preface
★ this is Xiao Leng's blog
‡ see the column for high-quality technical articles
The official account of the individual, sharing some technical articles, and the pit encountered.
Current series: data structure series
Source code git warehouse‘
Data structure code address Code Git warehouse address
Circular linked list
Understanding one-way circular linked list
Here we take the unidirectional ring linked list as an example
The next field of our last node points to the head node to form a closed loop
Reference scenarios and problems
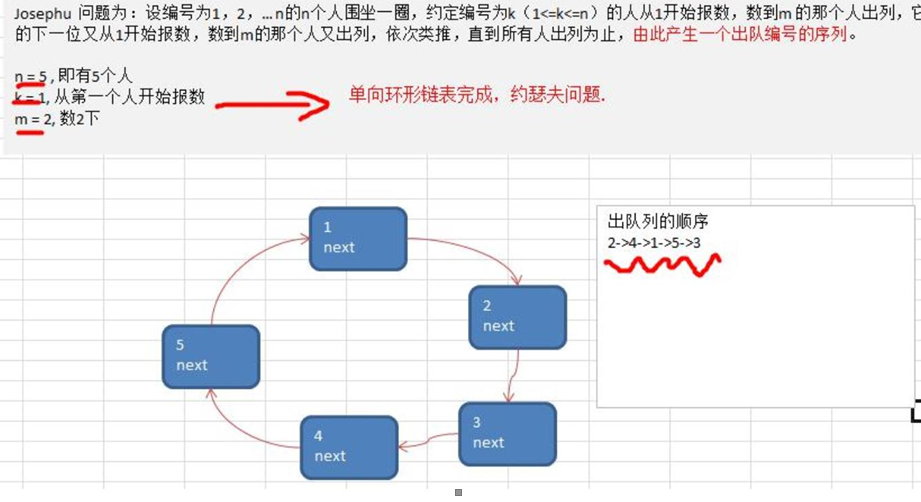
Josephu (Joseph, Joseph Ring) problem
Josephu's problem is: let n people with numbers 1, 2,... N sit around. It is agreed that the person with number k (1 < = k < = n) will count off from 1, the person who counts to m will be listed, its next person will count off from 1, the person who counts to m will be listed again, and so on until everyone is listed
This generates a sequence of outgoing numbers.

Train of thought tips:
Tip: use a circular linked list without leading nodes to deal with the Josephu problem: first form a single circular linked list with n nodes, and then count from 1 from node k. when m is counted, the corresponding node is deleted from the linked list, and then count from 1 from the next node of the deleted node until the last node is deleted from the linked list. The algorithm ends.
Joseph problem solving ideas
Understand the Joseph problem and the scenario we want to achieve,
- Write and implement one-way ring linked list
- Joseph's problem requires that the children who report the number according to the interval be listed
- coding out the requirements we need
Realize one-way circular linked list
thinking
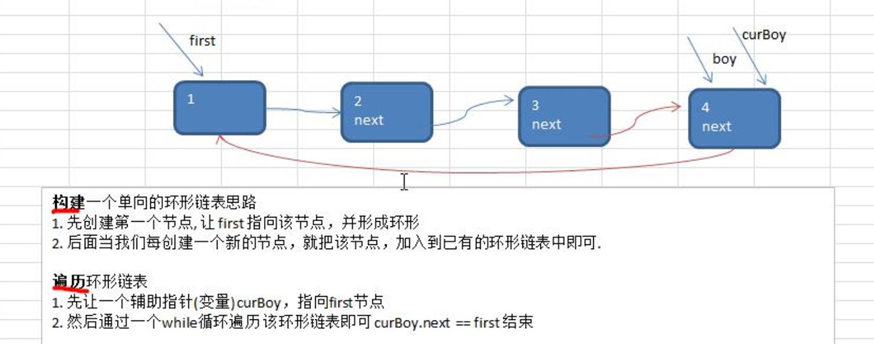
Generally, it is similar to our one-way linked list in that:
- When creating the linked list, we need to point the last of the tail node to the head node, which means that we need at least two pointers to record the head and tail nodes.
- The traversal method should also be slightly changed. The condition for ending the loop is from head Next = null changed to curboy Next (pointer to tail node) = first; When the last node is the head node, the traversal is the second node
We simply create a node object to implement the linked list
The nodes of ring linked list for Joseph problem
//Circular linked list node
class Boy {
private int No;
private Boy Next;
public Boy(int no) {
this.No = no;
}
public int getNo() {
return No;
}
public void setNo(int no) {
No = no;
}
public Boy getNext() {
return Next;
}
public void setNext(Boy next) {
Next = next;
}
}
Create a ring linked list object to generate and traverse the linked list, as well as the way to solve Joseph's problem (see code Notes for specific implementation ideas)
// Circular unidirectional linked list
class CircleSingleLinkeList {
Boy first = null;
/**
* @author Cold Huanyuan doorwatcher
* @context: A circular linked list parameter is the number of nodes in the linked list
* @date: 2021/12/21 15:47
* @param nums
* @return: void
*/
public void CreateListNode(int nums) {
if (nums < 1) {
System.out.println("The game cannot be started because the linked list is less than the minimum number of game nodes");
return;
}
// Create a helper between traversal and pointing nodes
Boy curBoy = null;
for (int i = 1; i <= nums; i++) {
Boy boy = new Boy(i);
//If there is only one node, a ring linked list can also be generated
if (i == 1) {
first = boy;
first.setNext(first);
curBoy = first;//Point the auxiliary pointer to the first node of the linked list to form a closed loop
} else {
// If not, multiple nodes will be generated
curBoy.setNext(boy);
boy.setNext(first);
curBoy = boy;
}
}
}
public void showListBoy() {
if (first == null) {
System.out.println("The linked list is empty and cannot be traversed");
return;
}
// The frist node cannot be moved. We create a pointer
Boy curboy = first;
while (true) {
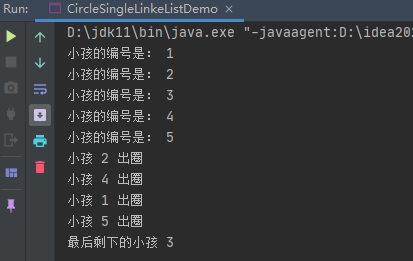
System.out.printf("The child's number is: %d \n", curboy.getNo());
// Description: the traversal has been completed
if (curboy.getNext() == first) {
break;
}
//Move cursor back
curboy = curboy.getNext();
}
}
/**
* @author Cold Huanyuan doorwatcher
* @context: Here we solve Joseph's problem by playing games with children,
* @date: 2021/12/22 21:16
* @param nums How many children are there altogether
* @param start Start counting off from that child
* @param index Count off every few children
* @return: void
*/
public void JosephuFunc(int nums, int start, int index) {
if (first == null || start < 1 || start > nums) {
System.out.println("The parameter is incorrect. Please re-enter the parameter");
return;
}
Boy helper = first;
//Traverse the helper to the last node
while (true) {
if (helper.getNext() == first) {
break;
}
helper = helper.getNext();
}
// Before the child counts off, traverse the pointer to the child's node starting from start
for (int i = 0; i < start - 1; i++) {
first = first.getNext();
helper = helper.getNext();
}
//When the child counts off, let the first and helper move m-1 times at the same time, and then make a circle
//Here, the loop operation knows a node in the circle
while (true) {
//The description list has only one node
if (helper == first) {
break;
}
//Move the pointer back after the loop
for (int i = 0; i < index - 1; i++) {
first = first.getNext();
helper = helper.getNext();
}
// At this time, the first selected node is the child to be out of the circle
System.out.printf("child %d Out of circle\n", first.getNo());
//Out of loop operation
first = first.getNext();
helper.setNext(first);
}
System.out.printf("The last remaining children %d \n", first.getNo());
}
}
Implementation results