I moved my notes on Nuggets: WebGL Basics,Personal blog
Why WebGL / Why GPU?
- What is WebGL?
- GPU ≠ WebGL ≠ 3D
- Why is WebGL not as simple as other front-end technologies?
Modern image system
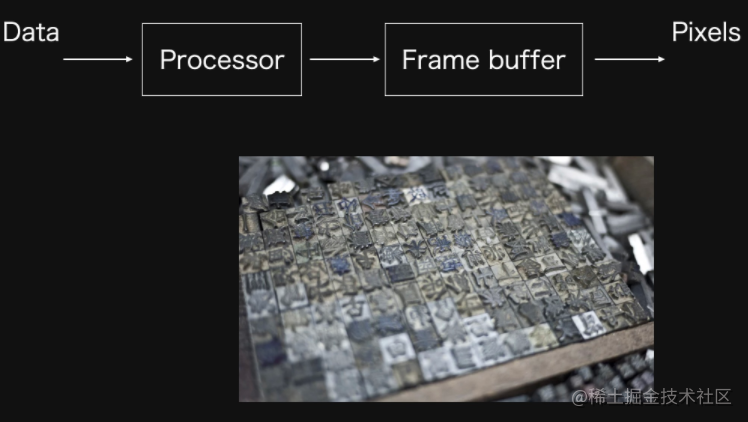
- Raster: almost all modern graphics systems draw graphics based on raster. Raster refers to the pixel array constituting the image.
- Pixel: a pixel corresponds to a point on the image. It usually saves the color and other information of a specific position on the image.
- Frame buffer: in the drawing process, pixel information is stored in the frame buffer, which is a memory address.
- CPU (Central Processing Unit): central processing unit, which is responsible for logic calculation.
- GPU (Graphics Processing Unit): graphics processing unit, which is responsible for graphics calculation.
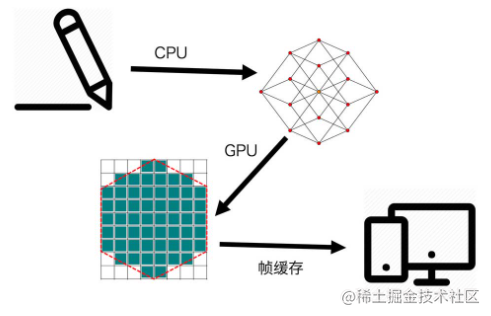
- As shown in the figure above, the rendering process of modern images is shown in the figure below
- Contour extraction / meshing
- Rasterization
- Frame buffer
- Render
The Pipeline
GPU
- GPU consists of a large number of small computing units
- Each arithmetic unit is only responsible for handling very simple calculations
- Each operation unit is independent of each other
- Therefore, all calculations can be processed in parallel
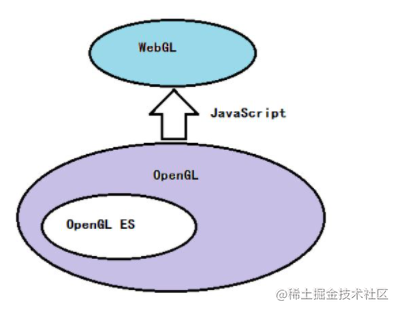
Webgl & OpenGL relationship
OpenGL, OpenGL ES, WebGL, GLSL, GLSL ES API Tables (umich.edu)
WebGL drawing steps
step
- Create WebGL context
- Create WebGL Program
- Store data in buffer
- Read buffer data to GPU
- GPU executes WebGL program and outputs results
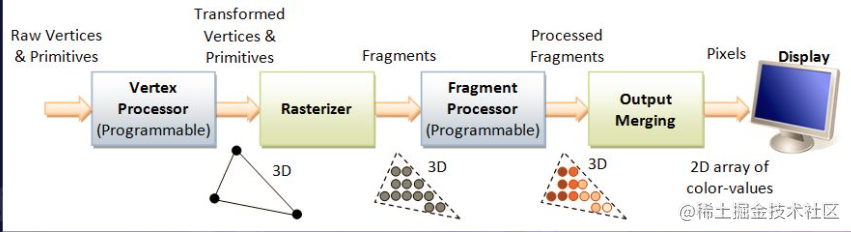
As shown in the figure, explain several words:
- Raw vertices & primitives
- Vertex Processor vertex shader
- After the operation, it is sent to the slice shader for processing: Fragment Processor
Create WebGL context
const canvas = document.querySelector('canvas');
const gl = canvas.getContext('webgl');
// Create context, pay attention to compatibility
function create3DContext(canvas, options) {
const names = ['webgl', 'experimental-webgL','webkit-3d','moz-webgl']; // Characteristic judgment
if(options.webgl2) names.unshift(webgl2);
let context = null;
for(let ii = 0; ii < names.length; ++ii) {
try {
context = canvas.getContext(names[ii], options);
} catch(e) {
// no-empty
}
if(context) {
break;
}
}
return context;
}
Create WebGL Program (The Shaders)
-
Vertex Shader
The position of each vertex is processed in parallel through the type array position
attribute vec2 position;// vec2 2D vector void main() { gl_PointSize = 1.0; gl_Position = vec4(position, 1.0, 1.0); } -
Fragment Shader
Shade all pixels in the area surrounded by the vertex contour
precision mediump float; void main() { gl_FragColor = vec4(1.0, 0.0, 0.0, 1.0);//Corresponding to rgba (255, 0, 0, 1.0), red }
The specific steps are as follows:
-
Create vertex shader and slice shader code:
// Vertex shader program code const vertexShaderCode = ` attribute vec2 position; void main() { gl_PointSize = 1.0; gl_Position = vec4(position, 1.0, 1.0); } `; // Chip shader program code const fragmentShaderCode = ` precision mediump float; void main() { gl_FragColor = vec4(1.0, 0.0, 0.0, 1.0); } `; -
use createShader() Create shader object
-
use shaderSource() Program code for setting shaders
-
use compileShader() Compile a shader
// Vertex Shader const vertexShader = gl.createShader(gl.VERTEX_SHADER); gl.shaderSource(vertexShader, vertex); gl.compileShader(vertexShader); // Fragment Shader const fragmentShader = gl.createShader(gl.FRAGMENT_SHADER); gl.shaderSource(fragmentShader, fragment); gl.compileShader(fragmentShader);
-
Use** createProgram() **Create WebGLProgram object
-
use attachShader() to WebGLProgram Add a clip or vertex shader.
-
Use** linkProgram() **Link given WebGLProgram To complete the process of preparing GPU code for the program's slice element and vertex shader.
-
use useProgram() Will be defined WebGLProgram Object is added to the current render state
// Create shader program and link const program = gl.createProgram(); gl.attachShader(program, vertexShader); gl.attachShader(program, fragmentShader); gl.linkProgram(program); gl.useProgram(program);
Save Data to Frame Buffer
- Coordinate axis: the coordinate system of webGL is normalized. The coordinate system of browser and canvas 2D takes the upper left corner as the coordinate origin, the y axis is downward, the x axis is right, and the coordinate value is relative to the origin. The coordinate system of webGL is a normal Cartesian coordinate system with the center point of the drawing canvas as the origin.
Represents its vertices through an array of vertices, using createBuffer() Create and initialize a for storing vertex data or shading data WebGLBuffer Object and return bufferId, and then use bindBuffer() Bind the given bufferId to the target and return it. Finally, use** bufferData() **, bind the data to the buffer.
// vertex data
const points = new Float32Array([
-1, -1,
0, 1,
1, -1,
]);
// Create buffer
const bufferId = gl.createBuffer();
gl.bindBuffer(gl.ARRAY_BUFFER, bufferId);
gl.bufferData(gl.ARRAY_BUFFER, points, gl.STATIC_DRAW);
Read buffer data to GPU (Frame Buffer to GPU)
-
getAttribLocation() The given is returned WebGLProgram The subscript of an attribute in the object points to the position.
-
vertexAttribPointer() Tell the graphics card to read vertex data from the currently bound buffer (the buffer specified by bindBuffer()).
-
enableVertexAttribArray() You can open the generic vertex attribute array at the specified index in the attribute array list.
const vPosition = gl.getAttribLocation(program, 'position'); // Gets the address of the position variable in the vertex shader gl.vertexAttribPointer(vPosition, 2, gl.FLOAT, false, 0, 0); // Set the length and type of the variable gl.enableVertexAttribArray(vPosition); // Activate this variable
Output
drawArrays() Draws an entity from a vector array
// output gl.clear(gl.COLOR_BUFFER_BIT); //Clear buffered data gl.drawArrays(gl.TRIANGLES, 0, points.length / 2);
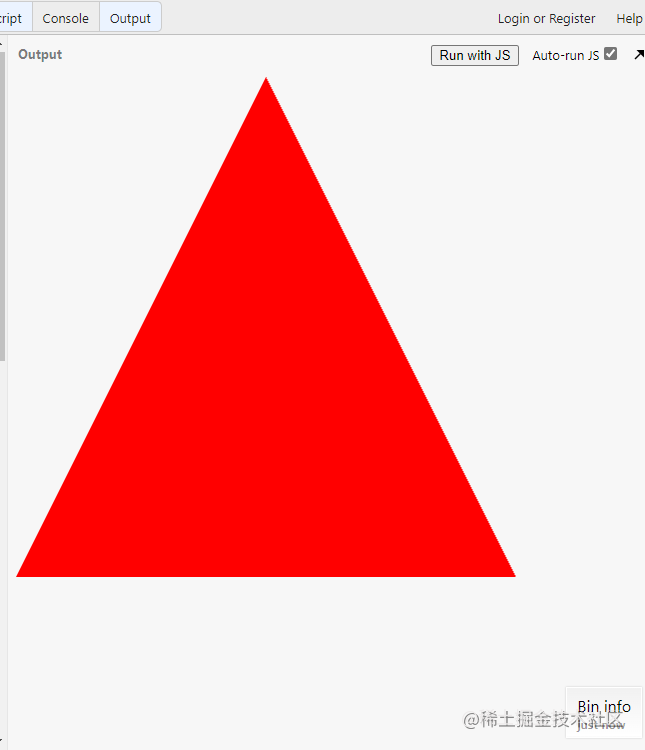
WebGL is too complicated? Other ways
canvas 2D
Look at canvas 2D and draw the same triangle:
// The canvas is simple and rough. It's all encapsulated
const canvas = document.querySelector('canvas');
const ctx = canvas.getContext('2d');
ctx.beginPath();
ctx.moveTo(250, 0);
ctx.lineTo(500, 500);
ctx.lineTo(0, 500);
ctx.fillStyle = 'red';
ctx.fill();
Mesh.js
mesh-js/mesh.js: A graphics system born for visualization 😘. (github.com)
const {Renderer, Figure2D, Mesh2D} = meshjs;
const canvas = document.querySelector ('canvas');
const renderer = new Renderer(canvas);
const figure = new Figure2D();
figurie.beginPath();
figure.moveTo(250, 0);
figure.lineTo(500,500);
figure.lineTo(0, 500);
const mesh = new Mesh2D(figure, canvas);
mesh.setFill({
color: [1, 0, 0, 1],
});
renderer.drawMeshes([mesh]);
Earcut
use Earcut Triangulate
const vertices = [
[-0.7, 0.5],
[-0.4, 0.3],
[-0.25, 0.71],
[-0.1, 0.56],
[-0.1, 0.13],
[0.4, 0.21],
[0, -0.6],
[-0.3, -0.3],
[-0.6, -0.3],
[-0.45, 0.0],
];
const points = vertices.flat();
const triangles = earcut(points)
3D Meshing
The designer exports it to us and then extracts it
SpriteJS/next - The next generation of spritejs.
Graphic transformations
This is the knowledge related to digital image processing (all learned are back. jpg)
translation
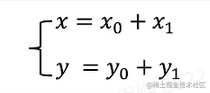
rotate
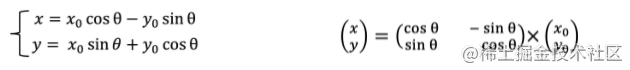
zoom
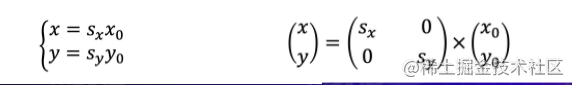
Linear transformation (rotate + scale)
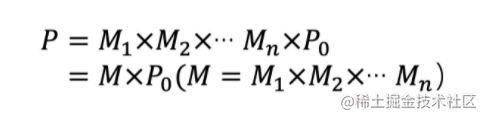
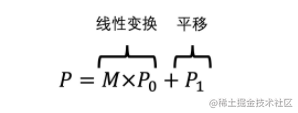
From linear transformation to homogeneous matrix

Another chestnut from the teacher: Apply Transforms
3D Matrix
Four homogeneous matrices of 3D standard model (mat4)
- Projection Matrix
- Model Matrix (Transform vertices)
- View Matrix view matrix (3D perspective, imagine a camera, in the viewport of the camera)
- Normal Matrix (normal vector perpendicular to the object surface, usually used to calculate the illumination of the object)
Read more
- The Book of Shaders (Introducing slice shader, very fun)
- Mesh.js (basement, hey)
- Glsl Doodle (a lightweight Library of slice shaders with many small demo s)
- SpriteJS (open source library written by teacher Yueying orz)
- Three.js (many interesting game items)
- Shadertoy BETA (many interesting projects)
Summarize your feelings
In this class, the teacher explained WebGL drawing and its related libraries in great detail, and showed many interesting WebGL small projects~
Most of the content cited in this article comes from teacher Yueying's class and MDN! Teacher Yueying, tql!