PYNQ get started
The purchased development board system has been burned and can be used directly through networking
There is no router. I found an industrial computer with two network ports. One is connected to the network, and the other is connected to the development board through the network cable. Set the static IP address of the network port computer connected to the development board as 192.168.2 xx (xx is greater than 0, less than 255, and not equal to 99, because 99 is assigned to the development board by default).
usb connection development board.
The development board is connected to the power supply and powered on
Enter in Google browser http://192.168.2.99 The account and password are xilinx.
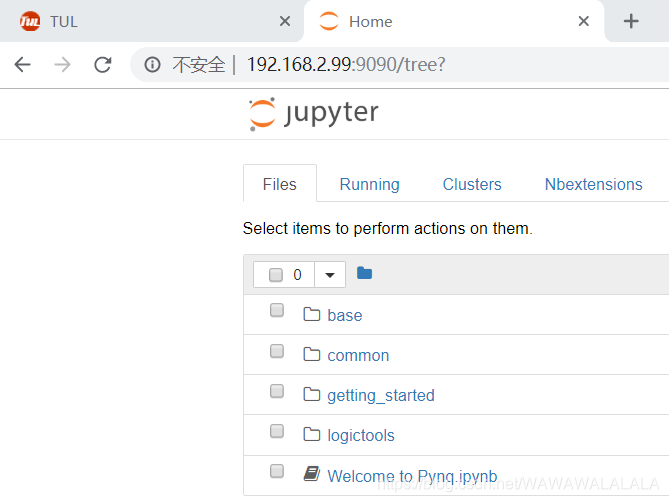
Call NYQ camera
Open home page
http://192.168.2.99:9090/notebooks/common/usb_webcam.ipynb
Then select usb webcam project in common, and the photo is the default photo. run, you can finally see an image taken by the camera.
Of course, you can also use xshell connection
Create a new session. The host number is 192.168.2.99
The serial port settings are shown in the figure. You can view the port number through the control panel
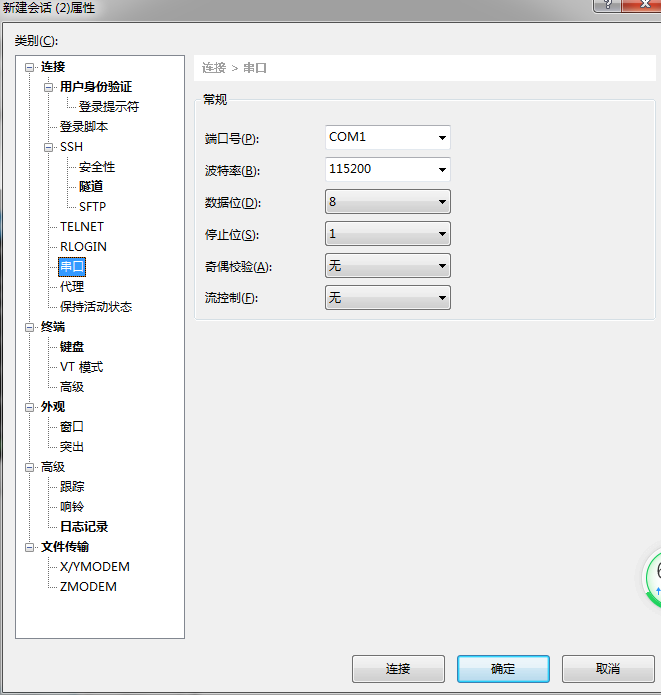
The account passwords are xilinx
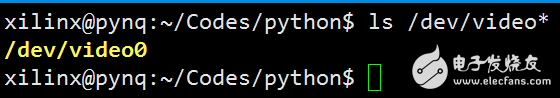
After logging in successfully, you can check whether the camera is connected successfully through ls
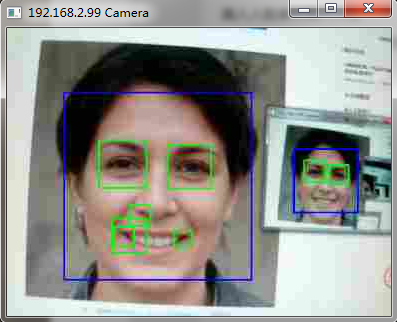
Use PYNQ to realize camera face recognition and display it on the computer
Code and operation
The code file is divided into two parts, sever Ipynb runs on the development board, client Py runs on the computer.
First, on the browser, jupyter and create sever Ipynb file, open and run.
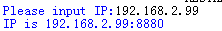
Then, on the computer side, run the client using pychar Py, input the IP address of the development board queried earlier according to the program prompt, and press Enter to pop up a window to dynamically display the picture captured by the camera and detect the face! (please install python and other packages before running.).
After running, let me input the board id and input 192.168.2.99
sever. All ipynb codes are as follows:
import socket
import threading
import struct
import time
import cv2
import numpy
class Carame_Accept_Object:
def __init__(self, S_addr_port=("", 8880)):
self.resolution = (640, 480) # resolving power
self.img_fps = 15 # How many frames are transmitted per second
self.addr_port = S_addr_port
self.Set_Socket(self.addr_port)
# Set socket
def Set_Socket(self, S_addr_port):
self.server = socket.socket(socket.AF_INET, socket.SOCK_STREAM)
self.server.setsockopt(socket.SOL_SOCKET, socket.SO_REUSEADDR, 1) # Port reusable
self.server.bind(S_addr_port)
self.server.listen(5)
# print("the process work in the port:%d" % S_addr_port[1])
def check_option(object, client):
# Decode according to the format to determine the number of frames and resolution
info = struct.unpack('lhh', client.recv(8))
if info[0] > 888:
object.img_fps = int(info[0]) - 888 # Get frames
object.resolution = list(object.resolution)
# Get resolution
object.resolution[0] = info[1]
object.resolution[1] = info[2]
object.resolution = tuple(object.resolution)
return 1
else:
return 0
def RT_Image(object, client, D_addr):
if (check_option(object, client) == 0):
return
camera = cv2.VideoCapture(0) # Get video from camera
img_param = [int(cv2.IMWRITE_JPEG_QUALITY), object.img_fps] # Set the format and number of frames of the transmitted image
while (1):
time.sleep(0.1) # Delay thread running for 0.1s
_, object.img = camera.read() # Read every frame of video
# Face recognition
np_frame = object.img
#face_cascade = cv2.CascadeClassifier(
# r'.\haarcascade_frontalface_default.xml')
#eye_cascade = cv2.CascadeClassifier(
# r'.\haarcascade_eye.xml')
face_cascade = cv2.CascadeClassifier(
'/home/xilinx/jupyter_notebooks/base/video/data/'
'haarcascade_frontalface_default.xml')
eye_cascade = cv2.CascadeClassifier(
'/home/xilinx/jupyter_notebooks/base/video/data/'
'haarcascade_eye.xml')
gray = cv2.cvtColor(np_frame, cv2.COLOR_BGR2GRAY)
faces = face_cascade.detectMultiScale(gray, 1.3, 5)
for (x, y, w, h) in faces:
cv2.rectangle(np_frame, (x, y), (x + w, y + h), (255, 0, 0), 2)
roi_gray = gray[y:y + h, x:x + w]
roi_color = np_frame[y:y + h, x:x + w]
eyes = eye_cascade.detectMultiScale(roi_gray)
for (ex, ey, ew, eh) in eyes:
cv2.rectangle(roi_color, (ex, ey), (ex + ew, ey + eh), (0, 255, 0), 2)
object.img = cv2.resize(object.img, object.resolution) # Resize the image as required (resolution must be a tuple)
_, img_encode = cv2.imencode('.jpg', object.img, img_param) # Generate pictures in format
img_code = numpy.array(img_encode) # Convert to matrix
object.img_data = img_code.tostring() # Generate the corresponding string
try:
# Package and send pictures according to the corresponding format
client.send(
struct.pack("lhh", len(object.img_data), object.resolution[0], object.resolution[1]) + object.img_data)
except:
camera.release() # Release resources
return
if __name__ == '__main__':
camera = Carame_Accept_Object()
while (1):
client, D_addr = camera.server.accept()
clientThread = threading.Thread(None, target=RT_Image, args=(camera, client, D_addr,))
clientThread.start()
client.py all codes are as follows:
#client
import socket
import cv2
import threading
import struct
import numpy
class Camera_Connect_Object:
def __init__(self,D_addr_port=["",8880]):
self.resolution=[384,288]
self.addr_port=D_addr_port
self.src=888+15 #Both parties determine the number of transmission frames, (888) is the check value
self.interval=0 #Picture playback interval
self.img_fps=15 #How many frames are transmitted per second
def Set_socket(self):
self.client=socket.socket(socket.AF_INET,socket.SOCK_STREAM)
self.client.setsockopt(socket.SOL_SOCKET,socket.SO_REUSEADDR,1)
def Socket_Connect(self):
self.Set_socket()
self.client.connect(self.addr_port)
print("IP is %s:%d" % (self.addr_port[0],self.addr_port[1]))
def RT_Image(self):
#The number of frames and resolution are packaged and sent according to the format
self.name=self.addr_port[0]+" Camera"
self.client.send(struct.pack("lhh", self.src, self.resolution[0], self.resolution[1]))
while(1):
info=struct.unpack("lhh",self.client.recv(8))
buf_size=info[0] #Gets the total length of the read picture
if buf_size:
try:
self.buf=b"" #Represents the type of bytes
temp_buf=self.buf
while(buf_size): #Read the length of each picture
temp_buf=self.client.recv(buf_size)
buf_size-=len(temp_buf)
self.buf+=temp_buf #Get picture
data = numpy.fromstring(self.buf, dtype='uint8') #Convert to image matrix by uint8
self.image = cv2.imdecode(data, 1) #Image decoding
cv2.imshow(self.name, self.image) #Show pictures
except:
pass;
finally:
if(cv2.waitKey(10)==27): #Refresh the picture every 10ms and press' ESC '(27) to exit
self.client.close()
cv2.destroyAllWindows()
break
def Get_Data(self,interval):
showThread=threading.Thread(target=self.RT_Image)
showThread.start()
if __name__ == '__main__':
camera=Camera_Connect_Object()
camera.addr_port[0]=input("Please input IP:")
camera.addr_port=tuple(camera.addr_port)
camera.Socket_Connect()
camera.Get_Data(camera.interval)error

There is an error: the port is occupied. It is found that several programs are running, including those calling usb, which are all closed. It's solved.