Tip: after the article is written, the directory can be generated automatically. Please refer to the help document on the right for how to generate it
preface
Review the steps of Android component development architecture
1, Create
Business component layer
The Module created by the business component layer adopts phone & table, which is the first option to create the Module, because we will debug each Module here
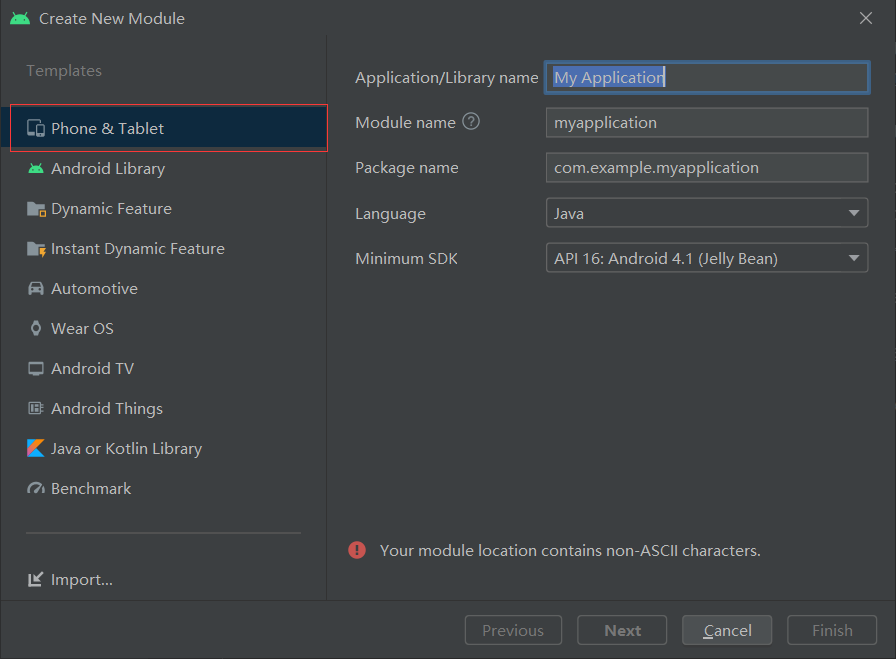
In order to make the hierarchical structure clearer, the hierarchical name is usually placed before the real name of the Module when naming the Module name
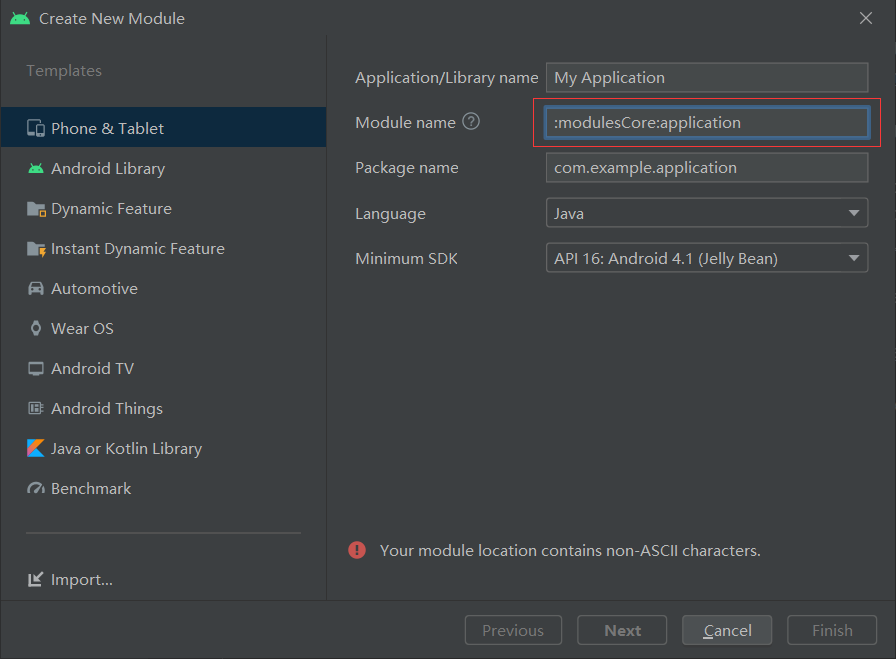
Basic component layer
Module s created in the basic component layer are usually created in the Library and placed in the specified hierarchical folder
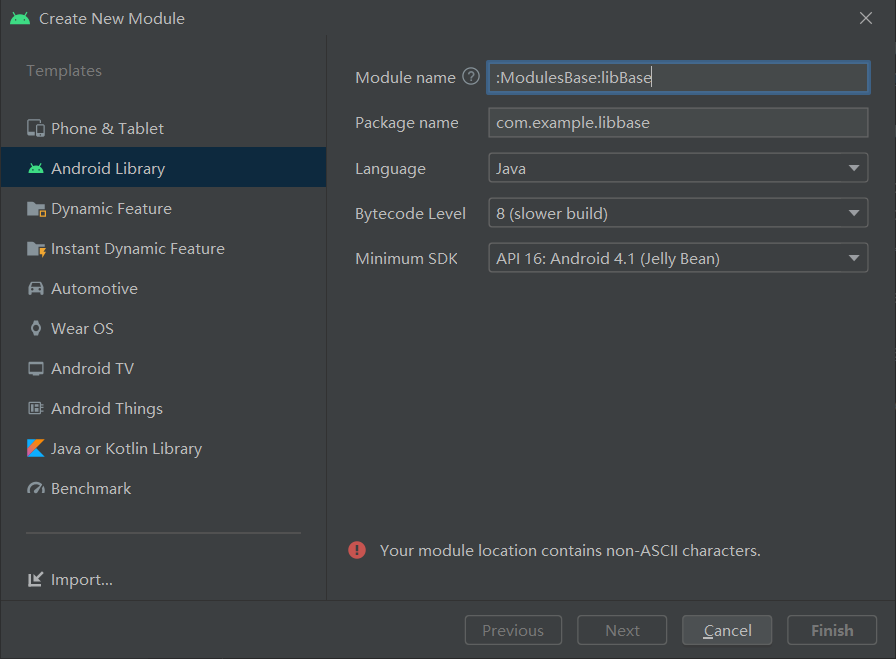
Functional component layer
The functional component layer relies on the basic component layer and does not need to switch from Module and Application, so it is built with Library
2, Version management
objective
Different Module dependent libraries may have different versions. If unified version management is not carried out, dependency conflicts may be caused by different versions of dependent libraries
The implementation scheme is as follows:
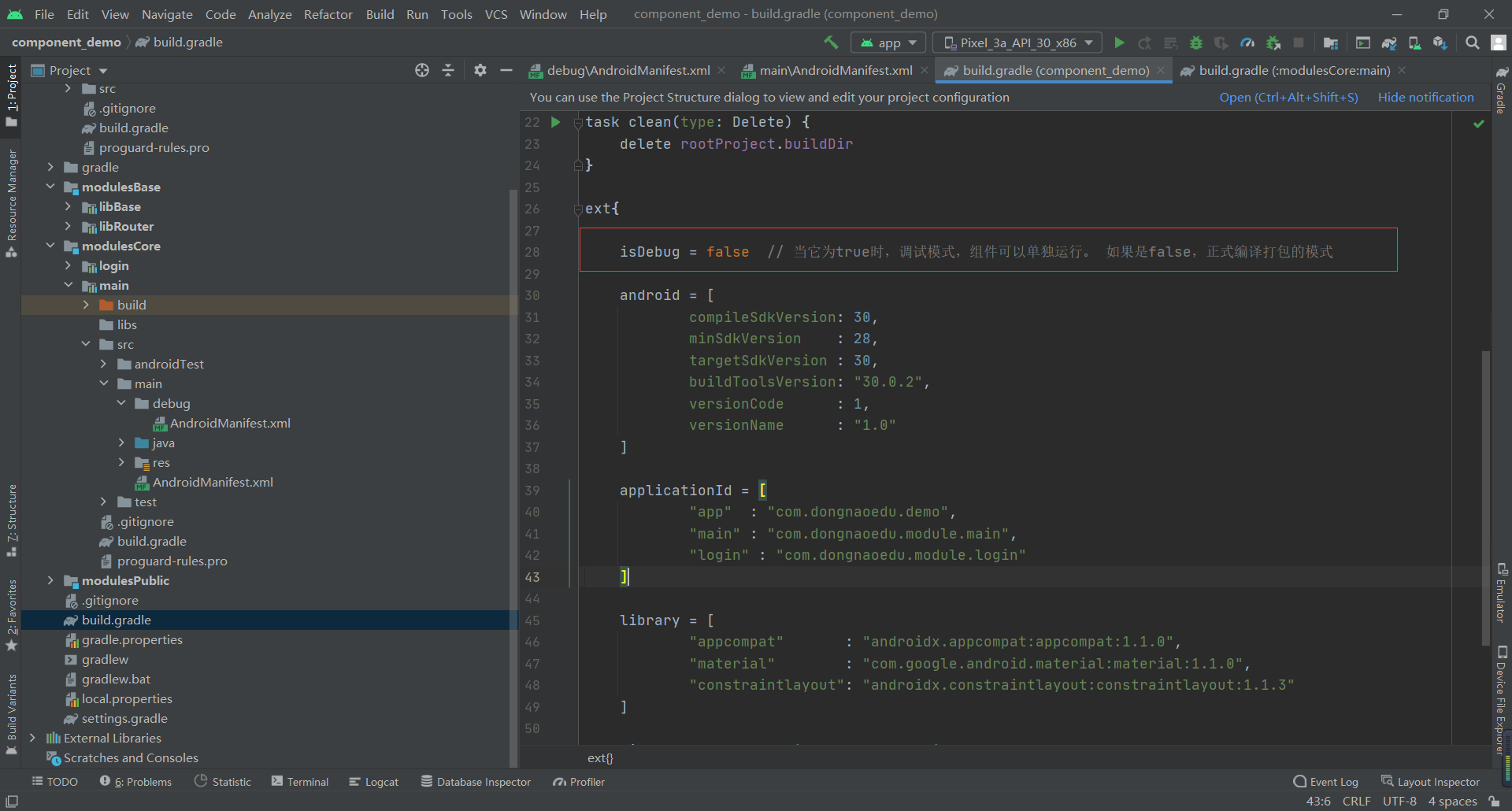
1. In Project build Add the following code under gradle
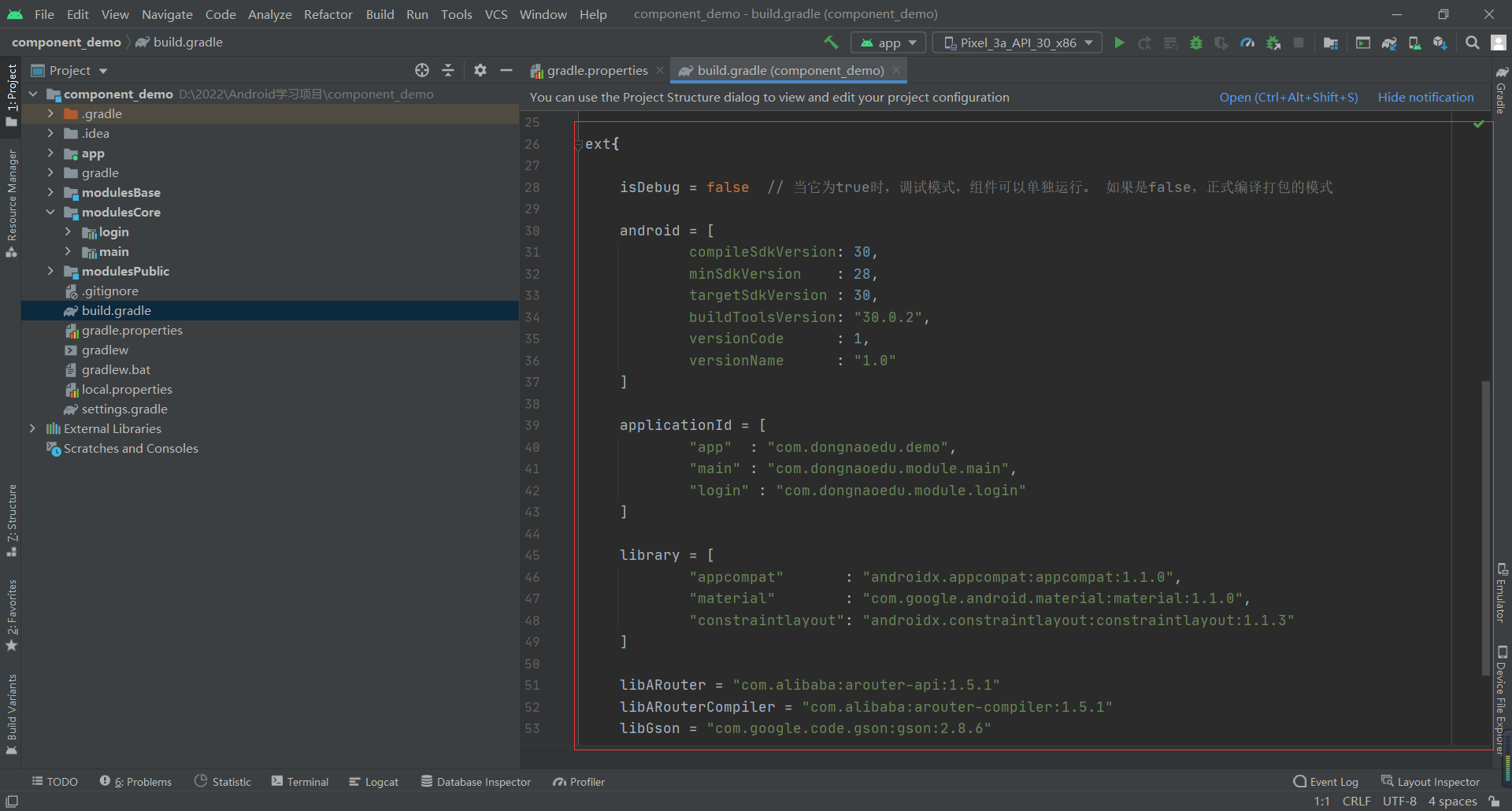
Contains the following information
- isDebug determines whether the component can run independently
- android compilation and debugging version information
- applicationId contains the package name that can run the Module separately
- Information about dependent libraries in the library SDK
- Other third parties rely on library information
2. Modify the information of other modules
For example, we are building the main of the business component layer The gradle information is modified as follows
def cfg = rootProject.ext
//plugins {
// id 'com.android.application'
//}
if (cfg.isDebug) {
apply plugin: 'com.android.application'
} else {
apply plugin: 'com.android.library'
}
android {
compileSdkVersion cfg.android.compileSdkVersion
buildToolsVersion cfg.android.buildToolsVersion
defaultConfig {
if (cfg.isDebug) {
applicationId cfg.applicationId.login
}
minSdkVersion cfg.android.minSdkVersion
targetSdkVersion cfg.android.targetSdkVersion
versionCode cfg.android.versionCode
versionName cfg.android.versionName
testInstrumentationRunner "androidx.test.runner.AndroidJUnitRunner"
javaCompileOptions {
annotationProcessorOptions {
arguments = [AROUTER_MODULE_NAME: project.getName()]
}
}
}
buildTypes {
release {
minifyEnabled false
proguardFiles getDefaultProguardFile('proguard-android-optimize.txt'), 'proguard-rules.pro'
}
}
compileOptions {
sourceCompatibility JavaVersion.VERSION_1_8
targetCompatibility JavaVersion.VERSION_1_8
}
sourceSets {
main {
if (cfg.isDebug) {
manifest.srcFile 'src/main/debug/AndroidManifest.xml'
} else {
manifest.srcFile 'src/main/AndroidManifest.xml'
}
}
}
}
dependencies {
implementation project(':modulesBase:libBase')
annotationProcessor cfg.libARouterCompiler
testImplementation 'junit:junit:4.+'
androidTestImplementation 'androidx.test.ext:junit:1.1.1'
androidTestImplementation 'androidx.test.espresso:espresso-core:3.2.0'
}
Define the cfg variable and reference the build. In the Project directory Gradle file, and then reference and modify it in the rest of the code
It should be noted that only in the Debug mode can each Module have its own application id, otherwise an error will be reported
3, Rely on LibBase
In the build. Of components requiring LibBase Add the following code to the dependencies in gradle
implementation project(':modulesBase:libBase')
Modify the build.of LibBase Gradle file, which uses api instead of dependency in dependencies to make it easy to pass up; This prevents repeated dependencies
The specific codes are as follows:
def cfg = rootProject.ext
apply plugin: 'com.android.library'
android {
compileSdkVersion cfg.android.compileSdkVersion
buildToolsVersion cfg.android.buildToolsVersion
defaultConfig {
minSdkVersion cfg.android.minSdkVersion
targetSdkVersion cfg.android.targetSdkVersion
versionCode cfg.android.versionCode
versionName cfg.android.versionName
testInstrumentationRunner "androidx.test.runner.AndroidJUnitRunner"
}
buildTypes {
release {
minifyEnabled false
proguardFiles getDefaultProguardFile('proguard-android-optimize.txt'), 'proguard-rules.pro'
}
}
compileOptions {
sourceCompatibility JavaVersion.VERSION_1_8
targetCompatibility JavaVersion.VERSION_1_8
}
}
dependencies {
api cfg.library.appcompat
api cfg.library.material
api cfg.library.constraintlayout
api cfg.libARouter
api project(':modulesBase:libRouter')
testImplementation 'junit:junit:4.+'
androidTestImplementation 'androidx.test.ext:junit:1.1.1'
androidTestImplementation 'androidx.test.espresso:espresso-core:3.2.0'
}
4, Modify functional component layer
Modify the build of functional component layer Gradle, but does not pass dependencies, because other modules may rely on both the basic component layer and the functional component layer
def cfg = rootProject.ext
//plugins {
// id 'com.android.application'
//}
if (cfg.isDebug) {
apply plugin: 'com.android.application'
} else {
apply plugin: 'com.android.library'
}
android {
compileSdkVersion cfg.android.compileSdkVersion
buildToolsVersion cfg.android.buildToolsVersion
defaultConfig {
if (cfg.isDebug) {
applicationId cfg.applicationId.login
}
minSdkVersion cfg.android.minSdkVersion
targetSdkVersion cfg.android.targetSdkVersion
versionCode cfg.android.versionCode
versionName cfg.android.versionName
testInstrumentationRunner "androidx.test.runner.AndroidJUnitRunner"
javaCompileOptions {
annotationProcessorOptions {
arguments = [AROUTER_MODULE_NAME: project.getName()]
}
}
}
buildTypes {
release {
minifyEnabled false
proguardFiles getDefaultProguardFile('proguard-android-optimize.txt'), 'proguard-rules.pro'
}
}
compileOptions {
sourceCompatibility JavaVersion.VERSION_1_8
targetCompatibility JavaVersion.VERSION_1_8
}
sourceSets {
main {
if (cfg.isDebug) {
manifest.srcFile 'src/main/debug/AndroidManifest.xml'
} else {
manifest.srcFile 'src/main/AndroidManifest.xml'
}
}
}
}
dependencies {
implementation project(':modulesBase:libBase')
annotationProcessor cfg.libARouterCompiler
testImplementation 'junit:junit:4.+'
androidTestImplementation 'androidx.test.ext:junit:1.1.1'
androidTestImplementation 'androidx.test.espresso:espresso-core:3.2.0'
}
5, Modify the main project
plugins {
id 'com.android.application'
}
def cfg = rootProject.ext
android {
compileSdkVersion cfg.android.compileSdkVersion
buildToolsVersion cfg.android.buildToolsVersion
defaultConfig {
applicationId cfg.applicationId.app
minSdkVersion cfg.android.minSdkVersion
targetSdkVersion cfg.android.targetSdkVersion
versionCode cfg.android.versionCode
versionName cfg.android.versionName
testInstrumentationRunner "androidx.test.runner.AndroidJUnitRunner"
}
buildTypes {
release {
minifyEnabled false
proguardFiles getDefaultProguardFile('proguard-android-optimize.txt'), 'proguard-rules.pro'
}
}
compileOptions {
sourceCompatibility JavaVersion.VERSION_1_8
targetCompatibility JavaVersion.VERSION_1_8
}
}
dependencies {
implementation project(':modulesBase:libBase')
if (!cfg.isDebug) {
implementation project(':modulesCore:main')
implementation project(':modulesCore:login')
}
implementation 'androidx.appcompat:appcompat:1.1.0'
implementation 'com.google.android.material:material:1.1.0'
implementation 'androidx.constraintlayout:constraintlayout:1.1.3'
testImplementation 'junit:junit:4.+'
androidTestImplementation 'androidx.test.ext:junit:1.1.1'
androidTestImplementation 'androidx.test.espresso:espresso-core:3.2.0'
}
6, Business component layer debug mode switching
In the business component layer, when debugging, you need to have your own Activity startup entry. When running, there can only be one entry for the whole APP, so it corresponds to different androidmanifest XML file
We can create different AndroidManifest files in the business component layer, and then in build Debug switch in gradle (use SourceSet to switch settings)
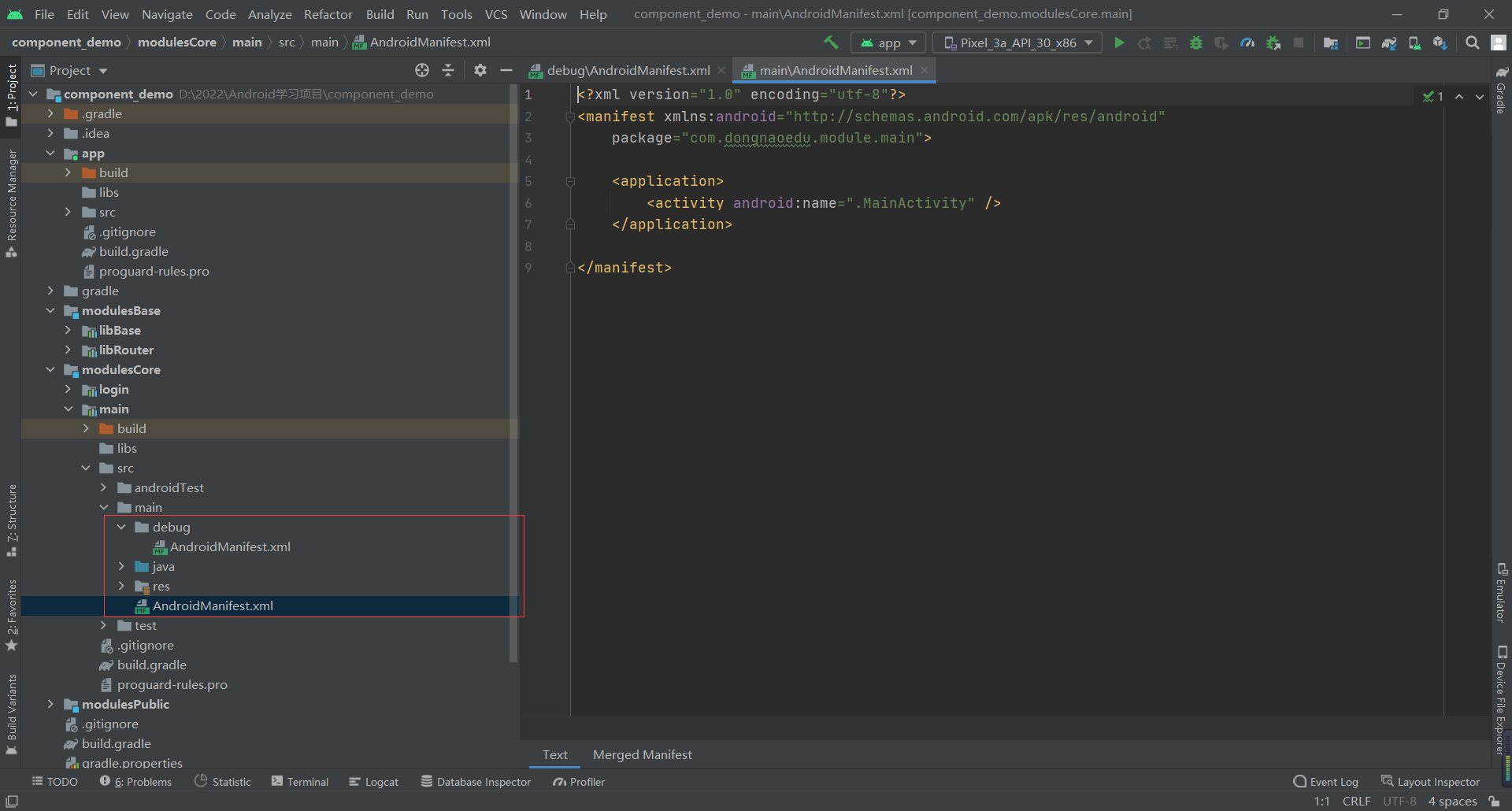
Androidmanifest. In the debug directory xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<manifest xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
package="com.dongnaoedu.module.main">
<application
android:allowBackup="true"
android:icon="@mipmap/ic_launcher"
android:label="@string/app_name"
android:roundIcon="@mipmap/ic_launcher_round"
android:supportsRtl="true"
android:theme="@style/Theme.Component_demo">
<activity android:name=".MainActivity">
<intent-filter>
<action android:name="android.intent.action.MAIN" />
<category android:name="android.intent.category.LAUNCHER" />
</intent-filter>
</activity>
</application>
</manifest>
Androidmanifest. Run as library xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<manifest xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
package="com.dongnaoedu.module.main">
<application>
<activity android:name=".MainActivity" />
</application>
</manifest>
7, Switch whether the Module can run independently
Modify the isDebug attribute under Project