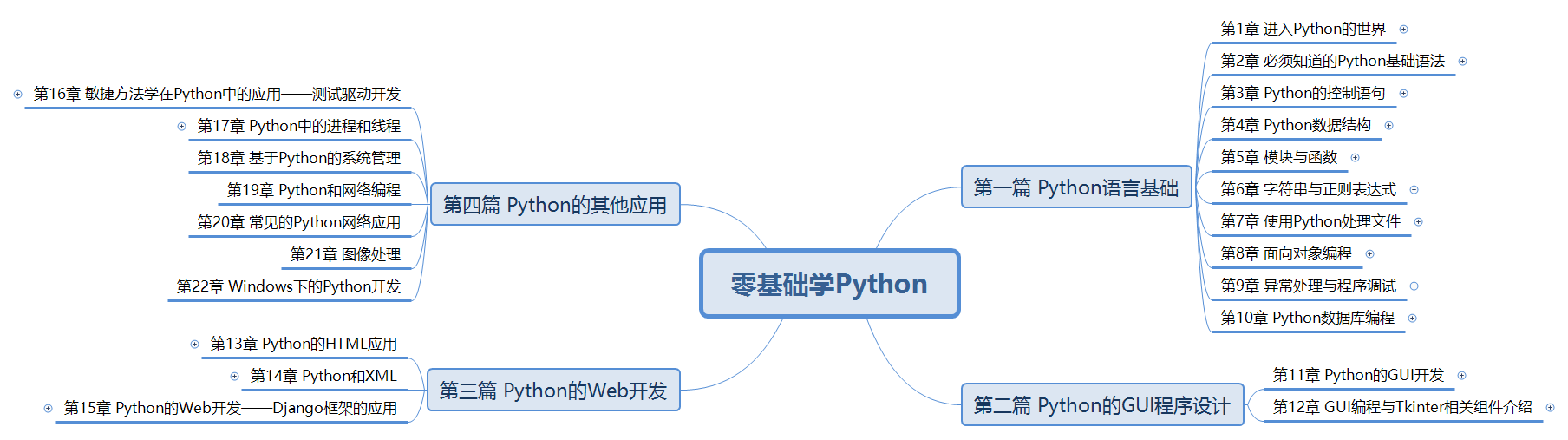
Overall article directory
1, Current chapter contents
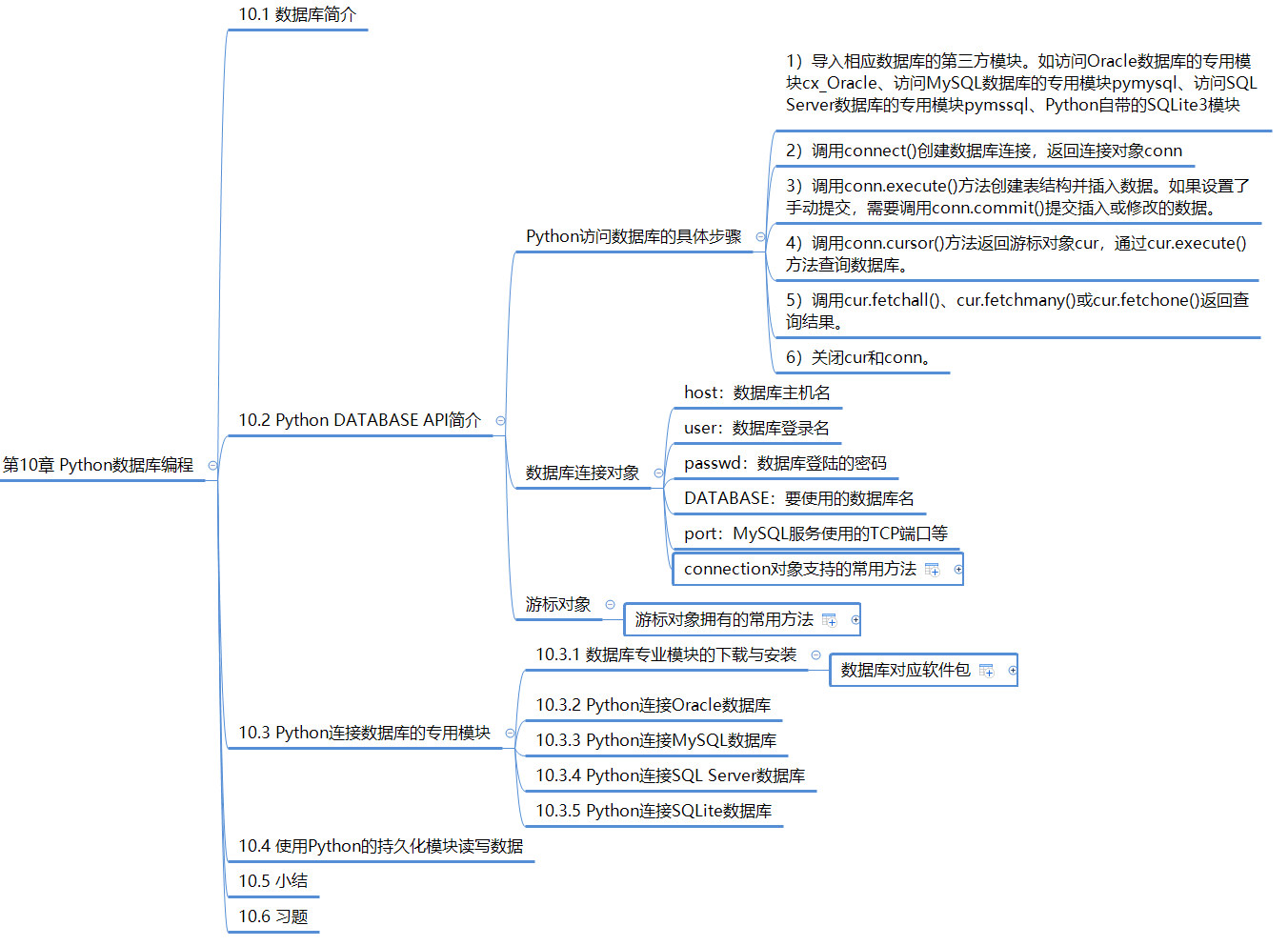
2, Database introduction
Database functions:
- Data definition function.
- DBMS provides corresponding data language to define database structure
- DDL usually includes creation, modification and deletion commands for each object.
- Data manipulation function.
- DBMS provides data manipulation language to realize the basic operation of database data.
- DML usually includes data addition, deletion, modification and query commands.
- Database management and maintenance functions.
- Data security, integrity and concurrency control.
- Loading of initial data of database.
- Dump, restore and reorganize the database.
- System performance monitoring, analysis and other functions.
Database type:
- Relational database: Oracle, MySQL, Microsoft SQL Server
- Non relational databases: NoSQL, MongoDB, Redis, HBase
3, Introduction to Python DATABASE API
- Specific steps for Python to access the database
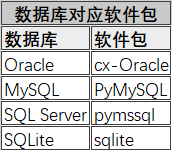
- Import the third-party module of the corresponding database. Such as the special module CX for accessing Oracle database_ Oracle, special module pymysql for accessing MySQL database, special module pymssql for accessing SQL Server database, and SQLite3 module of Python
- Call connect() to create a database connection and return the connection object conn
- Call the conn.execute() method to create a table structure and insert data. If the settings of commit. Commit () or commit () need to be modified manually.
- Call the conn.cursor() method to return the cursor object cur through cur The execute () method queries the database.
- Call cur fetchall(),cur.fetchmany() or cur Fetchone() returns the query result.
- Close cur and conn.
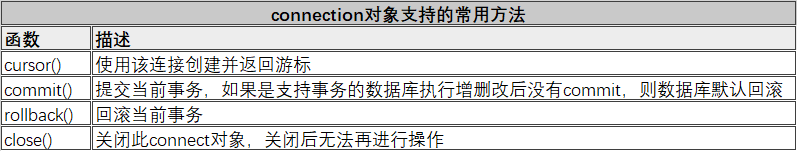
- Database connection object
- Host: database host name
- user: database login
- passwd: password for database login
- DATABASE: the name of the DATABASE to use
- Port: the TCP port used by MySQL service
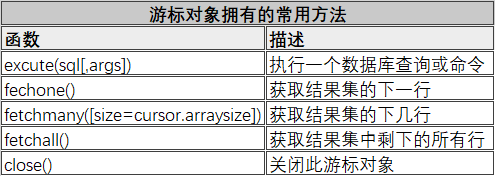
- Cursor object
4, Python special module for connecting to database
4.1 download and installation of database professional module
4.2 Python connection to Oracle Database
import cx_oracle # Import cx_Oracle module
connection = cx_oracle.connect("system", "123", "orcl") # Connect to Oracle Database
cursor = connection.cursor() # Get cursor object operation database
sql = """select empname full name, emptel Telephone, sal salary, deptname department # Define sql query statement
from emp e, dept d
where sal > 2500
and e.deptno = d.deptno
order by sal"""
cursor.execute(sql) # Execute sql statement
for x in cursor.fetchall(): # Get all data by external circulation
for value in x: # Output each line of data in
print(value, end=' ')
print() # Line feed
cursor.close() # Close cursor
connection.close() # Close connection
4.3 Python connection to MySQL database
import sys # Import sys module
import pymysql # Import pymysql module
try: # Catch exception
conn = pymysql.connect(host='127.0.0.1', port=3306, user='root', passwd='a',
db='mysql', charset='utf8') # Open database connection
except Exception as e: # exception handling
print(e) # Print exception information
sys.exit() # break link
cursor = conn.cursor() # Create a cursor object using the cursor() method
# Insert data into the teacherinfo table
sql_insert = "insert into teacherinfo(t_id, t_name, t_sex, t_pro, t_tel)values(%s, %s, %s, %s, %s)"
values = (("1113", "Zhang Hai", 'male', 'lecturer', '13891234456'), ("1114", "Liao Ming", 'female', 'professor', '13891232222'))
try: # Catch exception
cursor.executemany(sql_insert, values) # Insert multiple pieces of data
except Exception as e: # exception handling
print(e) # Print exception information
sql = "select t_id, t_name, t_sex, t_pro, t_tel from teacherinfo" # Define SQL query
cursor.execute(sql) # Execute the SQL query using the execute() method
print(cursor.rowcount) # Number of rows obtained by print cursor
for d in cursor.fetchall(): # Get all data by external circulation
for value in d: # The inner loop outputs each line of data
print(value, end=' ')
print() # Line feed
cursor.close() # Close cursor
conn.close() # Close connection
Operation results:
4.4 Python connection to SQL Server database
import pymssql # Import pymssql module
connection = pymssql.connect(host='127.0.0.1', user='root',password='123', database='mysql') #Connect to SQL Server database
cursor = connection.cursor() # Get cursor object operation database
sql = """select stcode Student number, stname full name, staddress address, class class, major major from
studentinfo where major='Computer Department' and class='Class one'""" # Define sql query statement
cursor.execute(sql) # Execute sql query statement
for d in cursor.fetchall(): # Get all data by external circulation
for value in d: # The inner loop outputs each line of data
print(value, end=' ')
print() # Line feed
cursor.close() # Close cursor
connection.close() # Close connection
4.5 Python connection to SQLite database
import sqlite3
# Connect database
conn = sqlite3.connect("D:\python Example source code\ch10code/schoolmanage.db")
# Create table
conn.execute("create table courseinfo(c_id char(10)primary key, c_name varchar(20) "
"not null, c_press varchar(50) not null, c_price float not null")
# insert data
conn.execute("insert into courseinfo(c_id, c_name, c_press, c_price)values('1001',"
"'Python development','People's Posts and Telecommunications Publishing House', 69")
conn.execute("insert into courseinfo(c_id, c_name, c_press, c_price)values('1002',"
"'Java development','Machinery Industry Press', 60")
conn.commit() # Submit data manually
cur = conn.cursor() # Get cursor object
cur.execute("select * from courseinfo") # Query data using cursors
res = cur.fetchall() # Get all results
print("courseinfo: ", res) # Output all course information
for line in res: # Loop through the output result set object res
for f in line:
print(f, end=" ")
print() # Line feed
cur.close() # Close cursor
conn.close() # Close connection
5, Use Python's persistence module to read and write data
import shelve # Import shelve module
addresses = shelve.open('addresses') # Open or create a database
addresses['1'] = ['Tom', 'Beijing road', '2008-01-03'] # insert data
addresses['2'] = ['Jerry', 'Shanghai road', '2008-03-30'] # insert data
if '2' in addresses: # Judge whether the keyword "2" is in addresses
del addresses['2'] # Delete the data corresponding to keyword "2"
for a in addresses.items(): # Loop through the contents of the output addresses object
print(a)
addresses.close() # Close connection