Today's goal:
1. One to many association configuration (database: master table, slave table, association through foreign keys)
2. Lazy loading
3. One to many autocorrelation
4. For many to many association, many to many cannot be directly mapped in the database (create a bridge table (intermediate table) and convert a many to many relationship into two one to many)
1, One to many association configuration
Example: Order and Order_item (multiple Order items corresponding to an Order, but one Order item has only one Order)
1.1, entity class Order
package com.whw.two.entity;
import java.util.HashSet;
import java.util.Set;
public class Order {
// create table t_hibernate_order
// (
// order_id int primary key auto_increment,
// order_no varchar(50) not null
// );
private Integer orderId;
private String orderNo;
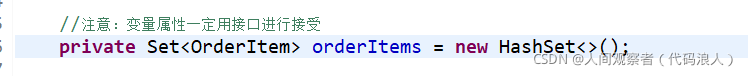
//Note: variable attributes must be accepted by the interface
private Set<OrderItem> orderItems = new HashSet<>();
private Integer initOrderItems = 0;//0 represents lazy loading and 1 represents forced loading
public Integer getInitOrderItems() {
return initOrderItems;
}
public void setInitOrderItems(Integer initOrderItems) {
this.initOrderItems = initOrderItems;
}
public Set<OrderItem> getOrderItems() {
return orderItems;
}
public void setOrderItems(Set<OrderItem> orderItems) {
this.orderItems = orderItems;
}
public Integer getOrderId() {
return orderId;
}
public void setOrderId(Integer orderId) {
this.orderId = orderId;
}
public String getOrderNo() {
return orderNo;
}
public void setOrderNo(String orderNo) {
this.orderNo = orderNo;
}
}
The order corresponds to multiple order items. The order items should be assembled
be careful:
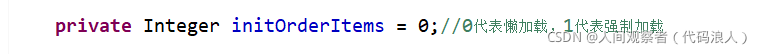
Order_item
package com.whw.two.entity;
public class OrderItem {
// create table t_hibernate_order_item
// (
// order_item_id int primary key auto_increment,
// product_id int not null,
// quantity int not null,
// oid int not null,
// foreign key(oid) references t_hibernate_order(order_id)
// );
private Integer orderItemId;
private Integer productId;
private Integer quantity;
private Integer oid;
private Order order;
public Order getOrder() {
return order;
}
public void setOrder(Order order) {
this.order = order;
}
public Integer getOrderItemId() {
return orderItemId;
}
public void setOrderItemId(Integer orderItemId) {
this.orderItemId = orderItemId;
}
public Integer getProductId() {
return productId;
}
public void setProductId(Integer productId) {
this.productId = productId;
}
public Integer getQuantity() {
return quantity;
}
public void setQuantity(Integer quantity) {
this.quantity = quantity;
}
public Integer getOid() {
return oid;
}
public void setOid(Integer oid) {
this.oid = oid;
}
}
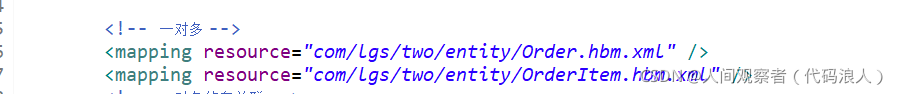
1.2. Configure the mapping file Order.hbm.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<!DOCTYPE hibernate-mapping PUBLIC
"-//Hibernate/Hibernate Mapping DTD 3.0//EN"
"http://www.hibernate.org/dtd/hibernate-mapping-3.0.dtd">
<hibernate-mapping>
<class name="com.lgs.two.entity.Order" table="t_hibernate_order">
<id name="orderId" type="java.lang.Integer" column="order_id">
<generator class="increment"></generator>
</id>
<property name="orderNo" type="java.lang.String" column="order_no"/>
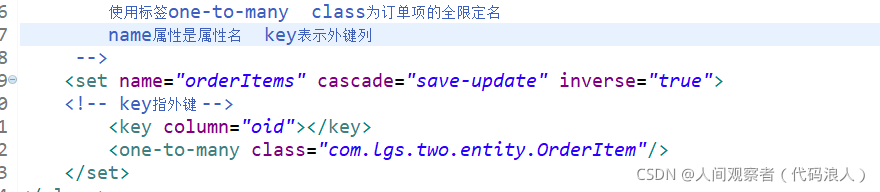
<!--
cascade:Cascade attribute configuration
inverse: Is the relationship maintained by the other party?
-->
<set name="orderItems" cascade="save-update" inverse="true">
<!-- key Finger foreign key -->
<key column="oid"></key>
<one-to-many class="com.lgs.two.entity.OrderItem"/>
</set>
</class>
</hibernate-mapping>
be careful:
OrderItem.hbm.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<!DOCTYPE hibernate-mapping PUBLIC
"-//Hibernate/Hibernate Mapping DTD 3.0//EN"
"http://www.hibernate.org/dtd/hibernate-mapping-3.0.dtd">
<hibernate-mapping>
<class name="com.lgs.two.entity.OrderItem" table="t_hibernate_order_item">
<id name="orderItemId" type="java.lang.Integer" column="order_item_id">
<generator class="increment"></generator>
</id>
<property name="productId" type="java.lang.Integer" column="product_id"/>
<property name="quantity" type="java.lang.Integer" column="quantity"/>
<property name="oid" type="java.lang.Integer" column="oid"/>
<!-- Repeated column in mapping for entity: com.zking.four.entity.OrderItem column: oid (should be mapped with insert="false" update="false") -->
<many-to-one name="order" class="com.lgs.two.entity.Order" insert="false" update="false" column="oid"></many-to-one>
</class>
</hibernate-mapping>
2, Lazy loading
2.1. Import tool class
package com.whw.two.util;
import org.hibernate.Session;
import org.hibernate.SessionFactory;
import org.hibernate.cfg.Configuration;
/**
* 1,Used to produce session
* 2,Used to test whether your hibernate configuration is correct
* @author Administrator
*
*/
public class SessionFactoryUtil {
static SessionFactory sessionFactory;
static {
Configuration configure = new Configuration().configure("hibernate.cfg.xml");
sessionFactory = configure.buildSessionFactory();
}
public static Session getSession() {
Session session = sessionFactory.getCurrentSession();
if(session == null) {
session = sessionFactory.openSession();
}
return session;
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
Session session = SessionFactoryUtil.getSession();
// Calling method 'isConnected' is not valid without an active transaction (Current status: NOT_ACTIVE)
session.beginTransaction();
System.out.println(session.isConnected());
session.close();
System.out.println(session.isConnected());
}
}
2.2. dao method (OrderDao, OrderItemDao)
package com.whw.two.dao;
import java.util.List;
import org.hibernate.Hibernate;
import org.hibernate.Session;
import org.hibernate.Transaction;
import com.whw.two.entity.Order;
import com.whw.two.entity.OrderItem;
import com.whw.two.util.SessionFactoryUtil;
public class OrderDao {
public Order get(Order order) {
Session session = SessionFactoryUtil.getSession();
Transaction transaction = session.beginTransaction();
Order o = session.get(Order.class, order.getOrderId());
// In addition, if you want to query the data of associated order items, you can use forced loading
if(o != null && new Integer(1).equals(order.getInitOrderItems())) {
// Force loading of order item data under order O management
Hibernate.initialize(o.getOrderItems());
}
transaction.commit();
session.close();
return o;
}
public List<Order> list() {
Session session = SessionFactoryUtil.getSession();
Transaction transaction = session.beginTransaction();
List<Order> list = session.createQuery("from Order").list();
for (Order o: list) {
Hibernate.initialize(o.getOrderItems());
}
transaction.commit();
session.close();
return list;
}
public void delete(Order order) {
Session session = SessionFactoryUtil.getSession();
Transaction transaction = session.beginTransaction();
Order o = session.get(Order.class, order.getOrderId());
for(OrderItem oi:o.getOrderItems()) {
session.delete(oi);
}
session.delete(o);
transaction.commit();
session.close();
}
}
package com.whw.two.dao;
import org.hibernate.Session;
import org.hibernate.Transaction;
import com.whw.two.entity.OrderItem;
import com.whw.two.util.SessionFactoryUtil;
public class OrderItemDao {
public OrderItem get(OrderItem orderItem) {
Session session = SessionFactoryUtil.getSession();
Transaction transaction = session.beginTransaction();
OrderItem oi = session.get(OrderItem.class, orderItem.getOrderItemId());
transaction.commit();
session.close();
return oi;
}
}
2.3. Test class (OrderDaoTest)
package com.whw.two.dao;
import java.util.List;
import org.junit.Test;
import com.whw.two.entity.Order;
public class OrderDaoTest {
private OrderDao orderDao = new OrderDao();
/**
* org.hibernate.LazyInitializationException: failed to lazily initialize a collection of role: com.zking.two.entity.Order.orderItems, could not initialize proxy - no Session
* 1.Normal query
* 2.Lazy load exception error
* 3.performance tuning
*/
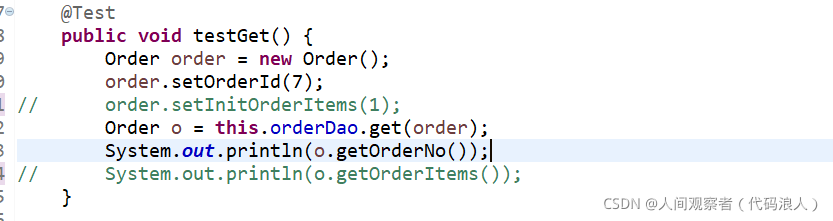
@Test
public void testGet() {
Order order = new Order();
order.setOrderId(7);
order.setInitOrderItems(1);
Order o = this.orderDao.get(order);
System.out.println(o.getOrderNo());
System.out.println(o.getOrderItems());
}
@Test
public void testList() {
List<Order> list = this.orderDao.list();
for (Order o : list) {
System.out.println(o.getOrderNo());
// System.out.println(o.getOrderItems().size());
}
}
@Test
public void testDelete() {
Order order = new Order();
order.setOrderId(6);
this.orderDao.delete(order);
}
}
When this state is running
Operation result: normal

When we need to get the order items together, unlock the notes

The output result is not obtained, and errors will occur
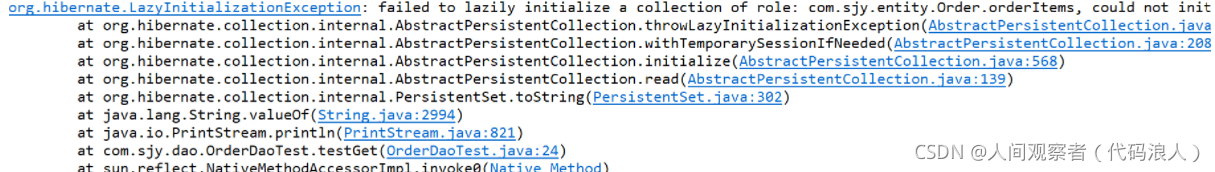
Problem: lazy loading is used by default. The session is closed when the above output is executed, so an error will be reported. This error requires forced loading, that is, forced loading of order item data associated with the order
Solution: Unlock the annotation and set it to one to force loading
Operation result: normal

Tip: this error occurs when you forget to configure the mapping
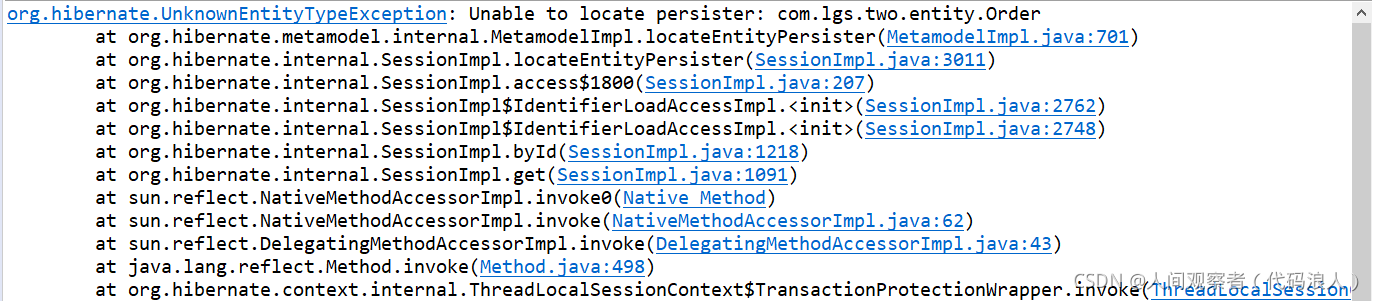
solve:
Run the query method:
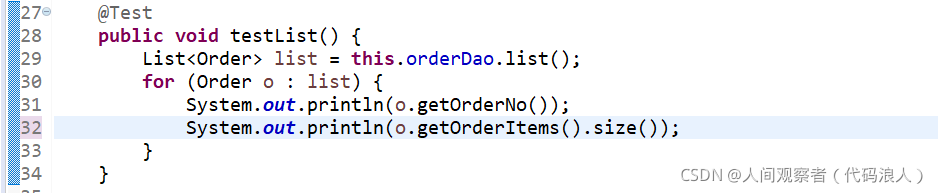
Operation results:
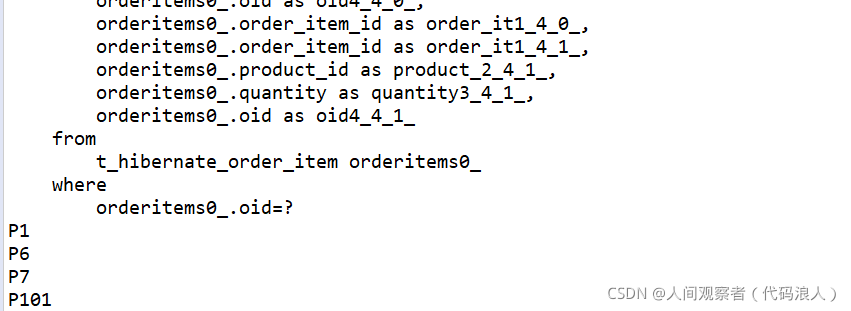
Generate a large number of SQL statements. If there is too much data, it will seriously slow down the performance
Performance optimization (when there is a lot of data)
If we only need to use the order table data, we will use lazy loading. If we need the data of two tables at the same time, we will not use lazy loading. It should be forced loading, that is, we will check what we want to use and not what we don't need
3, One to many autocorrelation
Analysis (simulation environment: tree menu):
One to many self association means that you can have multiple child nodes, but the parent node has only one and is in your own table
3.1 entity class
package com.whw.two.entity;
import java.util.HashSet;
import java.util.Set;
public class TreeNode {
private Integer nodeId;
private String nodeName;
private Integer treeNodeType;
private Integer position;
private String url;
private TreeNode parent;
private Set<TreeNode> children = new HashSet<TreeNode>();
private Integer initChildren = 0;
public Integer getNodeId() {
return nodeId;
}
public void setNodeId(Integer nodeId) {
this.nodeId = nodeId;
}
public String getNodeName() {
return nodeName;
}
public void setNodeName(String nodeName) {
this.nodeName = nodeName;
}
public Integer getTreeNodeType() {
return treeNodeType;
}
public void setTreeNodeType(Integer treeNodeType) {
this.treeNodeType = treeNodeType;
}
public Integer getPosition() {
return position;
}
public void setPosition(Integer position) {
this.position = position;
}
public String getUrl() {
return url;
}
public void setUrl(String url) {
this.url = url;
}
public TreeNode getParent() {
return parent;
}
public void setParent(TreeNode parent) {
this.parent = parent;
}
public Set<TreeNode> getChildren() {
return children;
}
public void setChildren(Set<TreeNode> children) {
this.children = children;
}
public Integer getInitChildren() {
return initChildren;
}
public void setInitChildren(Integer initChildren) {
this.initChildren = initChildren;
}
// @Override
// public String toString() {
// return "TreeNode [nodeId=" + nodeId + ", nodeName=" + nodeName + ", treeNodeType=" + treeNodeType
// + ", position=" + position + ", url=" + url + ", children=" + children + "]";
// }
@Override
public String toString() {
return "TreeNode [nodeId=" + nodeId + ", nodeName=" + nodeName + ", treeNodeType=" + treeNodeType
+ ", position=" + position + ", url=" + url + "]";
}
}
The first is the parent node (there is only one parent node)
The second is a child node (there may be multiple child nodes, so it is wrapped in a collection)
The third is lazy loading (0 is lazy loading and 1 is forced loading)

3.2, corresponding mapping relationship
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<!DOCTYPE hibernate-mapping PUBLIC
"-//Hibernate/Hibernate Mapping DTD 3.0//EN"
"http://www.hibernate.org/dtd/hibernate-mapping-3.0.dtd">
<hibernate-mapping>
<class name="com.lgs.two.entity.TreeNode" table="t_hibernate_sys_tree_node">
<id name="nodeId" type="java.lang.Integer" column="tree_node_id">
<generator class="increment" />
</id>
<property name="nodeName" type="java.lang.String"
column="tree_node_name">
</property>
<property name="treeNodeType" type="java.lang.Integer"
column="tree_node_type">
</property>
<property name="position" type="java.lang.Integer"
column="position">
</property>
<property name="url" type="java.lang.String"
column="url">
</property>
<many-to-one name="parent" class="com.lgs.two.entity.TreeNode" column="parent_node_id"/>
<set name="children" cascade="save-update" inverse="true">
<key column="parent_node_id"></key>
<one-to-many class="com.lgs.two.entity.TreeNode"/>
</set>
</class>
</hibernate-mapping>
3.3 method: TreeNodeDao
package com.whw.two.dao;
import org.hibernate.Hibernate;
import org.hibernate.Session;
import org.hibernate.Transaction;
import com.whw.two.entity.TreeNode;
import com.whw.two.util.SessionFactoryUtil;
public class TreeNodeDao {
public TreeNode load(TreeNode treeNode) {
Session session = SessionFactoryUtil.getSession();
Transaction transaction = session.beginTransaction();
TreeNode t = session.load(TreeNode.class, treeNode.getNodeId());
if(t != null && new Integer(1).equals(treeNode.getInitChildren())) {
Hibernate.initialize(t.getChildren());
Hibernate.initialize(t.getParent());
}
transaction.commit();
session.close();
return t;
}
}
3.4 test TreeNodeDaoTest
package com.whw.two.dao;
import org.junit.Test;
import com.whw.two.entity.TreeNode;
public class TreeNodeDaoTest {
private TreeNodeDao treeNodeDao = new TreeNodeDao();
@Test
public void testLoad() {
TreeNode treeNode = new TreeNode();
treeNode.setNodeId(6);
treeNode.setInitChildren(1);
TreeNode t = this.treeNodeDao.load(treeNode);
System.out.println(t);//Current node
System.out.println(t.getParent());//Parent node
System.out.println(t.getChildren());//Child of parent node
}
}
Operation result: successfully obtained
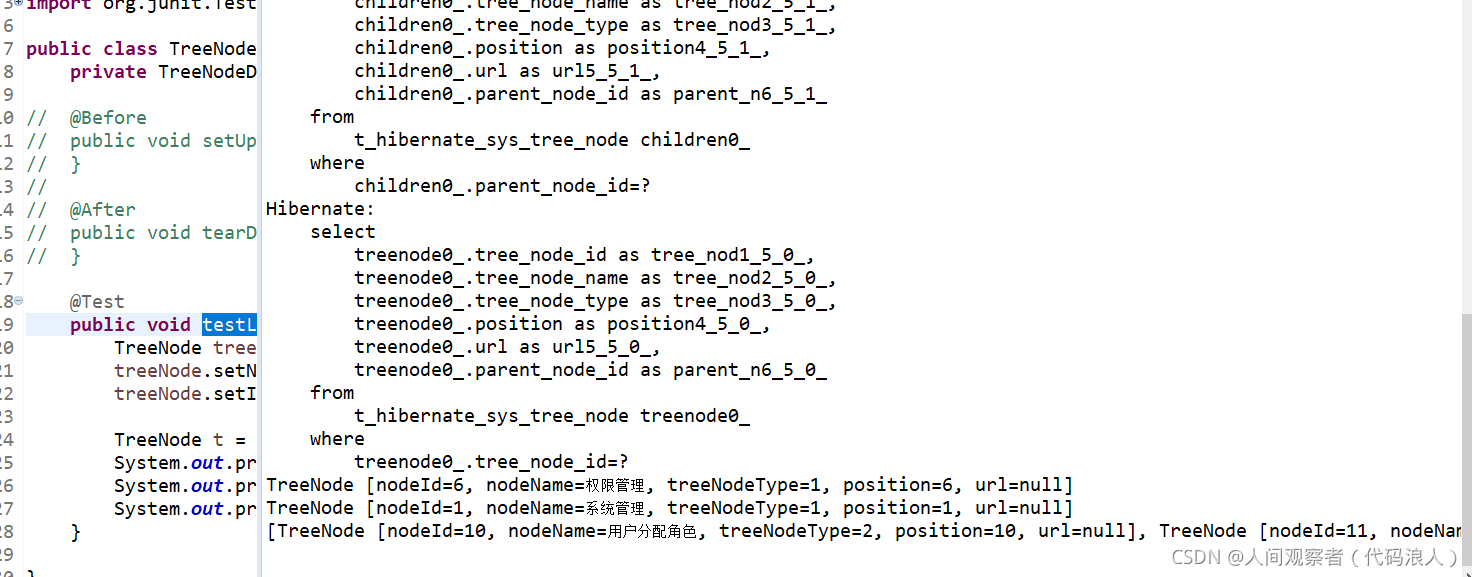
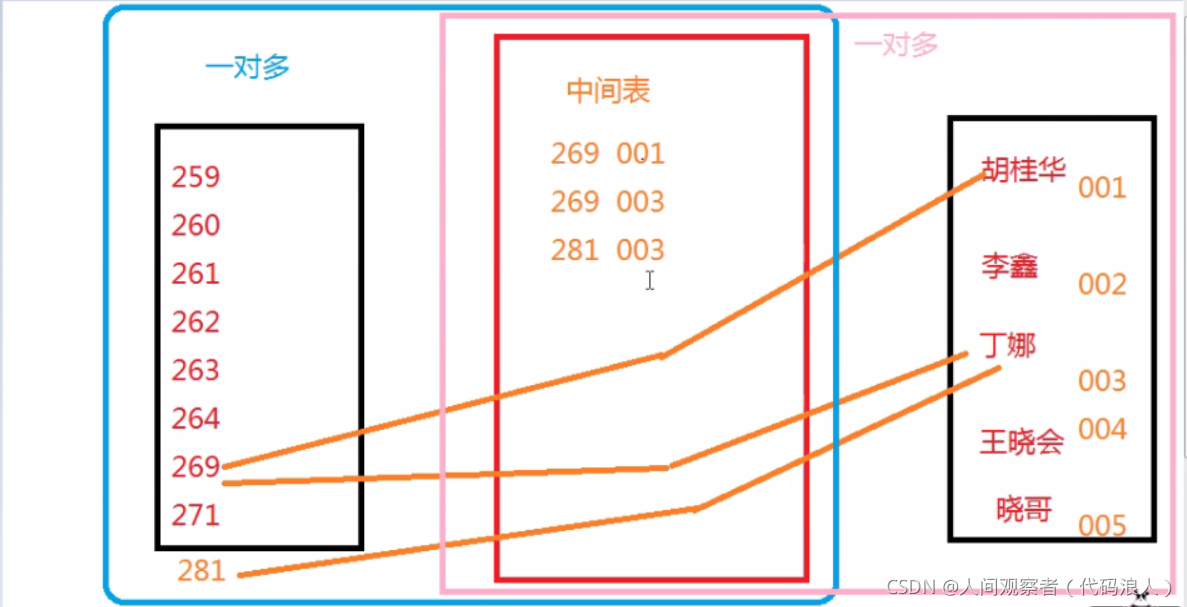
4, Many to many
It is equivalent to two many to one. There are foreign keys of two tables in the middle table. Both tables and the middle table are one to many
4.1 entity class
package com.whw.two.entity;
import java.io.Serializable;
import java.util.HashSet;
import java.util.Set;
public class Book implements Serializable{
// book_id int primary key auto_increment,
// book_name varchar(50) not null,
// price float not null
private Integer bookId;
private String bookName;
private Float price;
private Set<Category> categories = new HashSet<Category>();
private Integer initCategories = 0;
public Integer getInitCategories() {
return initCategories;
}
public void setInitCategories(Integer initCategories) {
this.initCategories = initCategories;
}
public Integer getBookId() {
return bookId;
}
public void setBookId(Integer bookId) {
this.bookId = bookId;
}
public String getBookName() {
return bookName;
}
public void setBookName(String bookName) {
this.bookName = bookName;
}
public Float getPrice() {
return price;
}
public void setPrice(Float price) {
this.price = price;
}
public Set<Category> getCategories() {
return categories;
}
public void setCategories(Set<Category> categories) {
this.categories = categories;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Book [bookId=" + bookId + ", bookName=" + bookName + ", price=" + price + "]";
}
public Book(Integer bookId, String bookName) {
super();
this.bookId = bookId;
this.bookName = bookName;
}
public Book() {
super();
}
}
Category
package com.whw.two.entity;
import java.io.Serializable;
import java.util.HashSet;
import java.util.Set;
public class Category implements Serializable{
// category_id int primary key auto_increment,
// category_name varchar(50) not null
private Integer categoryId;
private String categoryName;
private Set<Book> books = new HashSet<Book>();
public Integer getCategoryId() {
return categoryId;
}
public void setCategoryId(Integer categoryId) {
this.categoryId = categoryId;
}
public String getCategoryName() {
return categoryName;
}
public void setCategoryName(String categoryName) {
this.categoryName = categoryName;
}
public Set<Book> getBooks() {
return books;
}
public void setBooks(Set<Book> books) {
this.books = books;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Category [categoryId=" + categoryId + ", categoryName=" + categoryName + "]";
}
}
4.2, corresponding mapping configuration
book.hbm.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<!DOCTYPE hibernate-mapping PUBLIC
"-//Hibernate/Hibernate Mapping DTD 3.0//EN"
"http://www.hibernate.org/dtd/hibernate-mapping-3.0.dtd">
<hibernate-mapping>
<class name="com.lgs.two.entity.Book" table="t_hibernate_book">
<!-- <cache usage="read-only" region="com.zking.five.entity.Book"/> -->
<id name="bookId" type="java.lang.Integer" column="book_id">
<generator class="increment" />
</id>
<property name="bookName" type="java.lang.String"
column="book_name">
</property>
<property name="price" type="java.lang.Float"
column="price">
</property>
<!--
table:Intermediate table
name:Association properties
inverse:reversal
key:The primary key of the current table is the foreign key of the intermediate table
many-to-many:The primary key of the current table finds the foreign key of another table in the intermediate table
-->
<set table="t_hibernate_book_category" name="categories" cascade="save-update" inverse="false">
<!-- one -->
<key column="bid"></key>
<!-- many -->
<many-to-many column="cid" class="com.lgs.two.entity.Category"></many-to-many>
</set>
</class>
</hibernate-mapping>
category.hbm.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<!DOCTYPE hibernate-mapping PUBLIC
"-//Hibernate/Hibernate Mapping DTD 3.0//EN"
"http://www.hibernate.org/dtd/hibernate-mapping-3.0.dtd">
<hibernate-mapping>
<class name="com.lgs.two.entity.Category" table="t_hibernate_category">
<id name="categoryId" type="java.lang.Integer" column="category_id">
<generator class="increment" />
</id>
<property name="categoryName" type="java.lang.String"
column="category_name">
</property>
<set table="t_hibernate_book_category" name="books" cascade="save-update" inverse="true">
<key column="cid"></key>
<many-to-many column="bid" class="com.lgs.two.entity.Book"></many-to-many>
</set>
</class>
</hibernate-mapping>
Table: intermediate table
name: association attribute
Key: the primary key of the current table is the foreign key of the associated table
The inverse attribute is reverse, which is used for data maintenance
false indicates that the data of the intermediate table is maintained by itself
true indicates that the data of the intermediate table is maintained by the opposite party
One of the two tables must be true and the other false, so that the intermediate table can have data
4.3, dao method BookDao
package com.whw.two.dao;
import org.hibernate.Hibernate;
import org.hibernate.Session;
import org.hibernate.Transaction;
import com.whw.two.entity.Book;
import com.whw.two.entity.Category;
import com.whw.two.util.SessionFactoryUtil;
public class BookDao /*extends BaseDao*/{
public Integer addBook(Book book) {
Session session = SessionFactoryUtil.getSession();
Transaction transaction = session.beginTransaction();
Integer bid = (Integer) session.save(book);
transaction.commit();
session.close();
return bid;
}
public Integer addCategory(Category category) {
Session session = SessionFactoryUtil.getSession();
Transaction transaction = session.beginTransaction();
Integer cid = (Integer) session.save(category);
transaction.commit();
session.close();
return cid;
}
public Category getCategory(Category category) {
Session session = SessionFactoryUtil.getSession();
Transaction transaction = session.beginTransaction();
Category c = session.get(Category.class, category.getCategoryId());
transaction.commit();
session.close();
return c;
}
public Book getBook(Book book) {
Session session = SessionFactoryUtil.getSession();
Transaction transaction = session.beginTransaction();
Book b = session.get(Book.class, book.getBookId());
if (b != null && new Integer(1).equals(book.getInitCategories())) {
Hibernate.initialize(b.getCategories());
}
transaction.commit();
session.close();
return b;
}
public void delBook(Book book) {
Session session = SessionFactoryUtil.getSession();
Transaction transaction = session.beginTransaction();
session.delete(book);
transaction.commit();
session.close();
}
public void delCategory(Category category) {
Session session = SessionFactoryUtil.getSession();
Transaction transaction = session.beginTransaction();
Category c = session.get(Category.class, category.getCategoryId());
if(c!=null) {
for (Book b : c.getBooks()) {
// The accused party cancels the association relationship through the main control party, and finally the accused party deletes it
b.getCategories().remove(c);
}
}
session.delete(c);
transaction.commit();
session.close();
}
/*
* hql Explain (need to inherit BaseDao)
*/
/**
* No code before BaseDao is used
* @param book
* @param pageBean
* @return
*/
// public List<Book> list(Book book, PageBean pageBean) {
// Session session = SessionFactoryUtil.getSession();
// Transaction transaction = session.beginTransaction();
// String hql = "from Book where 1 = 1";
//
// if (StringUtils.isNotBlank(book.getBookName())) {
// hql += " and bookName like :bookName";
// }
//
// Query query = session.createQuery(hql);
//
// if (StringUtils.isNotBlank(book.getBookName())) {
// query.setParameter("bookName", book.getBookName());
// }
//
// if (pageBean != null && pageBean.isPagination()) {
// query.setFirstResult(pageBean.getStartIndex());
// query.setMaxResults(pageBean.getRows());
// }
// List<Book> list = query.list();
// transaction.commit();
// session.close();
// return list;
//
// }
/**
* Code after using BaseDao
* @param book
* @param pageBean
* @return
*/
// public List<Book> list2(Book book, PageBean pageBean) {
// Session session = SessionFactoryUtil.getSession();
// Transaction transaction = session.beginTransaction();
// String hql = "from Book where 1 = 1";
// Map<String, Object> map = new HashMap<String, Object>();
//
// if (StringUtils.isNotBlank(book.getBookName())) {
// hql += " and bookName like :bookName";
// map.put("bookName", book.getBookName());
// }
// List list = super.executeQuery(session, hql, map, pageBean);
// transaction.commit();
// session.close();
// return list;
// }
/**
* Use native SQL
* @param book
* @param pageBean
* @return
*/
// public List list3(Book book, PageBean pageBean) {
String sql = "select b.*,o.* from t_hibernate_book b,t_hibernate_Order o";
// String sql = "select * from t_hibernate_book";
// Session session = SessionFactoryUtil.getSession();
// Transaction transaction = session.beginTransaction();
// List list = session.createSQLQuery(sql).list();
// transaction.commit();
// session.close();
// return list;
// }
}
4.4 test BookDaoTest
package com.whw.two.dao;
import org.junit.Test;
import com.whw.two.entity.Book;
import com.whw.two.entity.Category;
public class BookDaoTest {
private BookDao bookDao = new BookDao();
@Test
public void testGetBook() {
Book book = new Book();
book.setBookId(8);
book.setInitCategories(1);
Book b = this.bookDao.getBook(book );
System.out.println(b.getBookName());
System.out.println(b.getCategories());
}
/**
* book.hbm.xml inverse=fasle
* category.hbm.xml inverse=true
* Data addition is normal
* Add a new piece of data to the book table and bridge table respectively
*/
@Test
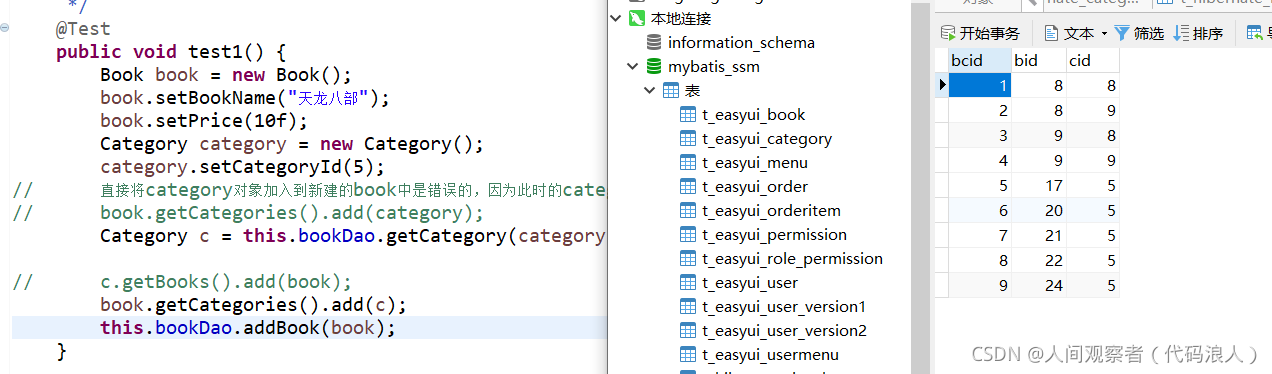
public void test1() {
Book book = new Book();
book.setBookName("Tianlong Babu");
book.setPrice(10f);
Category category = new Category();
category.setCategoryId(5);
// It is wrong to directly add the category object to the new book, because the category is temporary and hibernate will not manage it
// book.getCategories().add(category);
Category c = this.bookDao.getCategory(category);
// c.getBooks().add(book);
book.getCategories().add(c);
this.bookDao.addBook(book);
}
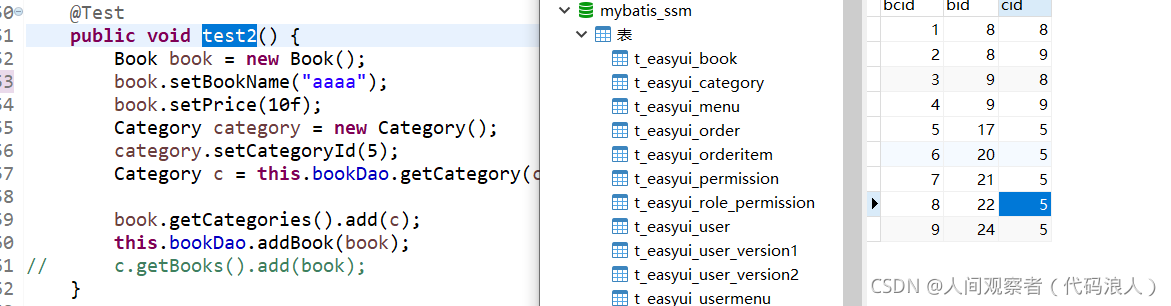
/**
* book.hbm.xml inverse=true
* category.hbm.xml inverse=true
* Only add book table data
* Bridge table without data
* Reason: neither side has maintained the relationship
*/
@Test
public void test2() {
Book book = new Book();
book.setBookName("dddd");
book.setPrice(10f);
Category category = new Category();
category.setCategoryId(5);
Category c = this.bookDao.getCategory(category);
book.getCategories().add(c);
this.bookDao.addBook(book);
// c.getBooks().add(book);
}
}
Test results:
When one is false and the other is true, the intermediate table has data
When one is true and the other is true, the intermediate table has no data
That's it. If there are any mistakes or additions, please comment. Thank you!