01
Internet access mode and theoretical network speed
As shown in Figure 1-1, broadband network is an extremely complex end-to-end system, including LAN side and WAN side. LAN side refers to the section from user to AR, including AP, S, user terminal and other equipment. WAN side refers to the connection between AR and the Internet, including optical cat, access network and core network equipment. However, these are provided by the operator and have nothing to do with the user and are not within the scope of this article.
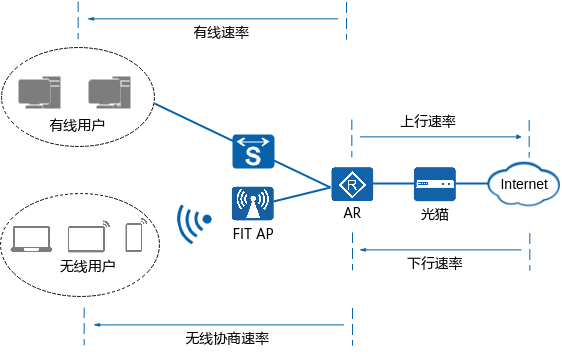
Fig. 1-1 networking diagram of users accessing the Internet
Downlink rate refers to the data transmission rate when the Internet sends information to users. The unit is Mbit/s, such as opening a browser, downloading files, etc. Uplink rate refers to the rate at which users can upload files to the Internet. For most users, the main online service is to download files from the Internet rather than upload files, so the downlink rate is generally higher than the uplink rate. The bandwidth value handled by the user from the broadband operator is the downlink rate. For example, if a user applies for a 200M broadband package, 200M here is the downlink rate, and the corresponding uplink rate may be only tens of meters.
The user terminal can access the Internet through wired mode or wireless mode. The maximum network speed that users can achieve is also different with different access modes. This paper discusses the slow downlink speed encountered by wired users when accessing the Internet, so the downlink speed is the theoretical value that wired users can achieve. In addition, the network speed of wired users is also related to network hardware facilities (optical cat, AR, S and network cable). Before solving the problem of slow network speed, please check that the network hardware facilities meet the requirements of network speed.
1.1 how to measure network speed
When the problem of slow Internet access is found, it is recommended to measure the actual network speed before handling the fault. The commonly used network speed measurement methods include website speed measurement, speed measurement tools, etc. The measurement results of different speed measurement methods are slightly different. It is recommended to use different speed measurement methods for several times:
- Use website speed measurement. The websites of major operators provide speed measurement functions, such as China Telecom broadband speed measurement network. The websites in different regions are different, such as Shanghai; You can also use some special speed measurement websites, such as speed measurement network.
- Use the speed measuring tool to measure the speed. Download and install tools for measuring network speed in the app store for speed measurement, such as network speed test, network speed measurement master, network speed measurement master, etc.
The measurement result of some speed measurement software is the download speed MB/s, but it will be synchronously converted into the corresponding bandwidth value Mbit/s. If not, you can convert it yourself according to the relationship of 1MB/s = 8Mbit/s.
02
Understand slow network speed fault scenarios
As the routing gateway equipment of enterprise network, AR plays a very important role in enterprise network and provides Internet services for users. In order to help users solve the problem of slow Internet access when accessing the Internet through AR, this paper summarizes two common slow Internet access fault scenarios from several real cases of existing networks: slow Internet access at single uplink exit and slow Internet access at double uplink / multi uplink exit.
2.1 slow Internet access at single uplink exit
Single uplink exit Internet access means that there is only one uplink connection between AR router and public network. As shown in Figure 1-2, there is only one connection between AR and the Internet. GE3/0/0 is the interface connecting the Internet, also known as the public network port, and Eth2/0/0 is the interface connecting the private network, also known as the private network port. Common reasons for slow Internet access in this scenario include: unreasonable configuration of MSS (Max Segment Size) value of TCP maximum message segment length, device Session resource depletion caused by network attack, interface mode negotiation error, etc. for specific positioning methods, please refer to the chapter on slow Internet access fault handling of single uplink exit.
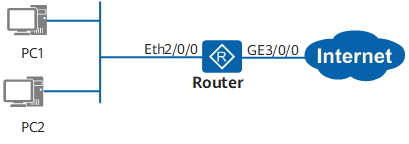
Figure 1-2 networking example of single uplink exit Internet access scenario
2.2 dual uplink / multi uplink exit slow Internet access
Dual uplink / multi uplink exit Internet access means that there are two or more uplink connections between the AR router and the public network. As shown in Figure 1-3, there are multiple connections between AR and Internet. GE0/0/1 and GE0/0/2 are public network ports, and GE0/0/3 is private network port. In addition to the common reasons listed in the single exit scenario, the common reasons for slow Internet access in this scenario also include some unique reasons, such as Dialer port routing problems, inconsistent message round-trip paths, equivalent routing problems, etc. for specific positioning methods, please refer to the chapter on slow Internet access fault handling of dual uplink exits / multiple uplink exits.
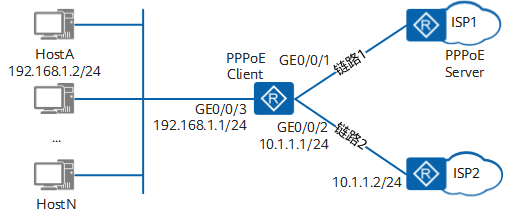
Figure 1-3 networking example of dual uplink / multi uplink exit Internet access scenario (PPPoE dialing)
03
Here is the reason why the Internet speed is slow
Figure 1-4 shows the fault tree of slow Internet access through AR, and lists the common reasons for slow Internet access in two scenarios: single uplink exit and double uplink exit.

Figure 1-4 why is the network speed so slow? Fault tree
04
Troubleshooting of slow Internet connection at single uplink outlet
4.1 message fragmentation leads to slow opening of some web pages
background information
If only some web pages are accessed slowly and other web pages are accessed normally, it is highly likely that the configuration of the MSS (Max Segment Size) value of the maximum TCP message segment length is unreasonable, resulting in the message being transmitted in pieces, affecting the user's Internet speed. At this time, you can refer to this section to modify the parameter value of message fragmentation.
The Maximum Transmission Unit (MTU) is an option used to identify whether IP messages are fragmented. If the length of the IP message sent by the opposite end exceeds the MTU value, the IP message will be segmented. In order to ensure that TCP messages are not fragmented, pay attention to the relationship between MSS and MTU during configuration. Generally, in order not to affect message transmission, MSS value plus message overhead (TCP header, IP header, etc.) shall not exceed MTU value. For example, the default MTU value of Ethernet interface is 1500 bytes. In order to ensure that the message is not fragmented, the maximum MSS value is 1460 (1500 − 20 (minimum length of TCP header) − 20 (minimum length of IP header)). It is recommended that the MSS value configured by the user is 1200 bytes.
Positioning steps
[1] Execute the command display ip interface brief to check whether the public network interface is a physical interface or a Dialer interface.
<Huawei> display ip interface brief *down: administratively down ^down: standby (l): loopback (s): spoofing (E): E-Trunk down The number of interface that is UP in Physical is 2 The number of interface that is DOWN in Physical is 3 The number of interface that is UP in Protocol is 2 The number of interface that is DOWN in Protocol is 3 Interface IP Address/Mask Physical Protocol Atm0/0/0 unassigned down down Bridge-if10 unassigned down down MFR0/0/1 unassigned down down NULL0 unassigned up up(s) GE0/0/1 x.x.x.x/24 up up GE0/0/2 x.x.x.x/24 up up
[2] If it is a physical interface, execute the command TCP adjust MSS in the physical interface view to configure the maximum TCP message segment length of the interface. The recommended value is 1200.
<Huawei> system-view [Huawei] interface GigabitEthernet 0/0/1 [Huawei-GigabitEthernet0/0/1] tcp adjust-mss 1200
[3] If it is a dialer interface, execute the command TCP adjust MSS in the Dialer Interface view to configure the maximum TCP message segment length of the interface, the recommended value is 1200, and execute the command mtu to configure the maximum transmission unit value of the interface is 1492. For the Dialer Interface, the adjust MSS value and mtu value cannot be configured the same.
[Huawei] interface Dialer 0 [Huawei-Dialer0] tcp adjust-mss 1200 [Huawei-Dialer0] mtu 1492 [Huawei-Dialer0] restart
[4] It is recommended to synchronously configure the maximum TCP message segment length of the private network interface to the recommended value of 1200. Assuming that the private network interface is GE0/0/2, configure the TCP adjust MSS 1200 command on the private network interface.
<Huawei> system-view [Huawei] interface GigabitEthernet 0/0/2 [Huawei-GigabitEthernet0/0/2] tcp adjust-mss 1200
4.2 the Session resources of the device are exhausted due to the large private network traffic
background information
When there are some attacks or more services in the network, the router will receive a large amount of traffic, and the router's Session and Block memory resources will soon be exhausted, exceeding the threshold. Other normal users may get online slowly because they cannot allocate Session and Block resources. At this time, you can refer to this section to check whether the Session and Block resources of the device are normal. If it is found that the resources are exhausted, the abnormal traffic on the port is prohibited through the traffic policy or traffic filter command, and the attack source is found for anti-virus. If the normal traffic itself is too much and exceeds the performance of the equipment, the equipment with higher performance needs to be replaced.
Positioning steps
[1] Execute the command display logbuffer to check whether there are a large number of logs of Session and Block memory resource overload in the information recorded in the Log buffer.
<Huawei> display logbuffer Logging buffer configuration and contents: enabled Allowed max buffer size: 1024 Actual buffer size: 512 Channel number: 4, Channel name: logbuffer Dropped messages: 0 Overwritten messages: 167 Current messages: 512 Mar 5 2021 15:47:25+08:00 Huawei %%01FORWARD/4/SESSION-RES-LACK(l)[135]:The device session resources were overloaded.(Usage = 94%) Mar 5 2021 16:29:25+08:00 Huawei %%01FORWARD/4/CAP-BLOCK-RES-LACK(l)[259]:The block memory resources were overloaded.(Usage = 97%) Mar 5 2021 16:34:25+08:00 Huawei %%01FORWARD/4/SESSION-RES-LACK(l)[261]:The device session resources were overloaded.(Usage = 92%) Mar 5 2021 16:43:25+08:00 Huawei %%01FORWARD/4/CAP-BLOCK-RES-LACK(l)[273]:The block memory resources were overloaded.(Usage = 96%)
[2] Enter the diagnosis view, execute the command display Session statistics Top 10 order by source IP, count the Session information of the Top 10 user according to the source IP address, and check whether the value of the Total Sessions field is close to the Session specification of the device. The Session specification of the device can be found in the specification query tool. Take AR1220C as an example, select "access router" - > "AR1220C" - > "software performance" - > "IP application" - > "NAT" - > "maximum concurrent connections".
[Huawei] diagnose [Huawei-diagnose] display session statistics top 10 order-by source-ip Session statistic top 10 (Condition: Source IP, Service: SESSION, Items: 10, Total Sessions: 25768) ------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- TOP-N IP/Port Counts Percentage(%) ------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- 1 192.168.1.99 19714 76.505744 2 192.168.1.88 5988 23.238125 3 192.168.1.165 9 0.034927
[3] If the number of sessions of the device has reached the specification of the device, and it is found that there are a large number of sessions established by private network terminals in the Top 10 Session (the source IP address is the IP address of private network terminals, such as 192.168.1.99 and 192.168.1.88 in step 1), it indicates that there may be attacks in the private network. At this time, execute the command display Session statistics Top 10 order by destination port to further view the port information of the Session established by the private network terminal. In this example, private network users have established a large number of sessions with destination ports 445 and 1433. It is recommended to configure ACL rules on the private network interface to reject traffic with destination ports 445 and 1433.
[Huawei-diagnose] display session statistics top 10 order-by destination-port Session statistic top 10 (Condition: Destination Port, Service: SESSION, Items: 10, Total Sessions: 25768) ------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- TOP-N IP/Port Counts Percentage(%) ------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- 1 445 15486 60.097796 2 1433 9565 37.119683 3 3389 648 2.514747 [Huawei-diagnose] quit [Huawei] interface GigabitEthernet 0/0/0 [Huawei-GigabitEthernet0/0/0] display this # ip address 192.168.1.255 255.255.255.0
Bind the ACL in the flow policy and apply the flow policy to the private network interface GE0/0/0. The traffic with destination ports 445 and 1433 is not allowed to pass through the private network interface, so as to solve the fault.
[Huawei] acl 3000 [Huawei-acl-adv-3000] rule 20 permit tcp destination-port eq 445 [Huawei-acl-adv-3000] rule 25 permit tcp destination-port eq 1433 [Huawei-acl-adv-3000] quit [Huawei] traffic classifier virus operator or [Huawei-classifier-virus] if-match acl 3000 [Huawei-classifier-virus] quit [Huawei] traffic behavior virus [Huawei-behavior-virus] deny [Huawei-behavior-virus] quit [Huawei] traffic policy virus [Huawei-trafficpolicy-virus] classifier virus behavior virus [Huawei-trafficpolicy-virus] quit [Huawei] interface GigabitEthernet 0/0/0 [Huawei-GigabitEthernet0/0/0] traffic-policy virus outbound [Huawei-GigabitEthernet0/0/0] traffic-policy virus inbound
[4] If no attack is found on the private network after inspection, it indicates that there are many private network services and large traffic, which is a normal phenomenon. The current equipment performance can no longer meet the private network services, so it is necessary to replace the equipment with higher performance.
4.3 ARP attacks on private networks cause users to surf the Internet intermittently
background information
If users find that the Internet is intermittent and the network speed is particularly slow, it is likely that there is an ARP attack on the private network. At this time, you can refer to this section to check whether there is ARP attack on the device.
Positioning steps
[1] Execute the command display logbuffer to check the device operation log to see if any ARP protocol messages are discarded due to the limitation of CPU threshold.
<Huawei> display logbuffer Sep 9 2021 16:01:55+00:00 Huawei %%01SECE/4/PORT_ATTACK(l)[0]:Port attack occurred.(Slot=MPU, SourceAttackInterface=GigabitEthernet0/0/0, OuterVlan/InnerVlan=0/0, AttackPackets=64 packets per second) Sep 9 2021 16:01:54+00:00 Huawei %%01DEFD/4/CPCAR_DROP_MPU(l)[1]:Some packets are dropped by cpcar on the MPU. (Packet-type=arp-miss, Drop-Count=770) Sep 9 2021 16:01:54+00:00 Huawei %%01DEFD/4/CPCAR_DROP_MPU(l)[2]:Some packets are dropped by cpcar on the MPU. (Packet-type=arp-request, Drop-Count=3458)
[2] If the ARP message in the log is discarded, it is suspected that there is an ARP attack in the private network to which the device is connected. At this time, the attack traceability function can be configured on the device for further troubleshooting.
<Huawei> system-view [Huawei] cpu-defend policy 1 [Huawei-cpu-defend-policy-1] auto-defend enable [Huawei-cpu-defend-policy-1] auto-defend threshold 40 //It can be adjusted appropriately. It is recommended not to be too small [Huawei-cpu-defend-policy-1] auto-defend attack-packet sample 5 [Huawei-cpu-defend-policy-1] auto-defend protocol all [Huawei-cpu-defend-policy-1] auto-defend trace-type source-ip source-mac source-portvlan [Huawei-cpu-defend-policy-1] auto-defend alarm enable [Huawei-cpu-defend-policy-1] quit [Huawei] cpu-defend-policy 1 [Huawei] cpu-defend-policy 1 global
[3] After configuring the attack traceability, when the network is abnormal, execute the command display auto defer attack source on the device to further confirm whether there is an ARP attack.
[Huawei] display auto-defend attack-source
Attack Source User Table:
-------------------------------------------------------------------------
MacAddress InterfaceName Vlan:Outer/Inner TOTAL
-------------------------------------------------------------------------
xxxx-xxxx-xxxx GigabitEthernet0/0/1 0 368
yyyy-yyyy-yyyy GigabitEthernet0/0/0 0 7152
-------------------------------------------------------------------------
Total: 2
Attack Source Port Table:
-----------------------------------------------------
InterfaceName Vlan:Outer/Inner TOTAL
-----------------------------------------------------
GigabitEthernet0/0/1 0 368
GigabitEthernet0/0/0 0 23472
-----------------------------------------------------
Total: 2
Attack Source IP Table:
-------------------------------------
IPAddress TOTAL Packets
-------------------------------------
x.x.x.x 368
y.y.y.y 7152
-------------------------------------
Total: 2As shown above, users with the source IP address of y.y.y.y and the source MAC of yyyy yyyy in the private network sent a large number of attack messages (in this example, GE0/0/1 is the public network interface, and the number of messages increased little, which can be ignored). At this time, find the attack source user layer by layer according to the attacked port GE0/0/0, and use the anti-virus software to solve the fault.
[4] If the attack source user cannot be found, ACL rules can be configured on the private network interface GE0/0/0 of the device to filter the layer-2 ARP traffic function, reject the message with the source MAC address of yyyy yyyy yyyy, and solve the fault through the private network interface.
[Huawei] acl number 4444 [Huawei-acl-L2-4444] rule 5 deny l2-protocol arp source-mac yyyy-yyyy-yyyy [Huawei] interface gigabitethernet 0/0/0 [Huawei-GigabitEthernet0/0/0] traffic-filter inbound acl 4444 [Huawei-GigabitEthernet0/0/0] quit [Huawei] quit
4.4 abnormal state of public network interface leads to slow network speed
background information
If the state of the public network interface is abnormal, it will also cause users to surf the Internet slowly. For example, the state of the interface is abnormal and the duplex mode of the interface is wrong. At this time, you can refer to this section to check whether the interface status of the AR device connected to the public network is normal.
Positioning steps
[1] Assuming that the interface of AR equipment connected to the public network is GE0/0/1, execute the command display interface to view the information of the public network interface, and pay attention to the parameter values of bold parts such as Duplex, Total Error, CRC and Giants.
<Huawei> display interface GigabitEthernet 0/0/1
GigabitEthernet0/0/1 current state : UP
Line protocol current state : UP
Last line protocol up time : 2021-10-08 09:00:00
Description:HUAWEI, AR Series, GigabitEthernet0/0/1 Interface
Route Port,The Maximum Transmit Unit is 1500
Internet Address is 120.44.5.15/24
IP Sending Frames' Format is PKTFMT_ETHNT_2, Hardware address is 60d7-55f0-42c1
Last physical up time : 2021-10-08 09:00:00
Last physical down time : 2021-10-08 08:58:09
Current system time: 2021-10-22 06:14:56
Port Mode: COMMON COPPER
Speed : 100, Loopback: NONE
Duplex: FULL, Negotiation: ENABLE
Mdi : AUTO, Clock : -
Last 300 seconds input rate 99992 bits/sec, 50 packets/sec
Last 300 seconds output rate 192 bits/sec, 0 packets/sec
Input peak rate 223880 bits/sec,Record time: 2021-10-13 14:13:56
Output peak rate 18464 bits/sec,Record time: 2021-10-20 07:27:05
Input: 55586497 packets, 13516267464 bytes
Unicast: 10526, Multicast: 195548
Broadcast: 55380423, Jumbo: -
Discard: 0, Total Error: 0
CRC: 0, Giants: 0
Jabbers: 0, Throttles: 0
Runts: 0, Symbols: 0
Ignoreds: 0, Frames: 0
Output: 9237 packets, 590811 bytes
Unicast: 9227, Multicast: 0
Broadcast: 10, Jumbo: -
Discard: 0, Total Error: 0
Collisions: 0, ExcessiveCollisions: 0
Late Collisions: 0, Deferreds: 0
Input bandwidth utilization threshold : 100.00%
Output bandwidth utilization threshold: 100.00%
Input bandwidth utilization : 0.11%
Output bandwidth utilization : 0.01%[2] If the Duplex mode of the public network interface is negotiated to half Duplex in the FULL Duplex mode, the public network interface will lose packets when sending messages, thus affecting the user's Internet speed. At this time, you can check whether the Duplex status of the public network interface negotiation is correct, that is, whether the Duplex is FULL.
If it is found that the duplex mode negotiation of the interface is wrong, it may be due to the wrong negotiation of the device itself, or the inconsistency between the rate of the opposite interface and the rate of the local interface. First, execute the command speed on the public network interface, and the rate of modifying the local interface is the same as that of the opposite end.
<Huawei> system-view [Huawei] interface GigabitEthernet 0/0/1 [Huawei-GigabitEthernet0/0/1] undo negotiation auto [Huawei-GigabitEthernet0/0/1] speed 100
After the rate is modified to be consistent, if the duplex mode of the interface is still negotiation error, you can execute the command duplex full to manually configure the duplex mode of the interface to full duplex.
<Huawei> system-view [Huawei] interface GigabitEthernet 0/0/1 [Huawei-GigabitEthernet0/0/1] duplex full [Huawei-GigabitEthernet0/0/1] quit [Huawei] quit
If the above steps cannot solve the duplex problem, it is recommended to directly replace a confirmed network cable and re connect the port.
[3] If there are some error packet counts on the interface, that is, the parameters such as Total Error and CRC are not 0, it indicates that the device has received an error message. There are many reasons why the equipment receives the error message, which may be the wrong cable type or the problem of the opposite end equipment.
[4] If none of the above operations can solve the interface exception problem, it may be a hardware fault. You can try to replace a new device to solve the fault.
05
Slow fault handling of dual uplink outlet / multi uplink outlet
5.1 the route does not fail after dialing failure of the Dialer Interface
background information
Under normal circumstances, in the dual link / multi link PPPoE dialing scenario, if one PPPoE link fails to dial, the user's Internet traffic will be switched to other normal links for forwarding. However, if the Dialer Interface corresponding to the dialing failure link is not Down, the routing of the Dialer Interface will continue to take effect. The user's Internet traffic will continue to be forwarded on the link that failed to dial up, resulting in the problem of slow access to some web pages. At this time, you can refer to this section to set the Dialer Interface status corresponding to the dialing failed link to Down and disable the corresponding route.
Positioning steps
[1] Execute the command display ip interface brief to view the brief IP related information of the Dialer Interface, including IP address, subnet mask, Up/Down status of physical link and protocol, etc.
<Huawei> display ip interface brief *down: administratively down ^down: standby (l): loopback (s): spoofing (E): E-Trunk down The number of interface that is UP in Physical is 2 The number of interface that is DOWN in Physical is 3 The number of interface that is UP in Protocol is 2 The number of interface that is DOWN in Protocol is 3 Interface IP Address/Mask Physical Protocol Dialer1 unassigned up up(s) Dialer2 100.64.40.165/32 up up(s)
[2] Execute the command display IP routing table to view the information of IPv4 routing table.
<Huawei> display ip routing-table
Route Flags: R - relay, D - download to fib, T - to vpn-instance
------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Routing Tables: Public
Destinations : 31 Routes : 32
Destination/Mask Proto Pre Cost Flags NextHop Interface
0.0.0.0/0 Static 60 0 D 0.0.0.0 Dialer1
Static 60 0 D 100.64.40.165 Dialer2[3] According to the information found in step 1 and step 2, it can be seen that although dialing fails and the Dialer1 interface is not assigned an IP address, the physical and protocol status of the interface is UP, resulting in the routing of Dialer1 interface still taking effect. At this time, it is recommended to configure the command dialer number 1 autodial under each Dialer Interface to convert the Dialer Interface to Down state after dialing failure. When the state of the Dialer Interface changes to Down, the corresponding route will also fail to synchronize.
<Huawei> system-view [Huawei] interface dialer 1 [Huawei-Dialer1] dialer number 1 autodial [Huawei-Dialer1] quit [Huawei] quit
5.2 the round-trip path of the message received on the public network interface is inconsistent
background information
In the scenario of dual outlet / multi outlet link Internet access, in order to ensure that private network users can access the Internet from any public network port, NAT function will be configured on each public network port. The NAT function of AR will check whether the round-trip path of the message received on the public network port is consistent, that is, the message sent from which public network port, and the message replied by the opposite end should also be received from the public network port. If it is found that the return path of the message received on a public network interface is inconsistent, the message will be discarded, resulting in the problem of slow Internet access.
For example, the dual uplink public network ports of Ar are GE1 and GE2 respectively. A message is sent from GE1 port, but the backhaul message comes back from GE2 port. At this time, AR will discard the backhaul message. This kind of inconsistency in the round-trip path of the message is generally caused by the wrong routing when the opposite end equipment sends the message. The content of this section is mainly to guide the user how to locate the problem of slow Internet access caused by inconsistent round-trip paths of messages on ar. The specific solution needs to contact the end-to-end network engineer for processing. You can check the networking of the end-to-end network or modify the configuration to ensure that the messages sent by the end-to-end equipment meet the requirements of source in and source out.
Positioning steps
[1] Assume that the AR dual uplink public network ports are GE0/0/1 and GE0/0/2 respectively, the network address of the opposite end device of GE1 port is 172.16.1.0/24, and the IP address and port number of a host accessing the network segment are 172.16.1.254/24 and 65532. Configure the ACL based filtering function on the GE0/0/2 port of AR, that is, only messages with source IP address 172.16.1.254/24 and source port number 65532 are allowed to pass on the GE0/0/2 port.
<Huawei> system-view [Huawei] acl 3000 [Huawei-acl-adv-3000] rule 5 permit tcp source 172.168.1.254 0.0.0.0 source-port eq 65532 [Huawei-acl-adv-3000] quit [Huawei] interface GigabitEthernet 0/0/2 [Huawei-GigabitEthernet0/0/2] traffic-filter inbound acl 3000 [Huawei-GigabitEthernet0/0/2] quit
[2] After configuring the traffic statistics function on GE0/0/2, execute the command display acl all to check whether there is ACL matching count on the device. If there are the following records in bold, it means that the message sent from GE1 is received on GE2 port, and the back and forth path of the message is inconsistent. You need to contact the end-to-end network engineer for handling.
[Huawei] display acl all Total quantity of nonempty ACL number is 1 Advanced ACL 3000, 1 rule Acl's step is 5 rule 5 permit tcp source 172.168.1.254 0 source-port eq 65532 (2 matches)
5.3 slow Internet access of users in load sharing scenario
background information
In the dual egress / multi egress scenario, the relationship between links is divided into load sharing and active / standby backup. Load sharing means that multiple links are forwarding traffic at the same time. Active and standby backup means that only one link is forwarding traffic at the same time, and the other is in the backup state. Load sharing can improve link efficiency and bandwidth, mainly by configuring multiple equivalent paths. Active and standby backup can improve link reliability by configuring multiple paths with different priorities.
Different enterprises use different methods, but using load sharing among multiple links with large quality differences may introduce the problem of slow Internet access. For example, AR distributes the message of a user accessing a web page to two links for forwarding. The link with poor quality forwards the message slowly and loses many packets, which will inevitably affect the user's Internet experience. Therefore, if you encounter the problem of slow Internet access in the load sharing scenario in the dual exit / multi exit scenario, you can refer to this section and change to the active and standby backup mode or configure the policy path.
Positioning steps
[1] Execute the command display IP routing table protocol static on the AR to view the configured static routing table information. If there are two routes with the same priority in the routing table to different next hops, it indicates that the two routes are equivalent routes and the relationship between links is load sharing.
<Huawei> display ip routing-table protocol static
Route Flags: R - relay, D - download to fib, T - to vpn-instance
------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Public routing table : Static
Destinations : 1 Routes : 2 Configured Routes : 2
Static routing table status : <Active>
Destinations : 0 Routes : 0
Static routing table status : <Inactive>
Destinations : 1 Routes : 2
Destination/Mask Proto Pre Cost Flags NextHop Interface
0.0.0.0/0 Static 60 0 172.16.1.2 Unknown
0.0.0.0/0 Static 60 0 10.1.1.2 Unknown[2] Delete one of the routes, visit the web page again, and check whether the Internet will be slow when using the single link. If not, the quality of the two links is very good. The slow access to the Internet is not caused by the equivalent routing, but may be caused by the unreasonable configuration of the load sharing algorithm. At this time, you can execute the command IP load balance hash to configure the load sharing mode of two equivalent routes. By default, IP messages share the load based on the source IP address and destination IP address; TCP or UDP messages share load based on source IP address, destination IP address, source port number and destination port number.
<Huawei> system-view [Huawei] ip load-balance hash src-ip //Configure load sharing based on source IP address
[3] If one of the routes goes online slowly, the quality of the link is poor. It is recommended to execute the command IP route static to modify the priority of this route so that it is less than that of another route and make this link a backup link. The higher the routing priority value, the lower the routing priority.
[Router] ip route-static 0.0.0.0 0 10.1.1.2 preference 100
[4] If the user does not want to change the two links into active and standby backup, he still hopes that both links can forward traffic. This problem can also be solved by configuring policy routing. The principle of policy routing configuration is to let the links with good quality forward more traffic and the links with poor quality forward less traffic. For example, 70% of user traffic is forwarded from good quality links and 30% of user traffic is forwarded from poor quality links.
5.4 users' slow Internet access in the scenario of active and standby links
background information
In the dual exit / multi exit scenario, some enterprise users have high requirements for link reliability and will deploy multiple links as primary and standby links at the same time. This networking can indeed improve link reliability and reduce packet loss, but it does not mean that there is no packet loss at all. When the main link fails, the AR will delete the relevant information of the link in the NAT table entry and wait for the client to send a new connection establishment request to the server. Ar reestablishes the session table entry according to the connection request sent by the client. The time for AR to re-establish session table entries depends on the message interaction time between the client and the server. In extreme cases, if the client does not make requests all the time, network access will be interrupted. Some users do not understand the connection mechanism of AR, and will mistakenly think that there is a failure. In fact, it is a normal slow Internet connection phenomenon. If you encounter the problem of slow Internet access in the scenario of active and standby links, you can refer to this section to check whether it is caused by re establishing the connection.
Positioning steps
[1] Execute the command display nat session multiple times on the AR router to check whether the NAT mapping table entry information has changed.
<Huawei> display nat session all verbose
NAT Session Table Information:
Protocol : TCP(6)
SrcAddr Port Vpn : 10.200.200.200 65532
DestAddr Port Vpn : 10.100.100.100 1024
Time To Live : 60 s
NAT-Info
New SrcAddr : 10.10.10.10
New SrcPort : 10240
New DestAddr : 10.30.30.30
New DestPort : 21
Protocol : UDP(6)
SrcAddr Port Vpn : 10.200.200.200 65532
DestAddr Port Vpn : 10.100.100.100 1024
Time To Live : 60 s
NAT-Info
New SrcAddr : 10.10.10.10
New SrcPort : 10240
New DestAddr : 10.30.30.3
New DestPort : 21
Total : 2[2] If the source port number of the "SrcAddr Port Vpn" field in the NAT table entry changes, it indicates that the NAT session table entry has been re established on the AR device. The slow Internet access is caused by the re establishment of the NAT table entry, which is normal and requires no additional processing.
06
Collect fault information of slow Internet access
If none of the above steps can solve your problem, please collect relevant information as follows, and then seek technical support.
[1] Collect fault related information
One click to collect all diagnostic information of the device and export the file.
In the user view, execute the display diagnostic information file name command to collect device diagnostic information and save it as a file.
<Huawei> display diagnostic-information dia-info.txt This operation will take several minutes, please wait......................... .................................................................. Info: The diagnostic information was saved to the device successfully.
[2] Collect the log and alarm information of the device and export the file.
In the user view, execute the save logfile command to save the log and alarm information of the buffer as a file.
<Huawei> save logfile Info: It may take several seconds,please wait... Save log file successfully.