Picture optimization
Use URL loader optimization to convert small pictures into base64 compression to prevent too many small pictures and too many requests.
Download URL loader
npm install -D url-loader
to configure
On webpack Configuration in prod.conf.js folder
module: {
rules: [{
test: /\.(png|svg|jpg|gif)$/,
use: [{
loader: 'url-loader', // Too many optimized small pictures cause too many requests
options: {
limit: 8192, // If the image is less than 8192 bytes, it is directly built into the template based on base64. Otherwise, it is copied
outputPath: 'img/'
}
}]
},
Separate third-party packages
Packaged bundle JS folder is large, so the request is slow every time it is loaded, so it is necessary to separate the third-party package during packaging. Use the Commons chunkplugin plug-in for configuration.
On webpack Configuration in prod.conf.js folder
//Introducing webpack
const webpack = require('webpack')
//Change entry to an object
entry: {
vendor: ['babel-polyfill', "axios", "marked", "react", "react-dom", "react-router-dom"], // Third party documents
app: './src/main.js'
},
plugins: [
new webpack.optimize.CommonsChunkPlugin({
name: "vendor", // When loading the resources in the vendor, merge these resources into the vendor JS file
filename: "js/vendor.js",
minChunks: Infinity,
})
],
Detach the css file and compress the css file
Use the extract text webpack plugin plug-in to separate the css files. In order to give priority to loading css styles as soon as possible when loading the project, and to solve the problem of too large js file volume
Download extract text webpack plugin
npm install -D extract-text-webpack-plugin
to configure
On webpack Configuration in prod.conf.js folder
//introduce
const ExtractTextPlugin = require("extract-text-webpack-plugin")
// Configure detach css file
plugins: [
new ExtractTextPlugin("css/styles.css"), // Package the extracted css files into styles css file
],
module: {
rules: [ {
test: /\.css$/,
use: ExtractTextPlugin.extract({
fallback: "style-loader",
use: {
loader: 'css-loader',
options: {
minimize: true
}
}
})
},
} ]
// Configure compressed css (option to directly configure css loader attribute)
module: {
rules: [
{
test: /\.css$/,
use: ExtractTextPlugin.extract({
fallback: "style-loader",
//This place configures an object and adds an attribute to compress the css file
use: {
loader: 'css-loader',
options: {
minimize: true // Configure the minimize value to true and compress the css file
}
}
})
},
Compress js file
Use uglifyjs webpack plugin to compress JS and reduce the number of packaged vendors js , bundle. JS file size
Download uglifyjs webpack plugin
npm install -D uglifyjs-webpack-plugin
to configure
On webpack Configuration in prod.conf.js folder
//introduce
const UglifyJsPlugin = require('uglifyjs-webpack-plugin')
//to configure
plugins: [
new UglifyJsPlugin(), // Compress JavaScript
],
Compressed Html
In order to reduce the file volume after packaging, make better performance, higher efficiency and improve the loading speed, it is necessary to compress when packaging.
Compress Using HTML webpack plugin
Download HTML webpack plugin
npm install -D html-webpack-plugin
to configure
On webpack Configuration in prod.conf.js file
// introduce
const HtmlWebpackPlugin = require('html-webpack-plugin')
// to configure
plugins: [
new HtmlWebpackPlugin({
template: './index.html', // Index Html is also packaged in the dist directory
// Compress html. The default is false and not compressed
minify: {
collapseWhitespace: true, // Remove carriage returns, line breaks, and extra spaces
removeComments: true, // Delete Note
}
}),]
The second method
New Vue config. JS, set the static resource path to '. /', Otherwise, the project cannot run after packaging
module.exports = {
publicPath: "./"
}
Close the SourceMap mapping file in the production environment and reduce the package size by 80%;
module.exports = {
productionSourceMap: false,
}
Cross domain configuration
module.exports = {
devServer: {
open: false, // Auto launch browser
host: '0.0.0.0', // localhost
port: 6060, // Port number
hotOnly: false, // Hot renewal
overlay: {
// Displays a full screen overlay in the browser when a compiler error or warning occurs
warnings: false,
errors: true
},
proxy: {
//Configure cross domain
'/api': {
target: 'https://www.test.com ', / / domain name of the interface
// ws: true, / / whether to enable websockets
changOrigin: true, // Open the agent and create a virtual server locally
pathRewrite: {
'^/api': '/'
}
}
}
}
}
Configure alias alias
//Load path module
const path = require('path')
//Define the resolve method to convert the relative path into the absolute path
const resolve = dir => path.join(__dirname, dir)
module.exports = {
chainWebpack: config => {
// add alias
config.resolve.alias
.set('@', resolve('src'))
.set('assets', resolve('src/assets'))
.set('api', resolve('src/api'))
.set('views', resolve('src/views'))
.set('components', resolve('src/components'))
}
}
After the configuration is completed, we can write the path like this in the project
//That's what I wrote before import Home from '../views/Home.vue' //After configuring alias alias import Home from 'views/Home.vue' //You can also write that import Home from '@/views/Home.vue'
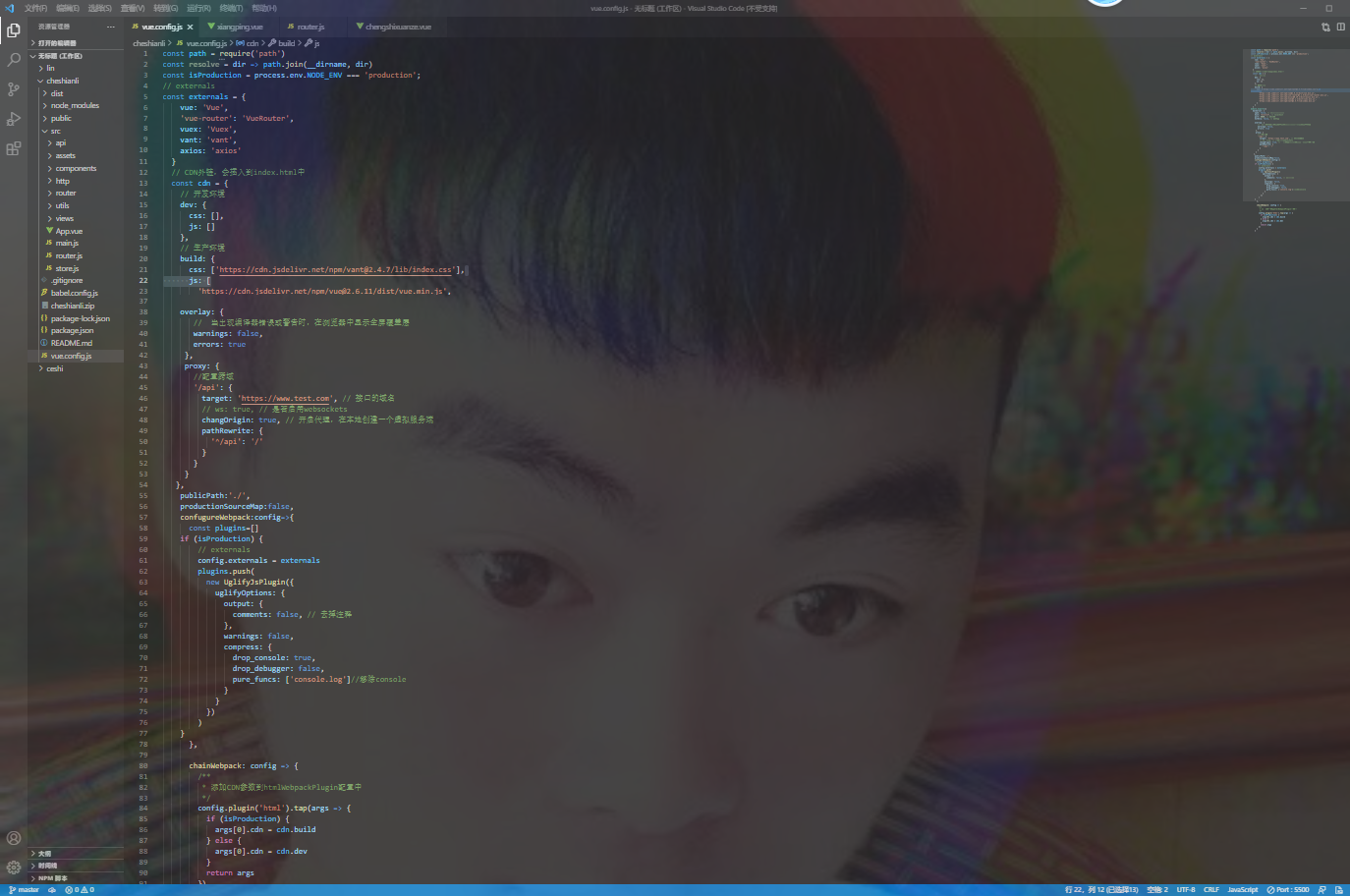
Accelerate optimization with CDN
cdn optimization refers to the introduction of third-party libraries (such as vue, vue router, axios) into the project through cdn JS will significantly reduce and greatly improve the loading speed of the home page of the project. The following are the specific operations:
const isProduction = process.env.NODE_ENV === 'production';
// externals
const externals = {
vue: 'Vue',
'vue-router': 'VueRouter',
vuex: 'Vuex',
vant: 'vant',
axios: 'axios'
}
// CDN external chain will be inserted into index HTML
const cdn = {
// development environment
dev: {
css: [],
js: []
},
// production environment
build: {
css: ['https://cdn.jsdelivr.net/npm/vant@2.12/lib/index.css'],
js: [
'https://cdn.jsdelivr.net/npm/vue@2.6.11/dist/vue.min.js',
'https://cdn.jsdelivr.net/npm/vue-router@3.1.5/dist/vue-router.min.js',
'https://cdn.jsdelivr.net/npm/axios@0.19.2/dist/axios.min.js',
'https://cdn.jsdelivr.net/npm/vuex@3.1.2/dist/vuex.min.js',
'https://cdn.jsdelivr.net/npm/vant@2.12/lib/vant.min.js'
]
}
}
module.exports = {
configureWebpack: config => {
// Modify configuration for production environment
if (isProduction) {
// externals
config.externals = externals
}
},
chainWebpack: config => {
/**
* Add CDN parameter to htmlWebpackPlugin configuration
*/
config.plugin('html').tap(args => {
if (isProduction) {
args[0].cdn = cdn.build
} else {
args[0].cdn = cdn.dev
}
return args
})
}
}
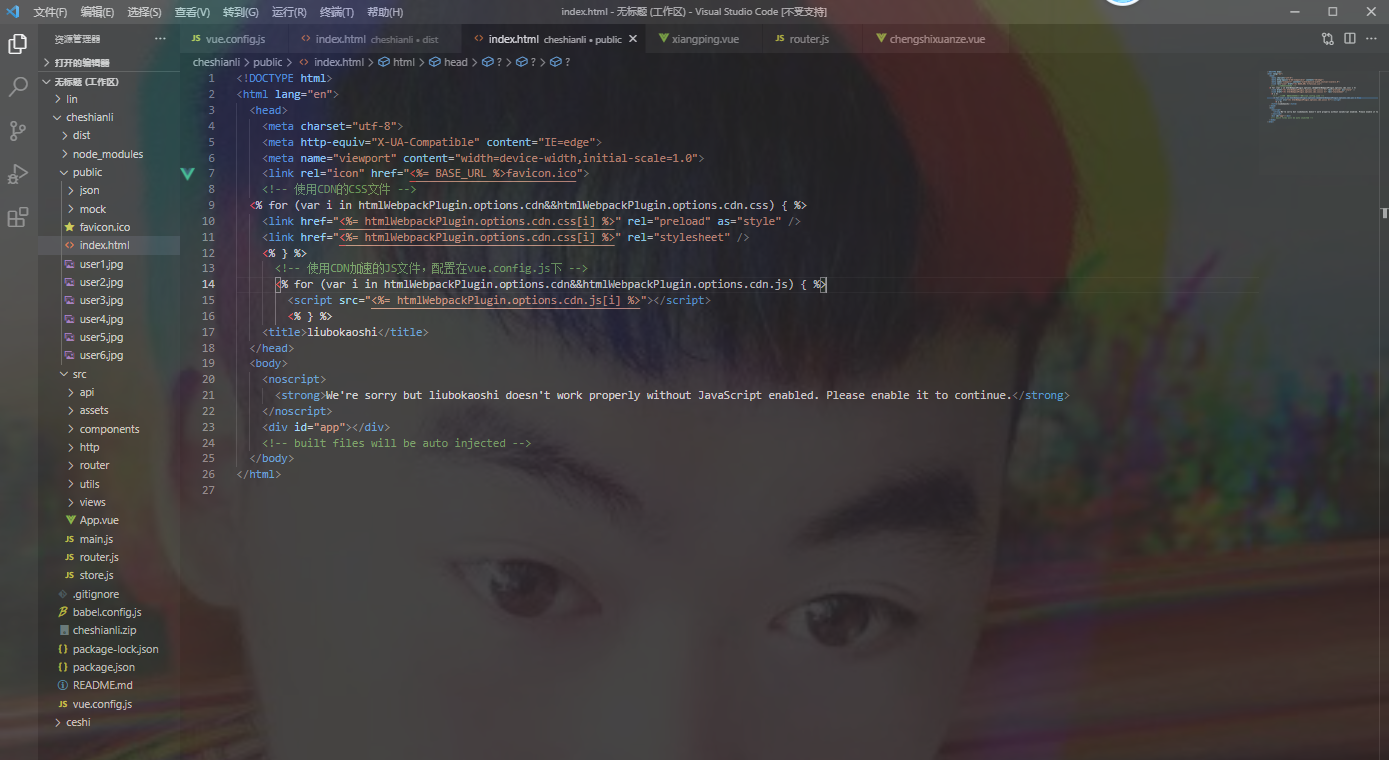
In public / index Add in HTML
<!-- use CDN of CSS file -->
<% for (var i in
htmlWebpackPlugin.options.cdn&&htmlWebpackPlugin.options.cdn.css) { %>
<link href="<%= htmlWebpackPlugin.options.cdn.css[i] %>" rel="preload" as="style" />
<link href="<%= htmlWebpackPlugin.options.cdn.css[i] %>" rel="stylesheet" />
<% } %>
<!-- use CDN Accelerated JS File, configuration in vue.config.js lower -->
<% for (var i in
htmlWebpackPlugin.options.cdn&&htmlWebpackPlugin.options.cdn.js) { %>
<script src="<%= htmlWebpackPlugin.options.cdn.js[i] %>"></script>
<% } %>
Conclusion: cdn introduction is configured, and the volume of 1.1M is less than 660kb. The effect is obvious.
Remove the console Log printing and comments
Download plug-ins
cnpm install uglifyjs-webpack-plugin --save-dev
const UglifyJsPlugin = require('uglifyjs-webpack-plugin')
const isProduction = process.env.NODE_ENV === 'production';
configureWebpack: config => {
const plugins = [];
if (isProduction) {
plugins.push(
new UglifyJsPlugin({
uglifyOptions: {
output: {
comments: false, // Remove comments
},
warnings: false,
compress: {
drop_console: true,
drop_debugger: false,
pure_funcs: ['console.log']//Remove console
}
}
})
)
}
},
In Vue config. JS, add
Conclusion: the volume of dist decreased little after repackaging. Because congsole Log () and comments do not take up too much volume, depending on the comments in the project and console Log () quantity
Final code completion diagram
In public / index Add in HTML