12 articles 1 subscription
Welcome to the blog home page: Wechat search: Import_ Bigdata, hard core original author in big data field_ import_bigdata_ CSDN blog
Welcome to like, collect, leave messages, and exchange messages!
This article was originally written by [Wang Zhiwu] and started on CSDN blog!
This article is the first CSDN forum. It is strictly prohibited to reprint without the permission of the official and myself!

This article is right [hard big data learning route] learning guide for experts from zero to big data (fully upgraded version) The Hive section of.
1 create database
CREATE DATABASE [IF NOT EXISTS] database_name [COMMENT database_comment] [LOCATION hdfs_path] [WITH DBPROPERTIES (property_name=property_value, ...)];
1) Create a database. The default storage path of the database on HDFS is / user/hive/warehouse/*.db.
hive (default)> create database db_hive;
2) To avoid existing errors in the database to be created, add the if not exists judgment. (standard writing)
hive (default)> create database db_hive; FAILED: Execution Error, return code 1 from org.apache.hadoop.hive.ql.exec.DDLTask. Database db_hive already exists hive (default)> create database if not exists db_hive;
3) Create a database and specify the location where the database is stored on HDFS
hive (default)> create database db_hive2 location '/db_hive2.db';
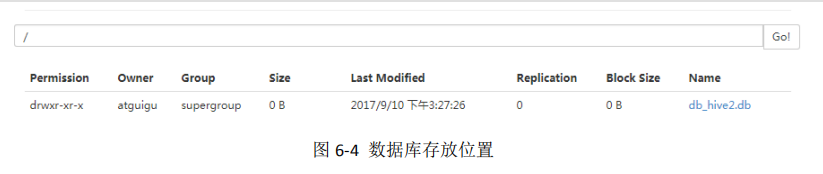
2 query database
2.1 display database
1. Display database
hive> show databases;
2. Filter and display the queried database
hive> show databases like 'db_hive*'; OK db_hive db_hive_1
2.2 view database details
1. Display database information
hive> desc database db_hive; OK db_hive hdfs://hadoop102:9000/user/hive/warehouse/db_hive.db atguiguUSER
2. Display database details, extended
hive> desc database extended db_hive; OK db_hive hdfs://hadoop102:9000/user/hive/warehouse/db_hive.db atguiguUSER
2.3 switching the current database
hive (default)> use db_hive;
3 modify database
Users can use the ALTER DATABASE command to set key value pair attribute values for DBPROPERTIES of a database to describe the attribute information of the database. Other metadata information of the database cannot be changed, including the database name and the directory location where the database is located.
hive (default)> alter database db_hive set dbproperties('createtime'='20170830');
View the modification results in hive
hive> desc database extended db_hive;
db_name comment location owner_name owner_type parameters
db_hive hdfs://hadoop102:8020/user/hive/warehouse/db_hive.db atguigu
USER {createtime=20170830}4 delete database
1. Delete empty database
hive>drop database db_hive2;
2. If the deleted database does not exist, it is better to use if exists to judge whether the database exists
hive> drop database db_hive; FAILED: SemanticException [Error 10072]: Database does not exist: db_hive hive> drop database if exists db_hive2;
3. If the database is not empty, you can use the cascade command to force deletion
hive> drop database db_hive; FAILED: Execution Error, return code 1 from org.apache.hadoop.hive.ql.exec.DDLTask. InvalidOperationException(message:Database db_hive is not empty. One or more tables exist.) hive> drop database db_hive cascade;
5 create table
1. Table creation syntax
CREATE [EXTERNAL] TABLE [IF NOT EXISTS] table_name [(col_name data_type [COMMENT col_comment], ...)] [COMMENT table_comment] [PARTITIONED BY (col_name data_type [COMMENT col_comment], ...)] [CLUSTERED BY (col_name, col_name, ...) [SORTED BY (col_name [ASC|DESC], ...)] INTO num_buckets BUCKETS] [ROW FORMAT row_format] [STORED AS file_format] [LOCATION hdfs_path] [TBLPROPERTIES (property_name=property_value, ...)] [AS select_statement]
2. Field explanation
(1) CREATE TABLE creates a table with the specified name. If a table with the same name already exists, an exception is thrown; The user can ignore this exception with the IF NOT EXISTS option.
(2) EXTERNAL keyword allows users to create an EXTERNAL table. While creating the table, you can specify a path (LOCATION) to the actual data. When deleting the table, the metadata and data of the internal table will be deleted together, while the EXTERNAL table only deletes the metadata and does not delete the data.
(3) COMMENT: adds comments to tables and columns.
(4) PARTITIONED BY create partitioned table
(5) CLUSTERED BY create bucket table
(6) SORTED BY is not commonly used. One or more columns in the bucket are sorted separately
(7)ROW FORMAT
DELIMITED [FIELDS TERMINATED BY char] [COLLECTION ITEMS TERMINATED BY char]
[MAP KEYS TERMINATED BY char] [LINES TERMINATED BY char]
| SERDE serde_name [WITH SERDEPROPERTIES (property_name=property_value,
property_name=property_value, ...)]
When creating tables, users can customize SerDe or use the self-contained SerDe. If ROWFORMAT or row format deleted is not specified, the self-contained SerDe will be used. When creating a table, the user
You also need to specify columns for the table. When you specify the columns of the table, you will also specify a custom SerDe. Hive determines the data of the specific columns of the table through SerDe.
Serde is short for Serialize/Deserilize. hive uses Serde to sequence and deserialize row objects.
(8) STORED AS specifies the storage file type
Common storage file types: sequence file, TEXTFILE RCFILE (column storage format file)
If the file data is plain text, you can use STORED AS TEXTFILE. If the data needs to be compressed, use stored as sequence file.
(9) LOCATION: Specifies the storage LOCATION of the table on HDFS.
(10) AS: followed by a query statement to create a table according to the query results.
(11) LIKE allows users to copy existing table structures without copying data.
5.1 management table
1. Theory
The tables created by default are so-called management tables, sometimes referred to as internal tables. Because of this table, hive controls (more or less) the life cycle of the data. Hive stores the data of these tables in the configuration items by default
Hive.metastore.warehouse.dir (for example, / user/hive/warehouse) is a subdirectory of the directory defined. When we delete a management table, hive will also delete the data in the table. Management tables are not suitable for sharing data with other tools.
2. Case practice
(0) raw data
1001 ss1 1002 ss2 1003 ss3 1004 ss4 1005 ss5 1006 ss6 1007 ss7 1008 ss8 1009 ss9 1010 ss10 1011 ss11 1012 ss12 1013 ss13 1014 ss14 1015 ss15 1016 ss16
(1) Normal create table
create table if not exists student2( id int, name string ) row format delimited fields terminated by '\t' stored as textfile location '/user/hive/warehouse/student2';
(2) Create a table based on the query results (the query results are added to the newly created table)
create table if not exists student3 as select id, name from student;
(3) Create a table based on an existing table structure
create table if not exists student4 like student;
(4) Type of query table
hive (default)> desc formatted student2; Table Type: MANAGED_TABLE
5.2 external table
1. Theory
Because the table is an external table, Hive does not think it has the data completely. Deleting the table will not delete the data, but the metadata information describing the table will be deleted.
2. Usage scenarios of management tables and external tables
The collected website logs are regularly flowed into HDFS text files every day. Do a lot of statistical analysis based on the external table (original log table). The intermediate table and result table used are stored in the internal table, and the data is entered into the internal table through SELECT+INSERT.
3. Case practice
Create external tables for departments and employees respectively, and import data into the tables.
(0) raw data
dept:
10 ACCOUNTING 1700 20 RESEARCH 1800 30 SALES 1900 40 OPERATIONS 1700
emp:
7369 SMITH CLERK 7902 1980-12-17 800.00 20 7499 ALLEN SALESMAN 7698 1981-2-20 1600.00 300.00 30 7521 WARD SALESMAN 7698 1981-2-22 1250.00 500.00 30 7566 JONES MANAGER 7839 1981-4-2 2975.00 20 7654 MARTIN SALESMAN 7698 1981-9-28 1250.00 1400.00 30 7698 BLAKE MANAGER 7839 1981-5-1 2850.00 30 7782 CLARK MANAGER 7839 1981-6-9 2450.00 10 7788 SCOTT ANALYST 7566 1987-4-19 3000.00 20 7839 KING PRESIDENT 1981-11-17 5000.00 10 7844 TURNER SALESMAN 7698 1981-9-8 1500.00 0.00 30 7876 ADAMS CLERK 7788 1987-5-23 1100.00 20 7900 JAMES CLERK 7698 1981-12-3 950.00 30 7902 FORD ANALYST 7566 1981-12-3 3000.00 20 7934 MILLER CLERK 7782 1982-1-23 1300.00 10
(1) Upload data to HDFS
hive (default)> dfs -mkdir /student; hive (default)> dfs -put /opt/module/datas/student.txt /student;
(2) Create table statement
Create external table
hive (default)> create external table stu_external( id int, name string) row format delimited fields terminated by '\t' location '/student';
(3) View created tables
hive (default)> select * from stu_external; OK stu_external.id stu_external.name 1001 lisi 1002 wangwu 1003 zhaoliu
(4) View table formatted data
hive (default)> desc formatted dept; Table Type: EXTERNAL_TABLE
(5) Delete external table
hive (default)> drop table stu_external;
After the external table is deleted, the data in hdfs still exists, but stu in metadata_ External metadata has been deleted
5.3 conversion between management table and external table
(1) Type of query table
hive (default)> desc formatted student2; Table Type: MANAGED_TABLE
(2) Modify the internal table student2 to an external table
alter table student2 set tblproperties('EXTERNAL'='TRUE');(3) Type of query table
hive (default)> desc formatted student2; Table Type: EXTERNAL_TABLE
(4) Modify the external table student2 to the internal table
alter table student2 set tblproperties('EXTERNAL'='FALSE');(5) Type of query table
hive (default)> desc formatted student2; Table Type: MANAGED_TABLE
Note: ('EXTERNAL'='TRUE') and ('EXTERNAL'='FALSE') are fixed and case sensitive!
6 modification table
6.1 rename table
1. Grammar
ALTER TABLE table_name RENAME TO new_table_name
2. Practical cases
hive (default)> alter table dept_partition2 rename to dept_partition3;
6.2 adding, modifying and deleting table partitions
6.3 add / modify / replace column information
1. Grammar
Update column
ALTER TABLE table_name CHANGE [COLUMN] col_old_name col_new_name column_type [COMMENT col_comment] [FIRST|AFTER column_name]
Add and replace columns
ALTER TABLE table_name ADD|REPLACE COLUMNS (col_name data_type [COMMENT col_comment], ...)
Note: ADD means to ADD a new field, the field position is after all columns (before the partition column), and REPLACE means to REPLACE all fields in the table.
2. Practical cases
(1) Query table structure
hive> desc dept_partition;
(2) Add column
hive (default)> alter table dept_partition add columns(deptdesc string);
(3) Query table structure
hive> desc dept_partition;
(4) Update column
hive (default)> alter table dept_partition change column deptdesc desc int;
(5) Query table structure
hive> desc dept_partition;
(6) Replace column
hive (default)> alter table dept_partition replace columns(deptno string, dname string, loc string);
(7) Query table structure
hive> desc dept_partition;
7 delete table
hive (default)> drop table dept_partition;