Relationship between class and interface
- Relationship between class and class
Inheritance relationship can only be inherited in single layer, but it can be inherited in multiple layers - Relationship between class and interface
The implementation relationship can be implemented alone or multiple, and multiple interfaces can be implemented while inheriting a class - Interface and interface relationship
Inheritance relationship can be single inheritance or multiple inheritance
public interface Inter1 {
}
public interface Inter2 {
}
//Interfaces and interfaces can be inherited, and multiple interfaces can be inherited
public interface Inter3 extends Inter1,Inter2{
}
//Class can inherit a class and implement multiple interfaces
public class InterClass extends Object implements Inter1,Inter2,Inter3{
}
The difference between abstract classes and interfaces
- Member difference
Abstract class - variable, constant; There are construction methods; There are abstract and non abstract methods
Interface - constant; Abstract method - Relationship difference
Class and class - inheritance, single inheritance
Classes and interfaces - implementation, either single or multiple
Interface and interface - inheritance, single inheritance, multiple inheritance - Difference of design concept
Abstract classes - abstract classes, including properties and behaviors
Interface - abstract behavior, mainly behavior
Examples of doors and alarms:
Door: both have open and close actions, and alarm is a function of individual doors. At this time, you can use abstract classes and interfaces to define them respectively
//abstract class
public abstract class Door {
public abstract void open();
public abstract void close();
}
//Interface
public interface Alram {
void alram();
}
public class AlramDoor extends Door implements Alram {
@Override
public void open() {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
System.out.println("Open the door");
}
@Override
public void close() {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
System.out.println("close");
}
@Override
public void alram() {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
System.out.println("call the police");
}
}
Abstract class is the abstraction of things, and interface is the abstraction of behavior
Case: athletes and coaches
Demand: we now have table tennis players and basketball players, table tennis coaches and basketball coaches. In order to communicate abroad, people related to table tennis need to learn English. Please analyze the specific classes, abstract classes and interfaces in this case with the knowledge learned, and implement them in code
Analysis: from concrete to abstract
Implementation: from abstract to concrete
Use: use specific class objects
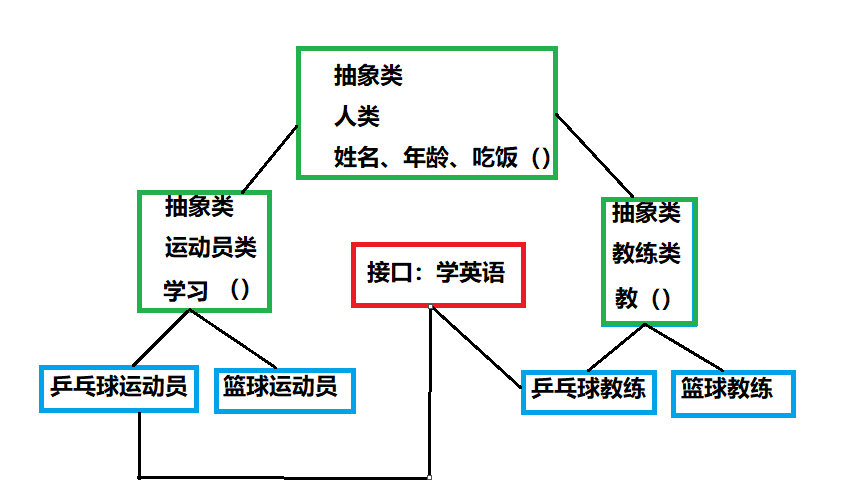
//Abstract human
public abstract class People {
String name;
int age;
// having dinner
public abstract void eat();
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public int getAge() {
return age;
}
public void setAge(int age) {
this.age = age;
}
public People() {
super();
}
public People(String name, int age) {
super();
this.name = name;
this.age = age;
}
}
//Abstract athlete class
public abstract class Athletes extends People {
// study
public abstract void study();
@Override
public void eat() {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
System.out.println("Athletes eat");
}
public Athletes() {
}
public Athletes(String name, int age) {
super();
this.name = name;
this.age = age;
}
}
//Abstract class coach class
public abstract class Coach extends People {
public abstract void teach();
@Override
public void eat() {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
System.out.println("Coach dinner");
}
public Coach() {
}
public Coach(String name, int age) {
super();
this.name = name;
this.age = age;
}
}
//Interface learning English
public interface English {
void english();
}
//Table tennis player
public class PPA extends Athletes implements English {
@Override
public void study() {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
System.out.println("Learn table tennis");
}
@Override
public void english() {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
System.out.println("learn English");
}
@Override
public void eat() {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
super.eat();
}
public PPA() {
}
public PPA(String name, int age) {
super();
this.name = name;
this.age = age;
}
}
//Table tennis coach
public class PPC extends Coach implements English {
@Override
public void teach() {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
System.out.println("Teach table tennis");
}
@Override
public void english() {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
System.out.println("learn English");
}
@Override
public void eat() {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
super.eat();
}
public PPC() {
}
public PPC(String name, int age) {
super();
this.name = name;
this.age = age;
}
}
//Basketball players
public class BA extends Athletes {
@Override
public void study() {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
System.out.println("Learning basketball");
}
@Override
public void eat() {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
super.eat();
}
public BA() {
}
public BA(String name, int age) {
super();
this.age = age;
this.name = name;
}
}
//Basketball coach
public class BC extends Coach {
@Override
public void teach() {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
System.out.println("Teach basketball");
}
@Override
public void eat() {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
super.eat();
}
public BC() {
}
public BC(String name, int age) {
super();
this.age = age;
this.name = name;
}
}
//Test class
public class Demo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
PPA p = new PPA("Xiaobai", 16);
System.out.println(p.getName() + "," + p.getAge());
p.eat();
p.study();
p.english();
System.out.println("-----");
PPC pc = new PPC("Big white", 44);
System.out.println(pc.getName() + "," + pc.getAge());
pc.eat();
pc.teach();
pc.english();
System.out.println("-----");
BA b = new BA("Xiao Hei", 14);
System.out.println(b.getName() + "," + b.getAge());
b.eat();
b.study();
System.out.println("-----");
BC bc = new BC("Big black", 54);
System.out.println(bc.getName() + "," + bc.getAge());
bc.eat();
bc.teach();
System.out.println("-----");
}
}
Operation results:
