options
this.$data = options.data
this.$el = typeof options.el ==='string'? document.querySelector(options.el) : options.el
// Inject into Vue instance;
this._proxyData(this.$data)
// vm.$ Data = > responsive
new Observer(this.$data)
// Template compilation: parse the specified interpolation expression
new Compiler(this)
}
// Data = > Data hijacking = > inject into Vue instance;
_proxyData(data){
// Traversal key
Object.keys(data).forEach(key=>{
Object.defineProperty(this,key,{
get(){
return data[key]
},
set(nValue){
if( data[key]===nValue){
return
}
data[key] = nValue
}
})
})
}
}
//Observer.js
class Observer{
constructor(data){
this.walk(data)
}
// Core traversal
walk(data){
if(!data || typeof data !=='object'){
return
}
Object.keys(data).forEach(key=>{
this.defineReactive(data,key,data[key])
})
}
// Define responsive data
defineReactive(data,key,value){
let publisher = new Publisher()
let that = this
// console.log(data[key]);
// Maximum call stack size exceeded at Object
// this.walk(data[key])
this.walk(value)
Object.defineProperty(data,key,{
get(){
// Collect dependencies and add observers
Publisher.target&&publisher.addSub(Publisher.target)
return value
},
set(nValue){
if( value===nValue){
return
}
// this points to data
// console.log('this',this);
value = nValue
// Attribute assignment is an object
that.walk(nValue)
console.log('set--notify()');
// Notification dependency
// Send notification: data change = > observer update() = > template DOM ({SS}} = > value) = > views
publisher.notify()
}
})
}
}
//index.html
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="IE=edge">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<title>Document</title>
</head>
<body>
<div id="app">
hello world {{msg}}
<h2 >
sss{{msg}}
<h3>hello {{msg}}</h3>
</h2>
<h2 v-text="msg"></h2>
<input type="text" v-model='msg'>
</div>
<script src="./js/publisher.js"></script>
<script src="./js/watcher.js"></script>
<script src="./js/compiler.js"></script>
<script src="./js/observer.js"></script>
<script src="./js/vue.js"></script>
<script>
let vm = new Vue({
el:'#app',
data:{
msg:'hello vue1',
friend:{
name:'zhangsan',
age:28
}
}
})
</script>
</body>
</html>
//publisher.js
class Publisher{
constructor(){
this.subs = []
}
// Add subscriber
addSub(sub){
if(sub && sub.update){
this.subs.push(sub)
}
}
// Notify subscribers
notify(){
console.log('publisher---notify()');
this.subs.forEach(w=>{
w.update() // appointment
})
}
}
// class Watcher{
// //Get publisher's notification information
// update(){
// console.log('update');
// }
// }
//watcher.js
class Watcher{
constructor(data,key,cb){
this.data = data
this.key = key
this.cb = cb
Publisher.target = this
this.oldValue = data[key]
}
// Get publisher's notification information
update(){
console.log('watcher --- update');
let newValue=this.data[this.key]
if(this.oldValue===newValue){
return
}
// Call the template to update the DOM
this.cb(newValue)
}
}