Docker Network Model
Docker has multiple network modes, including host, none,bridge Overay and so on. Next, we discuss the relationship between Docker network and iptables with Docker's default bridge network, Docker 0.
Docker 0 network is a virtual bridge network built by Docker. The default gateway address is 172.17.0.1. Docker's default network is the Docker 0 network, which means that any container of the specified network in Docker will join the bridge network, and the containers in the network can communicate with each other.
# ifconfig docker0: flags=4163<UP,BROADCAST,RUNNING,MULTICAST> mtu 1500 inet 172.17.0.1 netmask 255.255.0.0 broadcast 0.0.0.0 inet6 fe80::42:c0ff:febb:bb1e prefixlen 64 scopeid 0x20<link> ether 02:42:c0:bb:bb:1e txqueuelen 0 (Ethernet) RX packets 353181 bytes 163487291 (155.9 MiB) RX errors 0 dropped 0 overruns 0 frame 0 TX packets 297594 bytes 126028894 (120.1 MiB) TX errors 0 dropped 0 overruns 0 carrier 0 collisions 0
Container requests data externally
If the container in Docker 0 requests external data, its packet will be sent to gateway 172.17.0.1. When the packet arrives at the gateway, the host's routing table will be queried to determine from which network card the packet will be sent. iptables is responsible for snat conversion of data packets, and the original address is converted to the address of the corresponding network card, so the container is invisible to the outside world.
External requests for container data
To access the data in the container, the external needs to map the port of the container to the host. At this point, docker will add forwarding rules to iptables and forward the received data to the container.
Docker and iptables
The following figure shows the process of data packet transfer in iptable
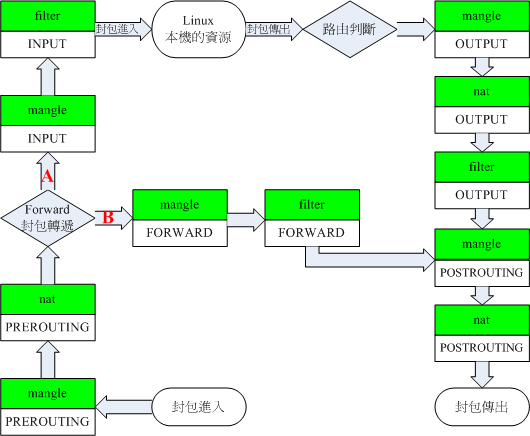
Create a container for port mapping
Next, let's look at how container packets are passed in the iptable Create a redis container that maps port 6379 to port 36379 of the host.
# docker run --name redistest -d -p 36379:6379 172.16.1.129/redis/3.0.7:v1.1 b4c3fc06cdaccc2080f9e4845ebb2d2b789632ddaecb6e7b2e3bdf863c416014
View the nat table of iptables
# iptables -t nat -L Chain PREROUTING (policy ACCEPT) target prot opt source destination DOCKER all -- anywhere anywhere ADDRTYPE match dst-type LOCAL Chain INPUT (policy ACCEPT) target prot opt source destination Chain OUTPUT (policy ACCEPT) target prot opt source destination DOCKER all -- anywhere !loopback/8 ADDRTYPE match dst-type LOCAL Chain POSTROUTING (policy ACCEPT) target prot opt source destination CATTLE_NAT_POSTROUTING all -- anywhere anywhere MASQUERADE all -- 172.17.0.0/16 anywhere MASQUERADE all -- 172.18.0.0/16 anywhere MASQUERADE tcp -- 172.17.0.3 172.17.0.3 tcp dpt:6379 Chain DOCKER (2 references) target prot opt source destination RETURN all -- anywhere anywhere RETURN all -- anywhere anywhere DNAT tcp -- anywhere anywhere tcp dpt:36379 to:172.17.0.3:6379
You can see that the nat table of iptables has a Docker subchain with a data in it.
DNAT tcp -- anywhere anywhere tcp dpt:36379 to:172.17.0.3:6379
This data is responsible for mapping the host tcp36379 port to 172.17.0.3:6379.
Docker subchains are referenced by PREROUTING and OUTPUT chains
-
PREROUTING: Change the destination address of a packet when it reaches the firewall
- OUTPUT: Filter all locally generated data packets (filtering of data packets from source addresses)
That is to say, the packets accessed by the external host 36379 are snat and pnat converted here in nat, and the destination address is 172.17.0.3:6379.
Container accesses external data packages for dnat and pnat, converting 172.17.0.3:6379 to 36379 ports of the host.
View the filter table for iptables
# iptables -L Chain INPUT (policy ACCEPT) target prot opt source destination ACCEPT all -- anywhere anywhere state RELATED,ESTABLISHED ACCEPT icmp -- anywhere anywhere ACCEPT all -- anywhere anywhere ACCEPT tcp -- anywhere anywhere state NEW tcp dpt:ssh Chain FORWARD (policy ACCEPT) target prot opt source destination DOCKER-ISOLATION all -- anywhere anywhere DOCKER all -- anywhere anywhere ACCEPT all -- anywhere anywhere ctstate RELATED,ESTABLISHED ACCEPT all -- anywhere anywhere ACCEPT all -- anywhere anywhere DOCKER all -- anywhere anywhere ACCEPT all -- anywhere anywhere ctstate RELATED,ESTABLISHED ACCEPT all -- anywhere anywhere REJECT all -- anywhere anywhere reject-with icmp-host-prohibited DROP all -- anywhere anywhere Chain OUTPUT (policy ACCEPT) target prot opt source destination Chain DOCKER (2 references) target prot opt source destination ACCEPT tcp -- anywhere 172.17.0.3 tcp dpt:6379 Chain DOCKER-ISOLATION (1 references) target prot opt source destination DROP all -- anywhere anywhere DROP all -- anywhere anywhere RETURN all -- anywhere anywhere
There is also a DOCKER subchain, which is referenced by the FORWARD chain.
- FORWARD Chain: Filter all data packets passing through the machine (source address and destination address are not local data packets)
That is to say, after switching the address through nat, the packet of the test container will be forwarded to 172.17.0.3 instead of the host, and the filtering rule is Accept, that is, through.
Matters needing attention
Some of the network functions of docker are accomplished by iptables forwarding. The forwarding rules are added dynamically after the start of the docker process, which means that if you restart iptables, the docker forwarding rules will be lost.
There are two solutions:
- Add iptables rules dynamically and modify / etc / sysconf / iptables (recommended)
Adding iptables rules dynamically can make the rules take effect immediately (restart invalidation)
iptables -A INPUT -p tcp --dport 46379 -j ACCEPT
Modify the / etc/sysconf/iptables file to save your changes. If the server restarts, this rule will be added automatically.
vi /etc/sysconf/iptables
- Restart docker after restarting iptable
Impact: Restarting docker will cause all containers to restart, possibly causing short-term business failures.
This method is not recommended. If the firewall has been restarted, leading to docker business failure, restart dcoker with the following command.
systemctl restart docker