1.1 ACL permission control:
scheme, id and permission are used to identify, mainly covering three aspects:
Permission scheme: authorization policy
Authorization object (id): the authorized object
Permission: the permission granted
1.2. Features of Zookeeper ACL:
Zookeeper's permission control is based on znode nodes, and permissions need to be set for each node.
Each znode supports setting multiple permission control schemes and multiple permissions.
Child nodes do not inherit the permissions of the parent node. A client cannot access a node, but can access its child nodes
1.3 permission mode
Scheme description
There is only one user in the world: anyone, which represents the owner who logs in to zokeeper (default)
IP uses IP address authentication for clients
auth uses user authentication with added authentication
digest uses "user name: password" to authenticate
1.4 authorization
create, delete, read, writer and admin are the add, delete, modify, query and management permissions. These five permissions are abbreviated as cdrwa. Note: among these five permissions, delete refers to the delete permission of child nodes, and the other four permissions refer to the operation permission of their own nodes.
Short description of permission ACL
create c can create child nodes
delete d can delete child nodes (only lower level nodes)
read r can read node data and display the list of child nodes
write w can set node data
admin a can set node access control list permissions
2.1. Start ZooKeeper cluster
Start the ZooKeeper cluster. Refer to ZooKeeper installation and deployment for specific steps.
2.2. Start zkCli client
cd /usr/cstor/zookeeper bin/zkClin.sh
2.3. View node ACL
create /node1 "node1" getAcl /node1

This is the default acl when creating a node, which means that any client connected to Zookeeper can cdrwa the node. The permission setting mode to use acl is scheme: id:permission, such as world:anyone:cdwa.
2.4 world permissions
The world permission mode has only one setting mode. setAcl world:anyone:[r][w][c][d][a]
(1) . cancel the node's permission to read data:
setAcl /node1 world:anyone:cdwa Cancel the node's permission to read data getAcl /node1 View node permissions get /node1 obtain node1 Node value
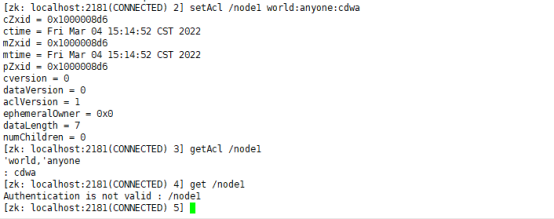
After setting, attempting to read the / node1 node will be unauthorized Authentication is not valid.
(2) . cancel the permission of the node to set data
setAcl /node1 world:anyone:cda Unset data permissions getAcl /node1 View node permissions set /node1 "node111111" modify node1 Node value
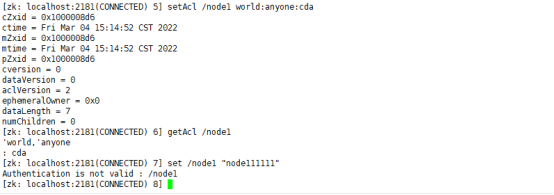
(3) . cancel the permission of the node to create child nodes
setAcl /node1 world:anyone:da Cancel the permission of creating child nodes getAcl /node1 View node permissions create /node1/node2 "node2" stay node1 Create child nodes under node node2 And assign value node2
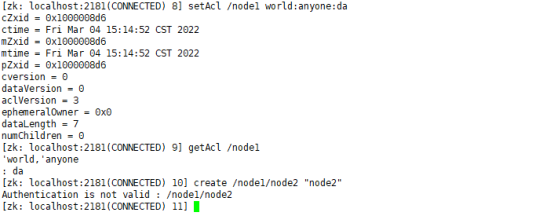
(4) . cancel permission to delete child nodes
create /node8 "888" create /node8/node9 "999" setAcl /node8 world:anyone:a Cancel permission to delete child nodes delete /node8/node9 delete node8 Child nodes under node node9
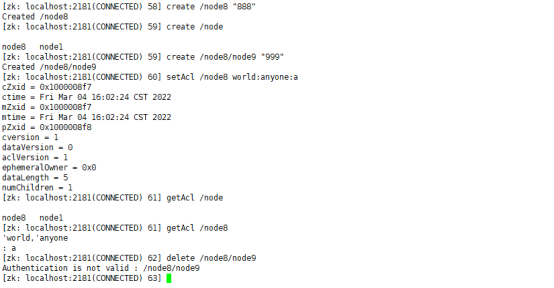
(5) . cancel ACL related permissions
create /node666 "666" setAcl /node666 world:anyone: cancel node666 Full permissions getAcl /node666 setAcl /node666 world:anyone:rwcda
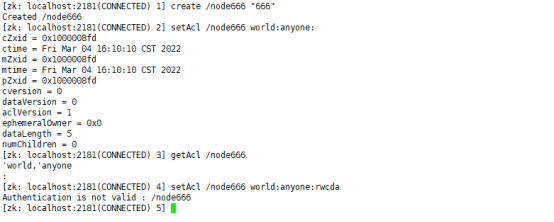
After canceling the a permission, the getAcl setAcl command has no permission.
2.5. IP permission mode
The ACL mode used in this mode is ip:10.30.196.4:[r][w][c][d][a]
create /node20 "node20" setAcl /node20 ip:10.30.196.4:rwcda getAcl /node20 get /node20
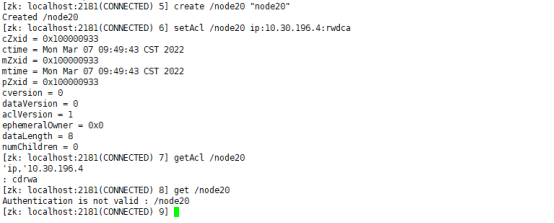
Set that only the client connection with ip 10.30.196.3 can carry out rwdca operation, and other ip can't do anything. Because the client setting the ACL in the figure is not this ip, after setting it, it will lose its permission to this node, so the getAcl command will have no permission.
getAcl /node20 get /node20
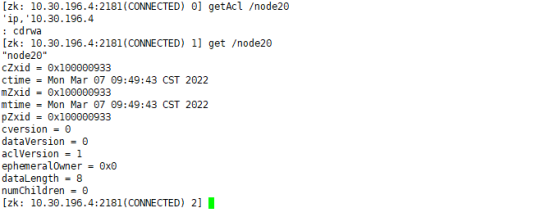
We use the client link with ip 10.30.196.4 and have rwdca permission, so we can perform getAcl operation and read node data.
2.6 auth authorization mode
This should be combined with the addauth command.
Step 1: add the authorized user addauth digest username:password first
Step 2: set this node. Only the client connection of the authorized user can be operated.
addauth digest admin:123456 create /nodeAuth "nodeAuth" setAcl /nodeAuth auth:admin:rwdca getAcl /nodeAuth
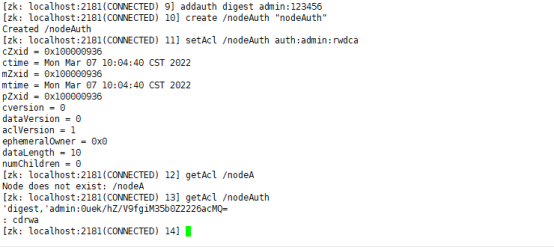
After quit ting and reconnecting the client:
get /nodeAuth

Lost permissions on this node. You need to use the addauth command to add authorization. You can only have permission on this node after logging in.
addauth digest admin: 123456 get /nodeAuth
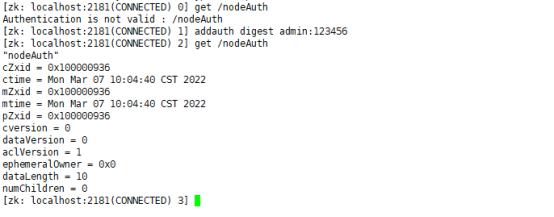
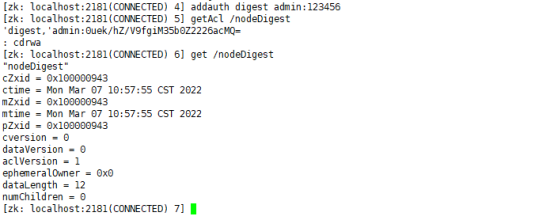
2.7 digest authorization mode
Digest authorization mode is based on the authorization mode of account and password, which is similar to Auth mode, but it does not use addauth digest username:password to add permission users before setting permissions. Directly use the command setAcl path digest:username:password:acl to authorize (only the password here should use the encrypted password, not the inscription password).
linux command line input
echo -n admin:123456 | openssl dgst -binary -sha1 | openssl base64
zkCli client input
create /nodeDigest "nodeDigest" setAcl /nodeDigest digest:admin:0uek/hZ/V9fgiM35b0Z2226acMQ=:rwdca getAcl /nodeDigest get /nodeDigest addauth digest admin:123456 getAcl /nodeDigest get /nodeDigest
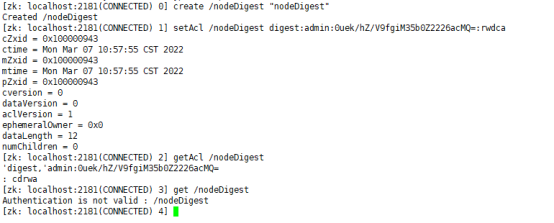
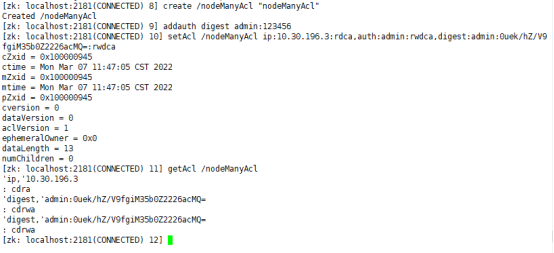
2.8 multiple authorization modes
The same node can use multiple authorization modes at the same time
create /nodeManyAcl "nodeManyAcl" addauth digest admin:123456 setAcl /nodeManyAcl ip:10.30.196.3:rdca,auth:admin:rwdca,digest:admin:0uek/hZ/V9fgiM35b0Z2226acMQ=:rwdca getAcl /nodeManyAcl