catalogue
Other digital summarization algorithms
Encryption mode
Encryption mode: https://docs.oracle.com/javase/8/docs/api/javax/crypto/Cipher.html
ECB
ECB: electronic codebook The message to be encrypted is divided into several blocks according to the block size of the block password, and each block is encrypted independently
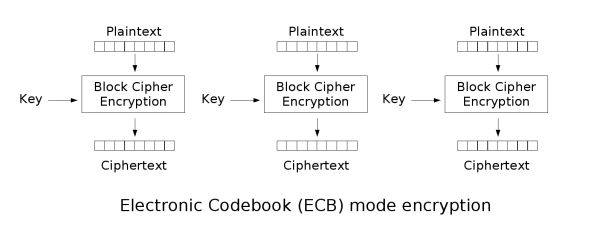
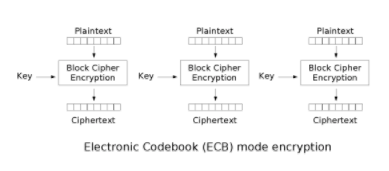
- Advantages: data can be processed in parallel
- Disadvantages: the same original text generates the same ciphertext, which can not protect the data well
- At the same time, the original text is the same, and the encrypted ciphertext is the same
CBC
CBC: cipher block chaining Each plaintext block is XOR with the previous ciphertext block before encryption. In this method, each ciphertext block depends on all plaintext blocks before it
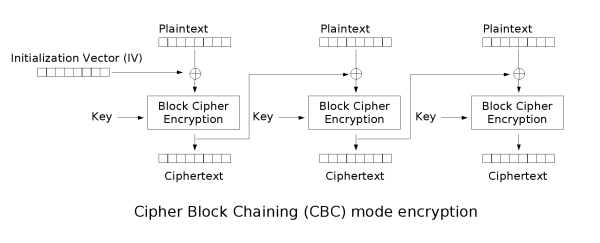
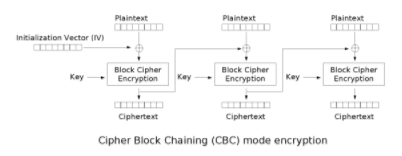
- Advantages: the ciphertext generated by the same original text is different
- Disadvantages: serial data processing
Fill mode
- When the length of data to be processed by block does not meet the requirements of block processing, fill the rule of full block length according to a certain method
NoPadding
- No filling
- Under DES encryption algorithm, the length of the original text must be an integer multiple of 8byte
- Under AES encryption algorithm, the length of the original text must be an integer multiple of 16byte
PKCS5Padding
The size of the data block is 8 bits. If it is not enough, it will be supplemented
Tips
- By default, the encryption mode and filling mode are ECB/PKCS5Padding
- If CBC mode is used, parameters need to be added when initializing the Cipher object. Initialization vector IV: ivparameterspec IV = new ivparameterspec (key. Getbytes());
Encryption mode and fill mode
AES/CBC/NoPadding (128) AES/CBC/PKCS5Padding (128) AES/ECB/NoPadding (128) AES/ECB/PKCS5Padding (128) DES/CBC/NoPadding (56) DES/CBC/PKCS5Padding (56) DES/ECB/NoPadding (56) DES/ECB/PKCS5Padding (56) DESede/CBC/NoPadding (168) DESede/CBC/PKCS5Padding (168) DESede/ECB/NoPadding (168) DESede/ECB/PKCS5Padding (168) RSA/ECB/PKCS1Padding (1024, 2048) RSA/ECB/OAEPWithSHA-1AndMGF1Padding (1024, 2048) RSA/ECB/OAEPWithSHA-256AndMGF1Padding (1024, 2048)
Encryption mode and fill mode examples
import com.sun.org.apache.xml.internal.security.utils.Base64;
import javax.crypto.Cipher;
import javax.crypto.spec.IvParameterSpec;
import javax.crypto.spec.SecretKeySpec;
public class DesDemo {
// DES encryption algorithm, the size of the key must be 8 bytes
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
String input ="silicon valley";
// DES encryption algorithm, the size of the key must be 8 bytes
String key = "12345678";
// Specify the algorithm for obtaining Cipher. If encryption mode and padding mode are not specified, ECB/PKCS5Padding is the default value
// String transformation = "DES"; // 9PQXVUIhaaQ=
//String transformation = "DES/ECB/PKCS5Padding"; // 9PQXVUIhaaQ=
// In CBC mode, the initial vector must be specified, and the length of the key in the initial vector must be 8 bytes
//String transformation = "DES/CBC/PKCS5Padding"; // 9PQXVUIhaaQ=
// In NoPadding mode, the length of the original text must be an integral multiple of 8 bytes, so Silicon Valley must be changed to Silicon Valley 12
String transformation = "DES/CBC/NoPadding"; // 9PQXVUIhaaQ=
// Specifies the algorithm for obtaining the key
String algorithm = "DES";
String encryptDES = encryptDES(input, key, transformation, algorithm);
System.out.println("encryption:" + encryptDES);
// String s = dncryptDES(encryptDES, key, transformation, algorithm);
// System.out.println("decryption:" + s);
}
/**
* Encrypt data using DES
*
* @param input : original text
* @param key : Key (DES, the length of the key must be 8 bytes)
* @param transformation : Algorithm to get Cipher object
* @param algorithm : Algorithm for obtaining key
* @return : ciphertext
* @throws Exception
*/
private static String encryptDES(String input, String key, String transformation, String algorithm) throws Exception {
// Get encrypted object
Cipher cipher = Cipher.getInstance(transformation);
// Create encryption rule
// Byte of the first parameter key
// The second parameter represents the encryption algorithm
SecretKeySpec sks = new SecretKeySpec(key.getBytes(), algorithm);
// ENCRYPT_MODE: encryption mode
// DECRYPT_MODE: decryption mode
// Initial vector. The parameter indicates who to XOR with. The length of the initial vector must be 8 bits
// IvParameterSpec iv = new IvParameterSpec(key.getBytes());
// Initialize encryption mode and algorithm
cipher.init(Cipher.ENCRYPT_MODE,sks);
// encryption
byte[] bytes = cipher.doFinal(input.getBytes());
// Output encrypted data
String encode = Base64.encode(bytes);
return encode;
}
/**
* Decryption using DES
*
* @param input : ciphertext
* @param key : secret key
* @param transformation : Algorithm to get Cipher object
* @param algorithm : Algorithm for obtaining key
* @throws Exception
* @return: original text
*/
private static String dncryptDES(String input, String key, String transformation, String algorithm) throws Exception {
// 1. Get Cipher object
Cipher cipher = Cipher.getInstance(transformation);
// Specify key rule
SecretKeySpec sks = new SecretKeySpec(key.getBytes(), algorithm);
// IvParameterSpec iv = new IvParameterSpec(key.getBytes());
cipher.init(Cipher.DECRYPT_MODE, sks);
// 3. Decryption
byte[] bytes = cipher.doFinal(Base64.decode(input));
return new String(bytes);
}
}
Running program:
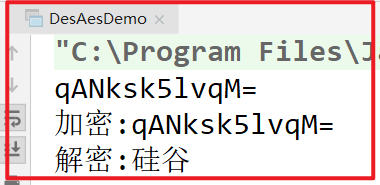
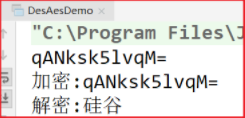
Change to # CBC # encryption mode
String transformation = "DES/CBC/PKCS5Padding";
An error is reported during operation. A parameter needs to be added
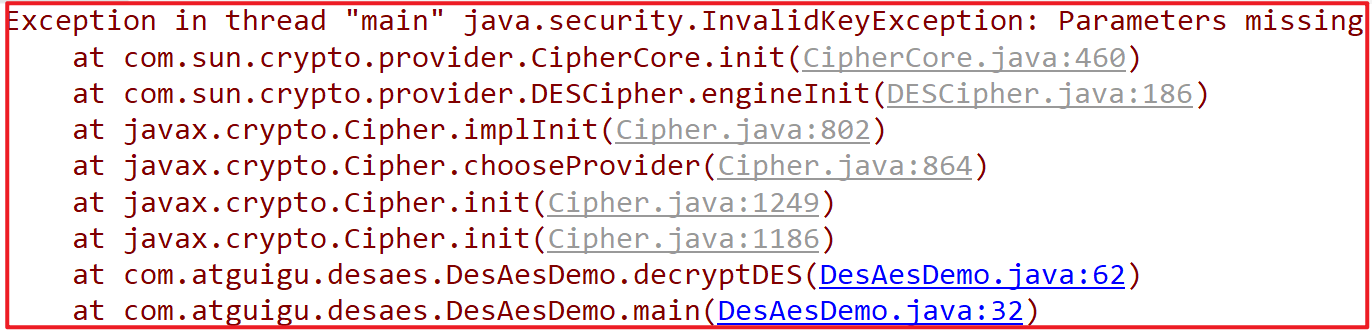
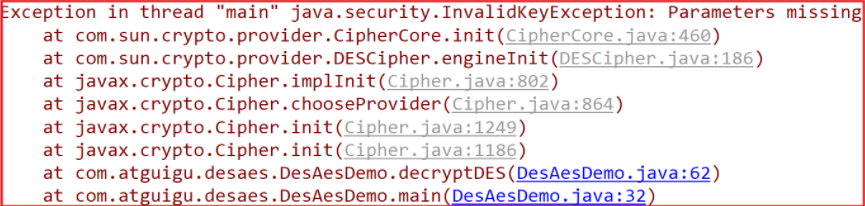
Modify encryption code:
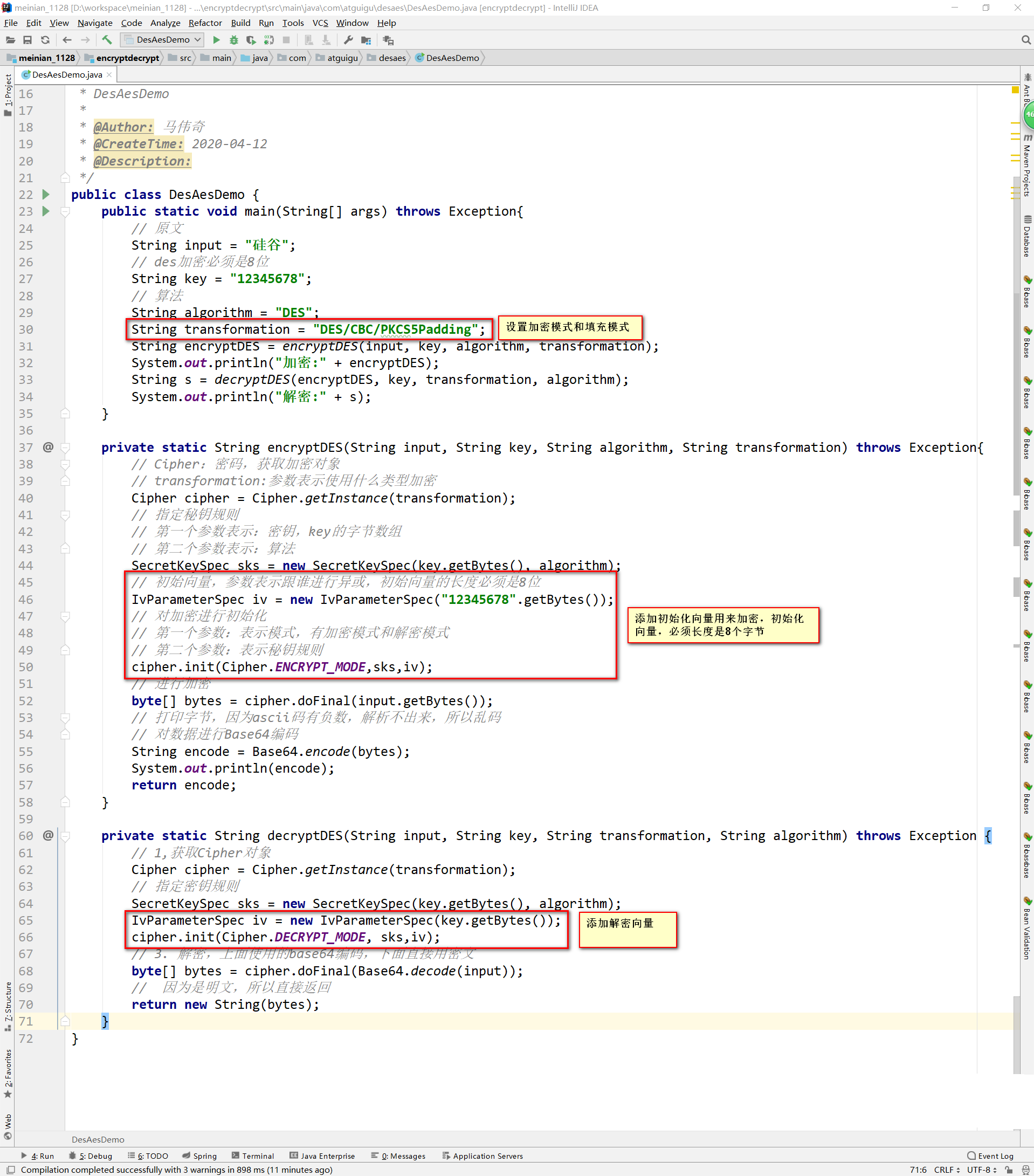
Run program


Modify fill mode
String transformation = "DES/CBC/NoPadding";
The operation reports an error. The original text of this filling mode must be an integer multiple of 8 bytes
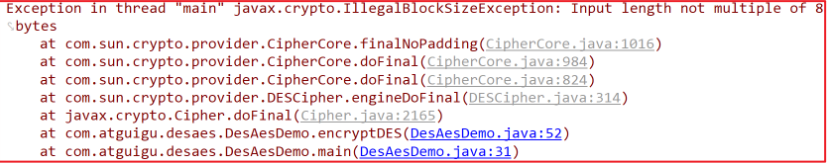
Modify run
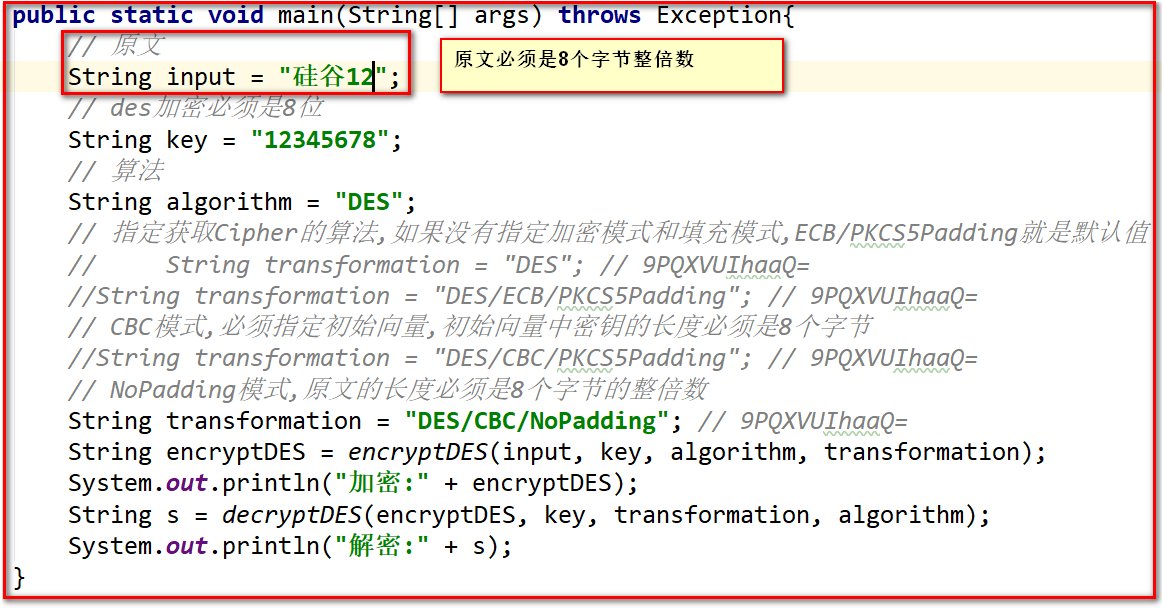
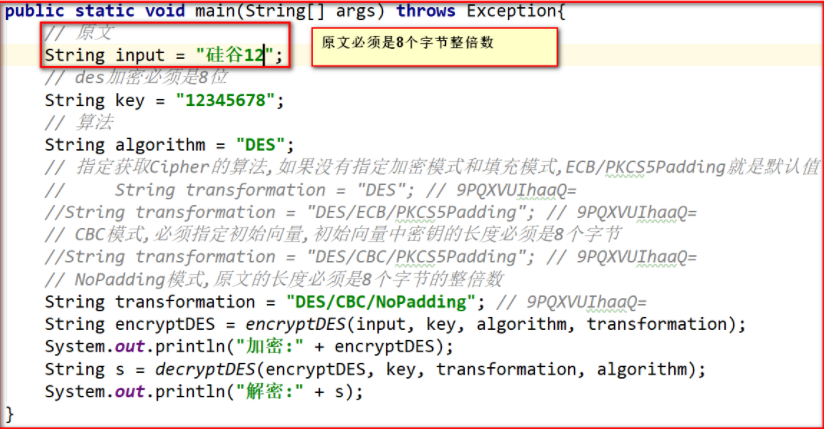
When testing # AES # it should be noted that the key needs 16 bytes and the encryption vector also needs 16 bytes. Other methods are the same as # DES #
Message summary
- Message Digest is also called digital digest
- It is a fixed length value that uniquely corresponds to a message or text. It is generated by a one-way Hash encryption function acting on the message
- The value generated by digital digest cannot be tampered with in order to ensure the security of files or values
characteristic
No matter how long the input message is, the length of the calculated message summary is always fixed. For example, the message abstracted by MD5 algorithm has 128 bits, and the message abstracted by SHA-1 algorithm finally has 160 bits of output
As long as the input messages are different, the summary messages generated after summarizing them must also be different; But the same input must produce the same output
Message digest is unidirectional and irreversible
Common algorithms:
- MD5 - SHA1 - SHA256 - SHA512
Baidu searches tomcat and downloads it on the official website. You will often find sha1 and sha512, which are digital summaries
Digital summary
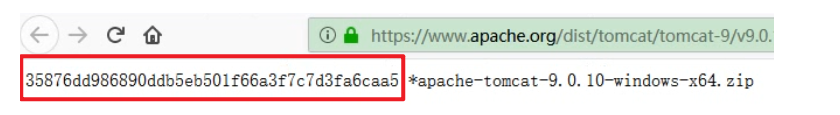
Get string message summary
import javax.sound.midi.Soundbank;
import java.security.MessageDigest;
public class DigestDemo1 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception{
// original text
String input = "aa";
// algorithm
String algorithm = "MD5";
// Get digital summary object
MessageDigest messageDigest = MessageDigest.getInstance(algorithm);
// Gets the byte array of the message digital digest
byte[] digest = messageDigest.digest(input.getBytes());
System.out.println(new String(digest));
}
}
function

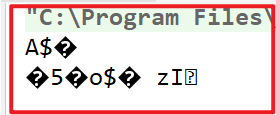
base64 encoding
import com.sun.org.apache.xml.internal.security.utils.Base64;
import javax.sound.midi.Soundbank;
import java.security.MessageDigest;
public class DigestDemo1 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception{
// original text
String input = "aa";
// algorithm
String algorithm = "MD5";
// Get digital summary object
MessageDigest messageDigest = MessageDigest.getInstance(algorithm);
// Message digital summary
byte[] digest = messageDigest.digest(input.getBytes());
// System.out.println(new String(digest));
// base64 encoding
System.out.println(Base64.encode(digest));
}
}
function
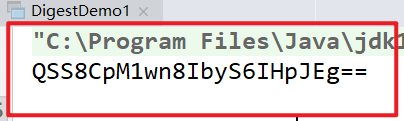
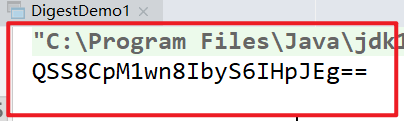
Using online md5 encryption, we found that the value we generated is different from the value generated by the code. That is because the message digest is not encoded by base64, so we need to convert the value to hexadecimal
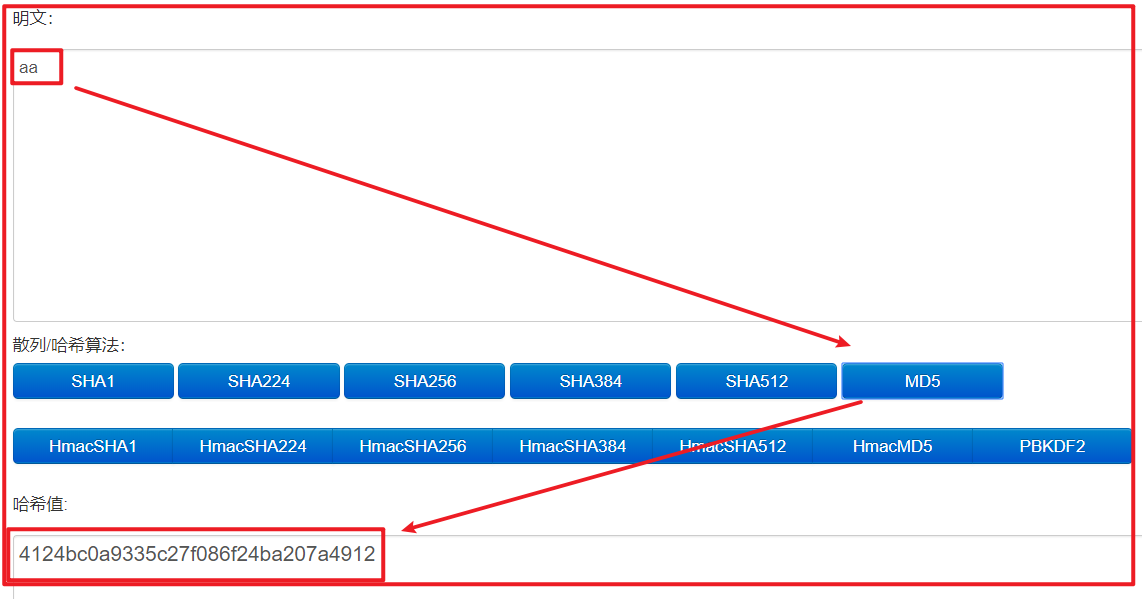
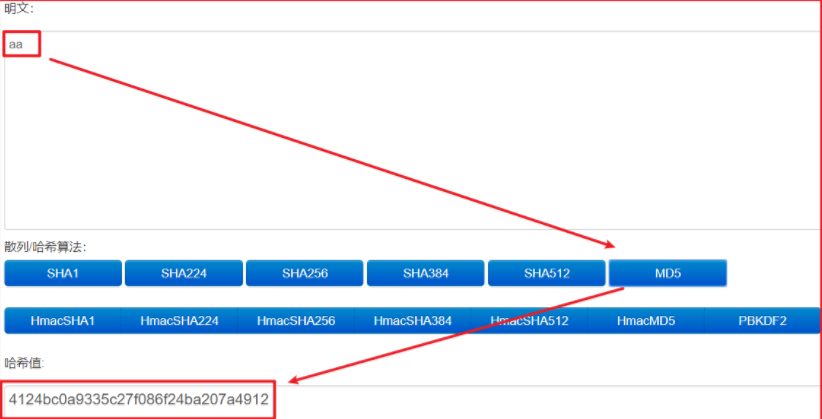
Convert numeric summary to hexadecimal
// 4124bc0a9335c27f086f24ba207a4912 MD5 online verification // QSS8CpM1wn8IbyS6IHpJEg = = the message digest uses hexadecimal
Convert code to hexadecimal
import com.sun.org.apache.xml.internal.security.utils.Base64;
import javax.sound.midi.Soundbank;
import java.security.MessageDigest;
public class DigestDemo1 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception{
// 4124bc0a9335c27f086f24ba207a4912 MD5 online verification
// QSS8CpM1wn8IbyS6IHpJEg = = the message digest uses hexadecimal
// original text
String input = "aa";
// algorithm
String algorithm = "MD5";
// Get digital summary object
MessageDigest messageDigest = MessageDigest.getInstance(algorithm);
// Message digital summary
byte[] digest = messageDigest.digest(input.getBytes());
// System.out.println(new String(digest));
// base64 encoding
// System.out.println(Base64.encode(digest));
// Create objects to splice
StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder();
for (byte b : digest) {
// Convert to hexadecimal
String s = Integer.toHexString(b & 0xff);
//System.out.println(s);
if (s.length() == 1){
// If there is only one character generated, fill 0 in front of it
s = "0"+s;
}
sb.append(s);
}
System.out.println(sb.toString());
}
}
function
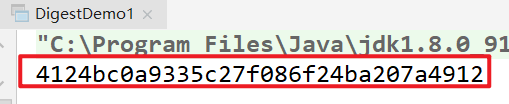
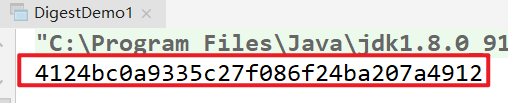
Other digital summarization algorithms
import com.sun.org.apache.xml.internal.security.utils.Base64;
import javax.sound.midi.Soundbank;
import java.security.MessageDigest;
import java.security.NoSuchAlgorithmException;
public class DigestDemo1 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception{
// 4124bc0a9335c27f086f24ba207a4912 MD5 online verification
// QSS8CpM1wn8IbyS6IHpJEg = = the message digest uses hexadecimal
// original text
String input = "aa";
// algorithm
String algorithm = "MD5";
// Get digital summary object
String md5 = getDigest(input, "MD5");
System.out.println(md5);
String sha1 = getDigest(input, "SHA-1");
System.out.println(sha1);
String sha256 = getDigest(input, "SHA-256");
System.out.println(sha256);
String sha512 = getDigest(input, "SHA-512");
System.out.println(sha512);
}
private static String toHex(byte[] digest) throws Exception {
// System.out.println(new String(digest));
// base64 encoding
// System.out.println(Base64.encode(digest));
// Create objects to splice
StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder();
for (byte b : digest) {
// Convert to hexadecimal
String s = Integer.toHexString(b & 0xff);
if (s.length() == 1){
// If there is only one character generated, fill 0 in front of it
s = "0"+s;
}
sb.append(s);
}
System.out.println("16 Length of hexadecimal data:" + sb.toString().getBytes().length);
return sb.toString();
}
private static String getDigest(String input, String algorithm) throws Exception {
MessageDigest messageDigest = MessageDigest.getInstance(algorithm);
// Message digital summary
byte[] digest = messageDigest.digest(input.getBytes());
System.out.println("Byte length of ciphertext:" + digest.length);
return toHex(digest);
}
}
function

Get file message summary
import com.sun.org.apache.xml.internal.security.utils.Base64;
import com.sun.scenario.effect.impl.sw.sse.SSEBlend_SRC_OUTPeer;
import sun.misc.BASE64Decoder;
import java.io.ByteArrayOutputStream;
import java.io.FileInputStream;
import java.security.MessageDigest;
public class DigestDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception{
String input = "aa";
String algorithm = "MD5";
// sha1 can realize the second transmission function
String sha1 = getDigestFile("apache-tomcat-9.0.10-windows-x64.zip", "SHA-1");
System.out.println(sha1);
String sha512 = getDigestFile("apache-tomcat-9.0.10-windows-x64.zip", "SHA-512");
System.out.println(sha512);
String md5 = getDigest("aa", "MD5");
System.out.println(md5);
String md51 = getDigest("aa ", "MD5");
System.out.println(md51);
}
private static String getDigestFile(String filePath, String algorithm) throws Exception{
FileInputStream fis = new FileInputStream(filePath);
int len;
byte[] buffer = new byte[1024];
ByteArrayOutputStream baos = new ByteArrayOutputStream();
while ( (len = fis.read(buffer))!=-1){
baos.write(buffer,0,len);
}
// Get message summary object
MessageDigest messageDigest = MessageDigest.getInstance(algorithm);
// Get message summary
byte[] digest = messageDigest.digest(baos.toByteArray());
System.out.println("Byte length of ciphertext:"+digest.length);
return toHex(digest);
}
private static String getDigest(String input, String algorithm) throws Exception{
MessageDigest messageDigest = MessageDigest.getInstance(algorithm);
byte[] digest = messageDigest.digest(input.getBytes());
System.out.println("Byte length of ciphertext:"+digest.length);
return toHex(digest);
}
private static String toHex(byte[] digest) {
// System.out.println(new String(digest));
// The message digest is represented in hexadecimal
StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder();
for (byte b : digest) {
// Convert to hexadecimal
String s = Integer.toHexString(b & 0xff);
// Maintain the integrity of the data. If the previous data is not enough, fill it with 0
if (s.length()==1){
s="0"+s;
}
sb.append(s);
}
System.out.println("16 Length of hexadecimal data:"+ sb.toString().getBytes().length);
return sb.toString();
}
}
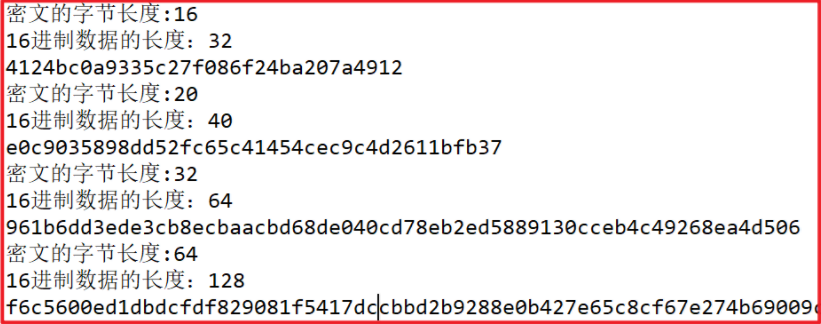
Run the program to obtain the values of , sha-1 , and , sha-512 ,
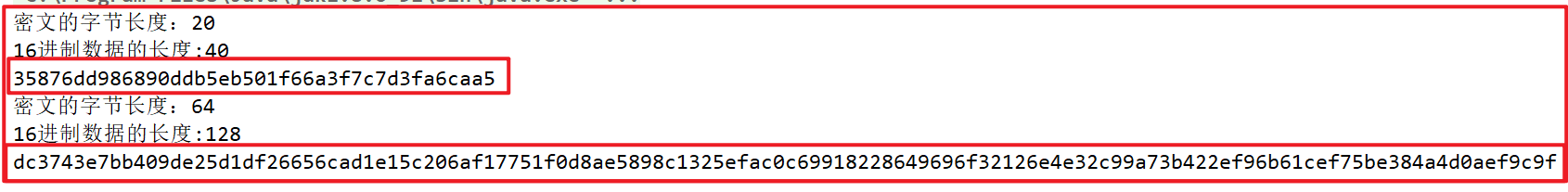
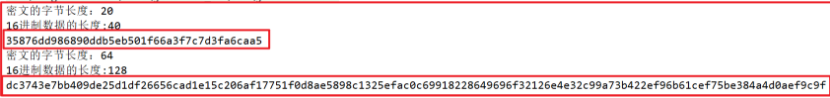
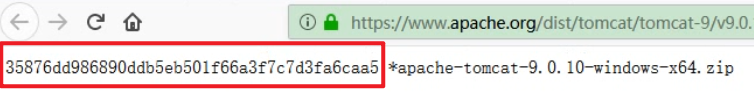
View the values of {sha-1} and {sha-512} on the tomcat official website
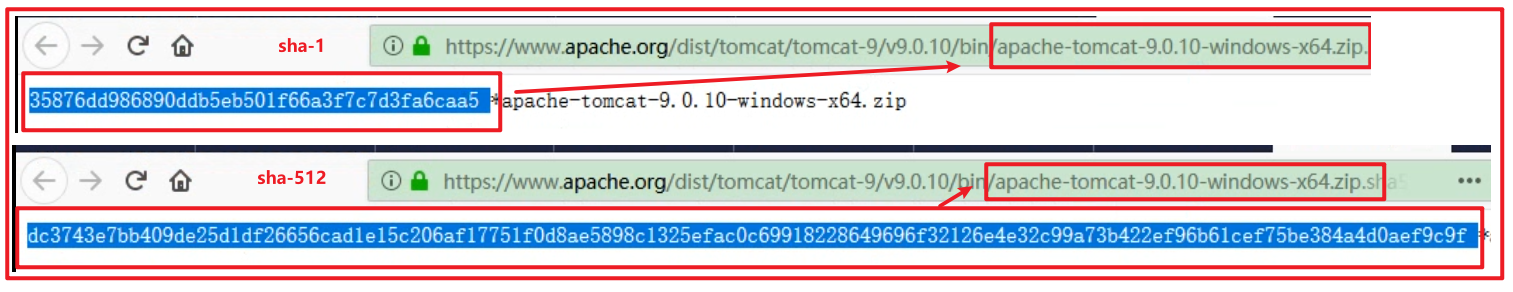
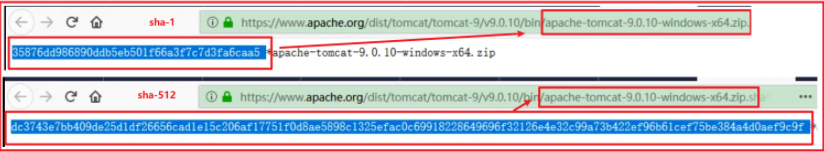
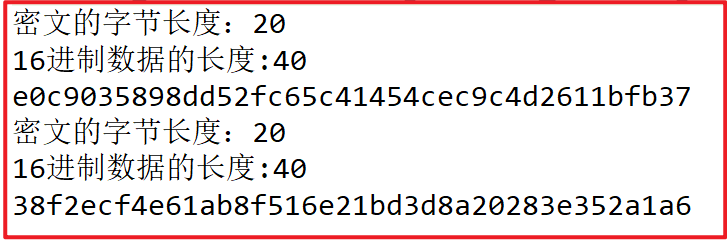
Using sha-1 algorithm, the second transmission function can be realized. No matter how we modify the file name, the final value is the same
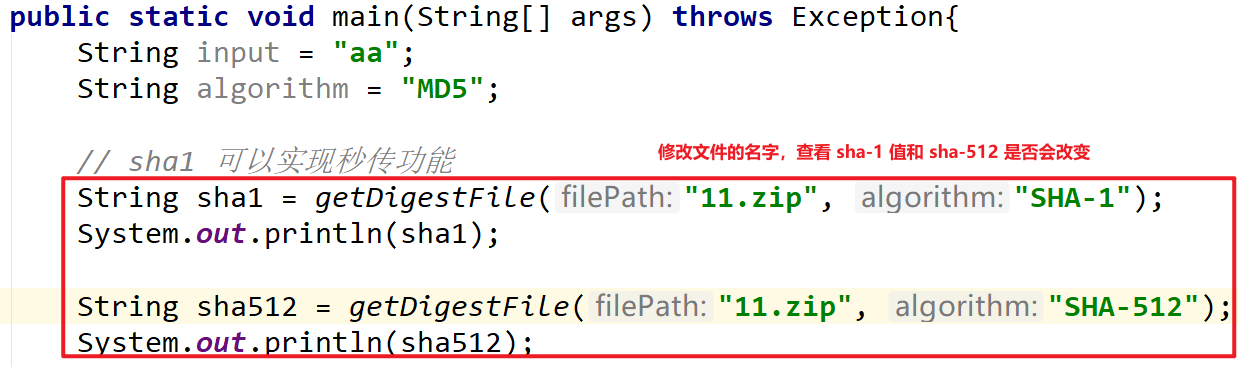
Run the program to obtain the values of , sha-1 , and , sha-512 ,
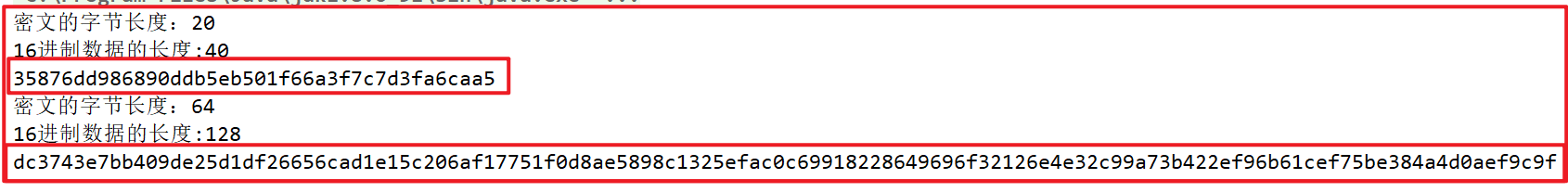
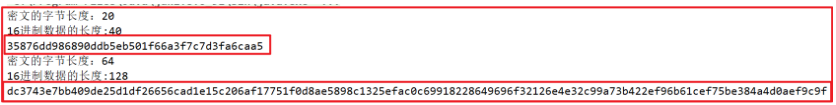
If the original text is modified, the sha-1 value will be different
Operation results:
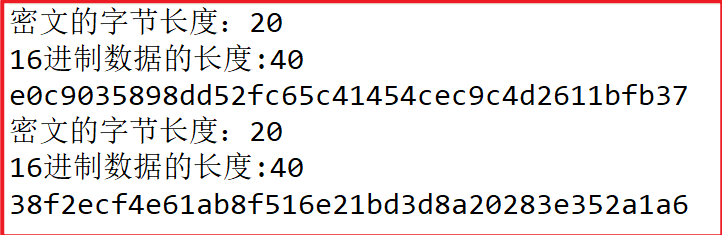
summary
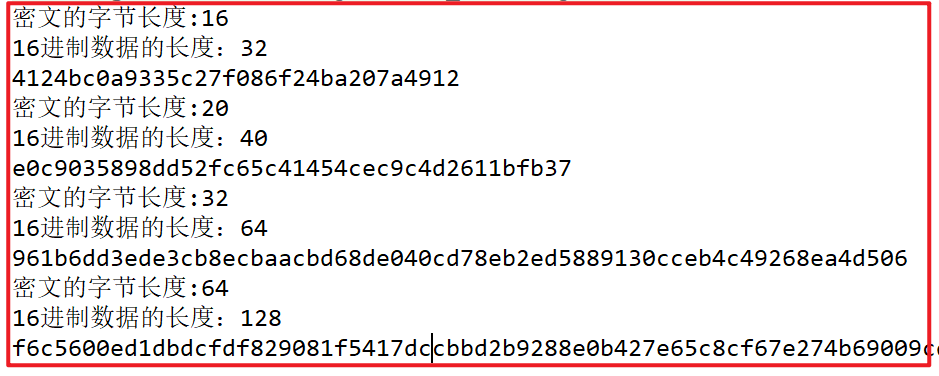
- MD5 algorithm: the summary result is 16 bytes and 32 bytes after hexadecimal conversion
- SHA1 algorithm: 20 bytes of summary results, 40 bytes after hexadecimal conversion
- SHA256 algorithm: the summary result is 32 bytes and 64 bytes after hexadecimal conversion
- SHA512 algorithm: the summary result is 64 bytes, 128 bytes after hexadecimal conversion