1, Background
As more and more pages are involved in our project, more and more functions and business codes will be involved, and the construction time of the corresponding "webpack" will be longer and longer
The construction time is closely related to our daily development efficiency. When we start devServer or build locally, if the time is too long, our work efficiency will be greatly reduced
Therefore, optimizing the construction speed of webpack is a very important link
2, How to optimize
Common methods to improve the construction speed are as follows:
-
Optimize loader configuration
-
Make rational use of resolve extensions
-
Optimize resolve modules
-
Optimize resolve alias
-
Using DLLPlugin plug-in
-
Using cache loader
-
terser start multithreading
-
Rational use of sourceMap
Optimize loader configuration
When using the loader, you can configure the include, exclude and test attributes to match the files. Contact the include and exclude to specify which matching application loaders
Take the project of ES6 as an example. When configuring} Babel loader, you can do the following:
module.exports = {
module: {
rules: [
{
//If the source code of the project contains only the js file, do not write it as / \ jsx?$/, Improve regular expression performance
test: /\.js$/,
//Babel loader , supports caching the converted results, which can be enabled through the , cacheDirectory , option
use: ['babel-loader?cacheDirectory'],
//Only the # Babel loader is used for files in the # src # directory under the root directory of the project
include: path.resolve(__dirname, 'src'),
},
]
},
};
Make rational use of resolve extensions
During development, we will have various module dependencies. These modules may come from the code written by ourselves or from a third-party library. resolve can help webpack find the appropriate module code to be introduced from each "require/import" statement
Through resolve Extensions is the extension name automatically added when parsing to a file. The default is as follows:
module.exports = {
...
extensions:[".warm",".mjs",".js",".json"]
}
When we import a file, if there is no file suffix, we will find it in turn according to the values in the array
When configuring, don't write all suffixes in it. This will call multiple file searches, which will slow down the packaging speed
Optimize resolve modules
resolve.modules , is used to configure the directories where , webpack , searches for third-party modules. The default value is ['node_modules'], so it will start from node by default_ Find the file in modules. When the installed third-party modules are placed in the root directory of the project/ node_ In the modules directory, you can specify the absolute path to store third-party modules to reduce searching. The configuration is as follows:
module.exports = {
resolve: {
//Use the absolute path to indicate the storage location of the third-party module to reduce the search steps
//Among them__ dirname indicates the current working directory, that is, the project root directory
modules: [path.resolve(__dirname, 'node_modules')]
},
};
Optimize resolve alias
Alias gives an alias to some common paths. Especially when our project directory structure is deep, the path of a file may be. /.. // Form of
Reduce the lookup process by configuring alias
module.exports = {
...
resolve:{
alias:{
"@":path.resolve(__dirname,'./src')
}
}
}
Using DLLPlugin plug-in
The full name of DLL is dynamic link library, which is an implementation method of sharing function library for software in winodw. Webpack also has the function of DLL built in, so that the code that can be shared and does not change frequently can be drawn into a shared library. This library will be introduced into the code of other projects in the subsequent compilation process
The use procedure is divided into two parts:
-
Package a DLL library
-
Import DLL library
Package a DLL library
webpack has a built-in DllPlugin, which can help us package a DLL library file
module.exports = {
...
plugins:[
new webpack.DllPlugin({
name:'dll_[name]',
path:path.resolve(__dirname,"./dll/[name].mainfest.json")
})
]
}
Import DLL library
Use the "DllReferencePlugin" plug-in provided with "webpack" to "mainfest" Analyze the JSON} mapping file to obtain the DLL library to be used
Then, through the AddAssetHtmlPlugin plug-in, we introduce our packaged DLL library into the Html module
module.exports = {
...
new webpack.DllReferencePlugin({
context:path.resolve(__dirname,"./dll/dll_react.js"),
mainfest:path.resolve(__dirname,"./dll/react.mainfest.json")
}),
new AddAssetHtmlPlugin({
outputPath:"./auto",
filepath:path.resolve(__dirname,"./dll/dll_react.js")
})
}
Using cache loader
Add cache loader in front of some high performance overhead cache loaders to cache the results to disk, significantly improving the speed of secondary construction
Saving and reading these cache files will have some time overhead, so please use this loader only for} loaders with high performance overhead
module.exports = {
module: {
rules: [
{
test: /\.ext$/,
use: ['cache-loader', ...loaders],
include: path.resolve('src'),
},
],
},
};
terser start multithreading
Use multi process parallel operation to improve the construction speed
module.exports = {
optimization: {
minimizer: [
new TerserPlugin({
parallel: true,
}),
],
},
};
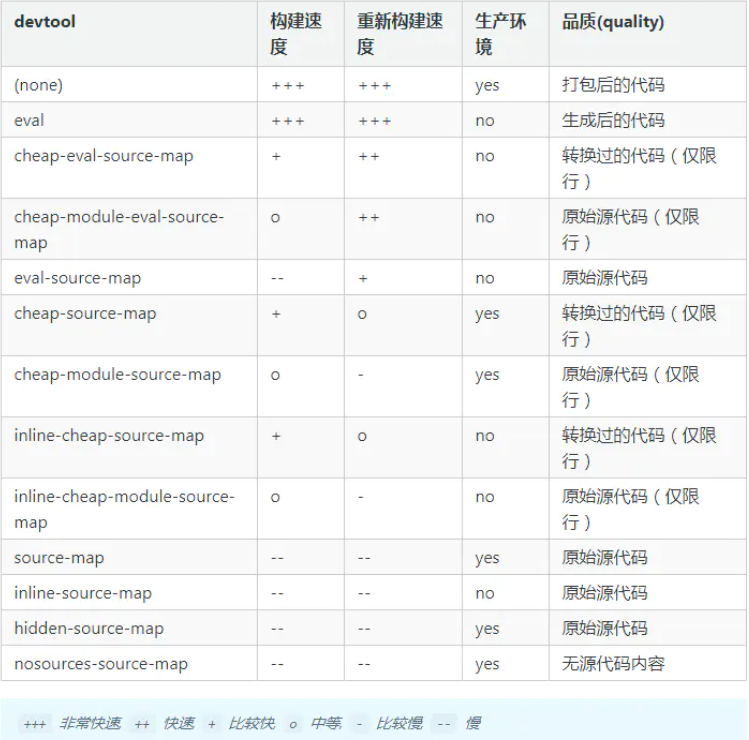
Rational use of sourceMap
When packaging to generate sourceMap, the more detailed the information, the slower the packaging speed will be. The corresponding attribute values are as follows:
3, Summary
It can be seen that there are many ways to optimize the construction of webpack, mainly from optimizing the search time, reducing the scope of file search, reducing unnecessary compilation and so on