What is the principle of Ajax? How?
Hello! This is the first time you have used the welcome page displayed by the Markdown editor. If you want to learn how to use the Markdown editor, you can read this article carefully to understand the basic grammar of Markdown.
1, What is it
Full name of AJAX (Async Javascript and XML)
Asynchronous JavaScript and XML is a web development technology for creating interactive web applications. It can exchange data with the server and update some web pages without reloading the whole web page
The principle of Ajax is simply to send an asynchronous request to the server through the XmlHttpRequest object, obtain data from the server, and then use JavaScript to operate the DOM to update the page
The flow chart is as follows:
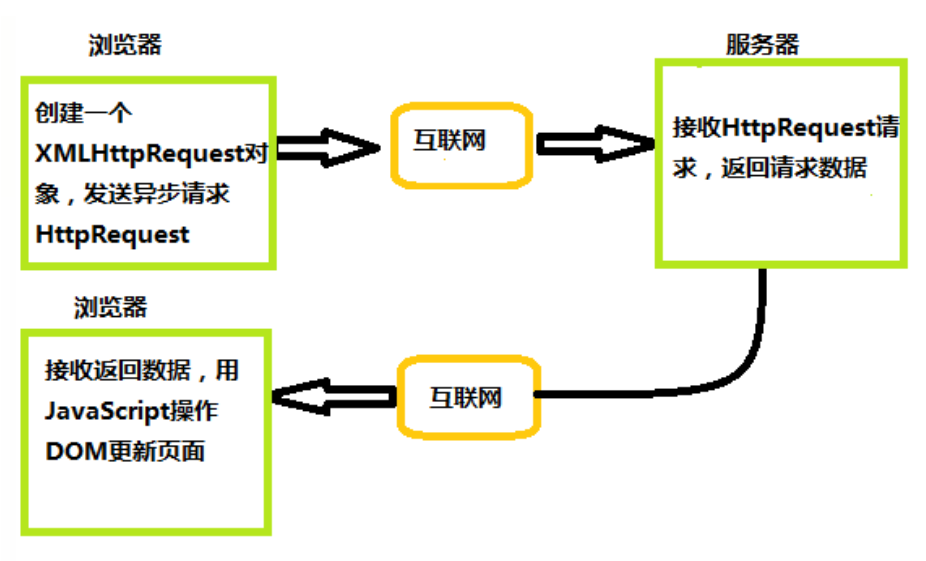
Here is an example:
When the leader wanted to report to Xiao Li, he entrusted the Secretary to call Xiao Li and then did other things until the secretary told him that Xiao Li had arrived. Finally, Xiao Li reported to the leader
The Ajax request data process is similar to "the leader wants to report to Xiao Li". The above secretary is equivalent to the XMLHttpRequest object, the leader is equivalent to the browser, and the response data is equivalent to Xiao Li
After sending the HTTP request, the browser can do other things, and then operate after receiving the data returned by XHR
2, Implementation process
The realization of Ajax asynchronous interaction requires the cooperation of server logic, and the following steps need to be completed:
Create the XMLHttpRequest object, the core object of Ajax
Establish a connection with the server through the open() method of the XMLHttpRequest object
Build the data content required by the request and send it to the server through the send() method of the XMLHttpRequest object
Listen for your communication status on the server side through the onreadystatechange event provided by the XMLHttpRequest object
Accept and process the data results responded by the server to the client
Update the processing results to the HTML page
Create XMLHttpRequest object
const xhr = new XMLHttpRequest();
Establish a connection with the server
Establish a connection with the server through the open() method of the XMLHttpRequest object
xhr.open(method, url, [async][, user][, password])
Parameter Description:
Method: indicates the current request method. Common methods include GET and POST
url: server address
async: Boolean value indicating whether to execute the operation asynchronously. The default value is true
User: user name for authentication; Default to ` null
Password: optional password for authentication purposes. The default value is ` null
Send data to the server
Send the data of the client page to the server through the send() method of the XMLHttpRequest object
xhr.send([body])
Body: the data body to be sent in the XHR request. If no data is passed, it is null
If you use GET request to send data, you should pay attention to the following:
Add the request data to the url address in the open() method
The parameter in the send() method in the send request data is set to null
Bind onreadystatechange event
The onreadystatechange event is used to listen to the communication status of the server. The main listening attribute is XMLHttpRequest readyState ,
About XMLHttpRequest The readyState property has five states, as shown in the following figure
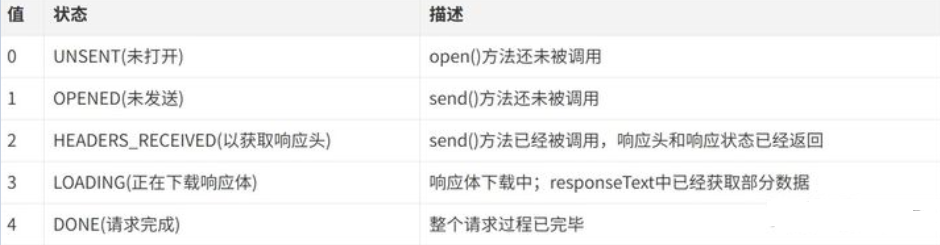
Whenever the readyState property value changes, a readystatechange event is triggered
***XMLHttpRequest. The responseText * * * property is used to receive the response result from the server
for instance:
const request = new XMLHttpRequest()
request.onreadystatechange = function(e){
if(request.readyState === 4){ // The whole request process is completed
if(request.status >= 200 && request.status <= 300){
console.log(request.responseText) // Results returned by the server
}else if(request.status >=400){
console.log("Error message:" + request.status)
}
}
}
request.open('POST','http://xxxx ') ` insert code slice here`
request.send()
3, Encapsulation
From the above understanding of the XMLHttpRequest object, let's encapsulate a simple ajax request
//Encapsulate an ajax request
function ajax(options) {
//Create XMLHttpRequest object
const xhr = new XMLHttpRequest()
//Contents of initialization parameters
options = options || {}
options.type = (options.type || 'GET').toUpperCase()
options.dataType = options.dataType || 'json'
const params = options.data
//Send request
if (options.type === 'GET') {
xhr.open('GET', options.url + '?' + params, true)
xhr.send(null)
} else if (options.type === 'POST') {
xhr.open('POST', options.url, true)
xhr.send(params)
//Receive request
xhr.onreadystatechange = function () {
if (xhr.readyState === 4) {
let status = xhr.status
if (status >= 200 && status < 300) {
options.success && options.success(xhr.responseText, xhr.responseXML)
} else {
options.fail && options.fail(status)
}
}
}
}
Use as follows
ajax({
type: 'post',
dataType: 'json',
data: {},
url: 'https://xxxx',
success: function(text,xml){//Callback function after successful request
console.log(text)
},
fail: function(status){Callback function after request failure
console.log(status)
}
})