Effective Hybrid Genetic Algorithm (EHGA)

STEP 1: input image
Read image
X
(
i
,
j
)
X(i,j)
X(i,j), where
i
,
j
∈
[
0
,
255
]
i,j\in[0,255]
i,j∈[0,255]
STEP 2: initialize initial population
Through the image
X
(
i
,
j
)
X(i,j)
X(i,j) execute DAMF, AWMF and FNAFSM to obtain the initial population composed of three individuals:
D
=
{
X
D
A
M
F
,
X
A
W
M
F
,
X
N
A
F
S
M
}
D=\{X_{DAMF},X_{AWMF},X_{NAFSM}\}
D={XDAMF,XAWMF,XNAFSM}. Then, from the collection
D
D
D randomly select two individuals and use pixel merging for the two individuals: apply pixel by pixel random selection between the two selected individuals to obtain a new individual and add it to the population until the number of populations reaches
N
p
N_p
Np
STEP 3: evaluation image
Fitness value
fitness
(
F
)
=
λ
∣
F
−
X
∣
+
(
∑
Ω
1
+
β
2
∣
∇
F
∣
2
)
\text { fitness }(F)=\lambda|F-X|+\left(\sum_{\Omega} \sqrt{1+\beta^{2}|\nabla F|^{2}}\right)
fitness (F)=λ∣F−X∣+(Ω∑1+β2∣∇F∣2
)
Ω
\Omega
Ω: a collection of all pixels of an image.
F
F
F: Evaluated image
X
X
10: Noise diagram
∇
F
\nabla F
≓ F: total variation loss, the difference between adjacent pixels. The smaller the value, the smoother the image
∇
F
i
j
=
∣
F
i
+
1
,
j
−
F
i
,
j
∣
+
∣
F
i
,
j
+
1
−
F
i
,
j
∣
\nabla F_{ij}=\left|F_{i+1, j}-F_{i, j}\right|+\left|F_{i, j+1}-F_{i, j}\right|
∇Fij=∣Fi+1,j−Fi,j∣+∣Fi,j+1−Fi,j∣
β
,
λ
\beta,\lambda
β,λ: Trade off factor
∣ F − X ∣ |F-X| ∣ F − X ∣: approximation term to ensure a certain fidelity between the original image and the evaluated image
The purpose of the adaptation function is to smooth the noise while maintaining the fidelity term with the original image.
STEP 4: new individual
The roulette algorithm is used to select a pair of initial individuals (parents).
Crossover: randomly select one of the four crossover operations.
(i) Single point
Choose one of the following two actions at random:
- One point column: randomly select a column. On both sides of the column are the pixels corresponding to two parent s.

- One point row: similar to One point column.

(ii) Two point
Choose one of the following two actions at random:
- Two point column: randomly select two columns, and the pixels between and outside the columns are filled with the pixels of two individuals of the parent.

- Two point row: similar to Two point column.

(iii) Cross grid
Randomly select a row and a column, divide the image into four blocks, and fill the two diagonal parts with the pixels corresponding to the two individuals of the parent.

(iv) Pixel-by-pixel random
Pixels are randomly selected from two individuals of the parent pixel by pixel.
Variation: for each new individual
N
m
N_m
Nm, and one of the four mutation operations is randomly applied.
(i) NAFSM.
(ii) DAMF.
(iii) AWMF
(iv) Random: keep
X
(
i
,
j
)
X(i,j)
On the premise that the non noise points of X(i,j) are unchanged, multiply a random number of [0.8,1.2] per pixel.
Until the number of individuals in the new population reaches N c ⋅ N p N_c\cdot N_p Nc⋅Np.
STEP 5: evaluate new populations
Calculate the fitness of the new population
STEP 6:
The population (initial population and new species population) is sorted according to the fitness value
N
p
N_p
Np # is the best individual, and they are taken as the initial population of the next iteration.
STEP7: end
Repeat steps 4 through 6
i
t
e
r
m
a
x
iter_{max}
itermax # times, the best individual in the last generation is the result of denoising
# -*- coding:utf-8 -*-
'''
@paper:Effective hybrid genetic algorithm for removing salt and pepper noise
'''
import numpy as np
from awmf import Awmf
from damf import Damf
from nafsmf import Nafsmf
# Effective hybrid genetic algorithm
class Ehga(object):
def __init__(self, pop_num, crossover_num, mutation_rate, lambda_, beta, iter_max):
self.dam_filter = Damf()
self.awm_filter = Awmf(h=1, w_max=39)
self.nafsm_filter = Nafsmf(h=1, s_max=3, T1=10, T2=30)
self.pop_num = pop_num
self.iter_max = iter_max
self.crossover_num = crossover_num
self.mutation_rate = mutation_rate
self.m = None # Gray image size (m,n)
self.n = None
self.lambda_ = lambda_ # balancing parameters of fidelity term
self.beta = beta # balancing parameters of total variation regularising term
def init_population(self, img_noise):
X_damf = self.dam_filter.process_image(img_noise)
X_awmf = self.awm_filter.process_image(img_noise)
X_nafsm = self.nafsm_filter.process_image(img_noise)
init_pop = np.zeros((self.pop_num, self.m, self.n))
init_three = np.stack((X_damf, X_awmf, X_nafsm))
init_pop[0:3] = init_three.copy()
for n in range(3, self.pop_num):
index = np.random.choice(3, 2, replace=False)
X_pair = init_three[index]
new_individual = np.zeros((self.m, self.n))
for i in range(self.m):
for j in range(self.n):
new_individual[i, j] = X_pair[np.random.randint(2)][i, j]
init_pop[n] = new_individual
return init_pop
def cal_fit_value(self, X, F):
'''
:param X: Noise image
:param F: Filtered image
:return: Fitness value
'''
fitness = []
for F_i in F:
fidelity_term = self.lambda_ * np.sum(np.abs(F_i - X))
regularising_term = 0
for i in range(self.m - 1):
for j in range(self.n - 1):
nabla_F = np.abs(F_i[i + 1, j] - F_i[i, j]) + np.abs(F_i[i, j + 1] - F_i[i, j])
regularising_term += np.sqrt(1 + self.beta ** 2 * nabla_F ** 2)
fitness_i = fidelity_term + regularising_term
fitness.append(fitness_i)
return fitness
def selection(self, pop, fit_value):
'''Select the two individuals with the largest fitness value from the population'''
# So find the minimum value
fit_value = -np.array(fit_value)
# Calculate the sum of fitness values
total_fit = np.sum(fit_value)
# Make the sum of probabilities 1
p_fit_value = fit_value / total_fit
# Probabilistic summation sort
p_fit_value = np.cumsum(p_fit_value)
random_p = np.sort(np.random.random(2))
# roulette wheel selection
fit_index = 0
new_index = 0
parent = np.zeros((2, self.m, self.n))
while new_index < 2:
# If this probability is greater than the random one, choose this one
if p_fit_value[fit_index] > random_p[new_index]:
parent[new_index] = pop[fit_index]
new_index = new_index + 1
else:
fit_index = fit_index + 1
return parent
def crossover(self, parent):
'''
crossover_type:
0: One point column
1: One point row
2: Two point column
3: Two point row
4: Cross grid
5: Pixel-by-pixel random
'''
crossover_type = np.random.randint(6)
if crossover_type == 0:
n = np.random.randint(self.n)
new_individual = parent[0].copy()
new_individual[:, n:] = parent[1][:, n:]
elif crossover_type == 1:
m = np.random.randint(self.m)
new_individual = parent[0].copy()
new_individual[m:, :] = parent[1][m:, :]
elif crossover_type == 2:
n = np.sort(np.random.randint(0, self.n, 2))
new_individual = parent[0].copy()
new_individual[:, 0:n[0]] = parent[1][:, 0:n[0]]
new_individual[:, n[1]:] = parent[1][:, n[1]:]
elif crossover_type == 3:
m = np.sort(np.random.randint(0, self.m, 2))
new_individual = parent[0].copy()
new_individual[0:m[0], :] = parent[1][0:m[0], :]
new_individual[m[1]:, :] = parent[1][m[1]:, :]
elif crossover_type == 4:
n = np.random.randint(self.n)
m = np.random.randint(self.m)
new_individual = parent[0].copy()
new_individual[0:m, 0:n] = parent[1][0:m, 0:n]
new_individual[m:, n:] = parent[1][m:, n:]
else:
new_individual = np.zeros((self.m, self.n))
for i in range(self.m):
for j in range(self.n):
if np.random.random() <= 0.5:
new_individual[i, j] = parent[0][i, j]
else:
new_individual[i, j] = parent[1][i, j]
return new_individual
def mutation(self, new_individual, img_noise):
'''
mutation_type:
0: NAFSM
1: DAMF
2: AWMF
3: Random
'''
if np.random.random(1) < self.mutation_rate:
mutation_type = np.random.randint(4)
if mutation_type == 0:
new_individual = self.nafsm_filter.process_image(img_noise)
elif mutation_type == 1:
new_individual = self.dam_filter.process_image(img_noise)
elif mutation_type == 2:
new_individual = self.awm_filter.process_image(img_noise)
else:
tem = np.random.random(size=(self.m, self.n)) * 0.4 + 0.8
new_individual = new_individual * tem
mask = (img_noise != 0) | (img_noise != 255)
new_individual[mask] = img_noise[mask]
return new_individual
def process_image(self, img_noise):
self.m, self.n = np.shape(img_noise)
pop = self.init_population(img_noise)
for iter in range(self.iter_max):
print('iter:', iter)
fit_value = self.cal_fit_value(img_noise, pop)
pop_new = np.zeros((self.pop_num + self.crossover_num, self.m, self.n))
pop_new[:self.pop_num] = pop
for i in range(self.crossover_num):
print(i)
parent = self.selection(pop, fit_value)
new_individual = self.crossover(parent)
new_individual = self.mutation(new_individual, img_noise)
pop_new[self.pop_num + i] = new_individual
fit_value = self.cal_fit_value(img_noise, pop_new)
sort_fit_value = np.argsort(fit_value)
pop_new = pop_new[sort_fit_value[0:self.pop_num]]
return pop_new[0].astype(int)

| Noise level | Noise image | DAMF | NAFSM | AWMF | EHGA |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 90% |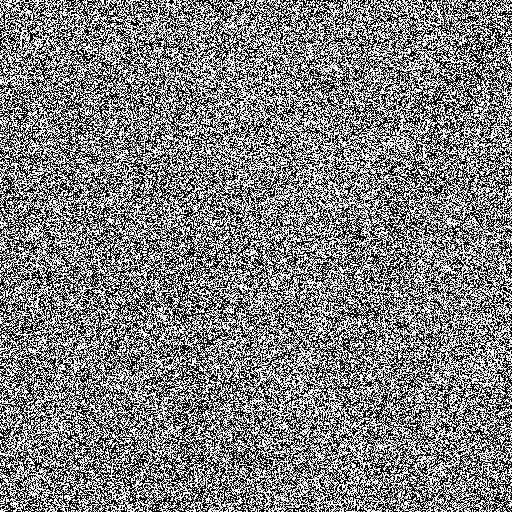  |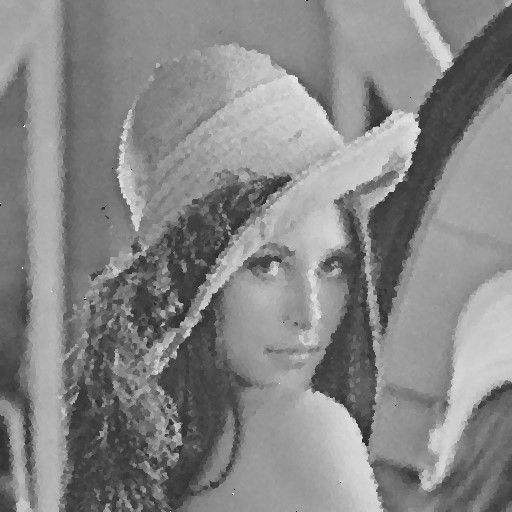  |  |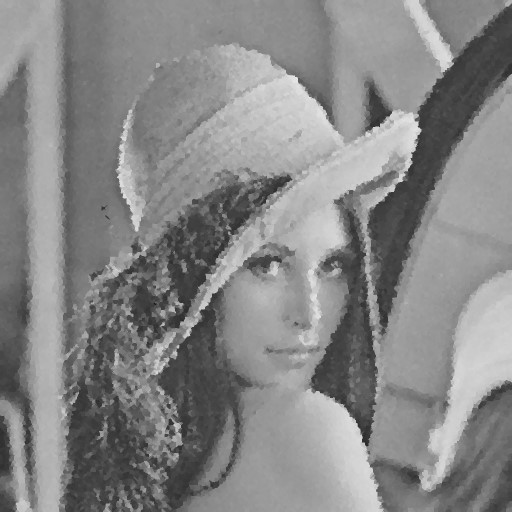  |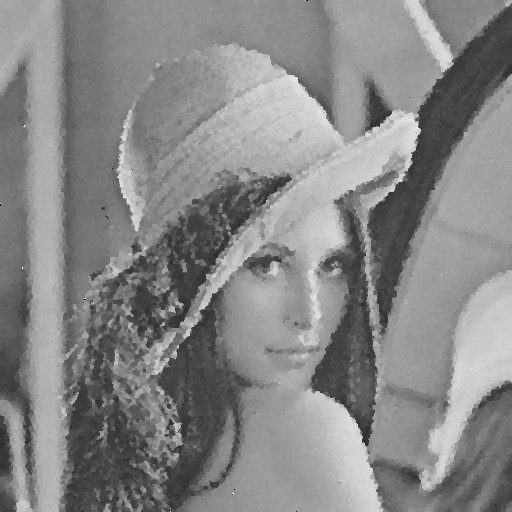  |
| 95% |  |  | 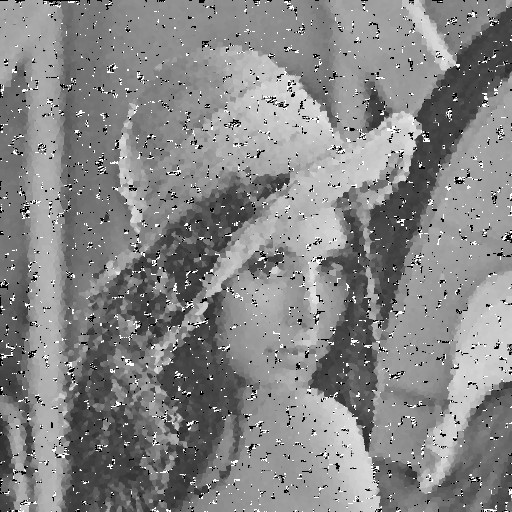 |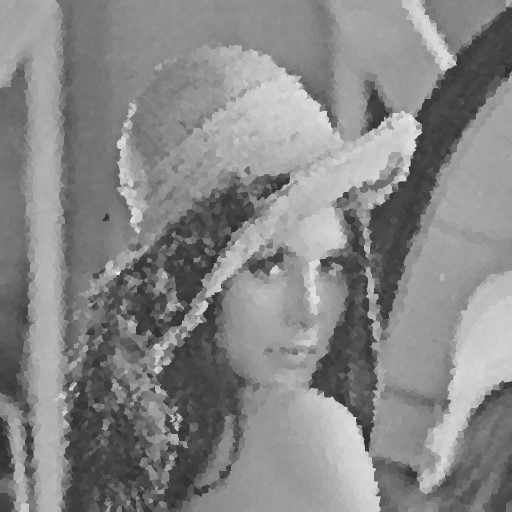  |  |
| 99% |  | 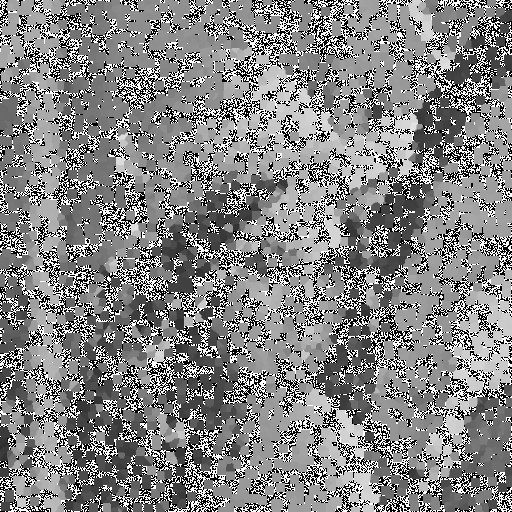 |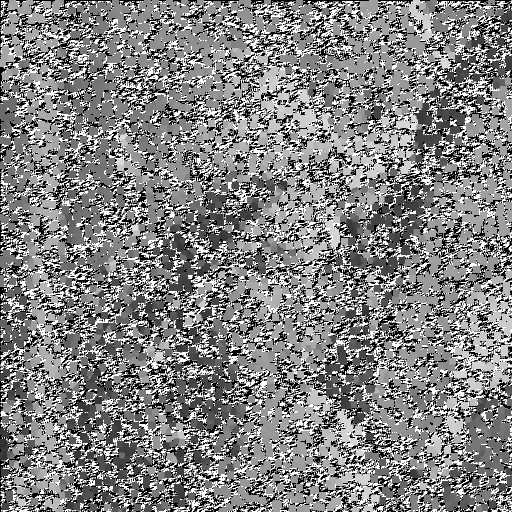  |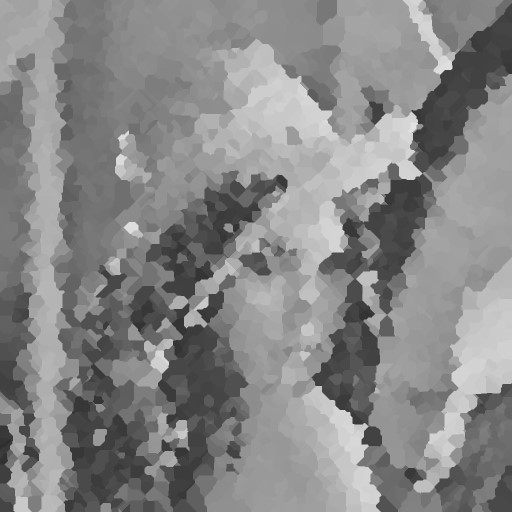  |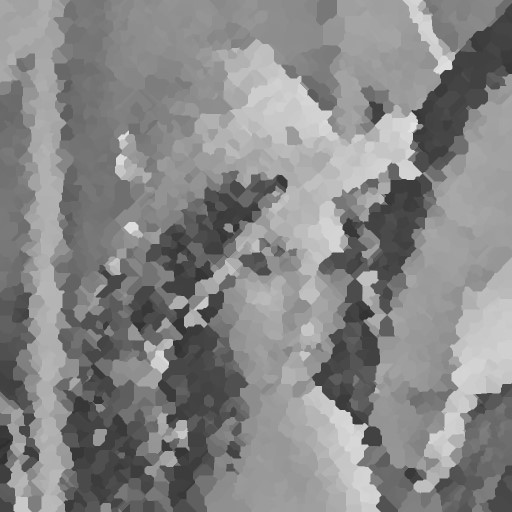  |