First, build Hive programming environment, Click me to check!
Chapter 2 basic operation
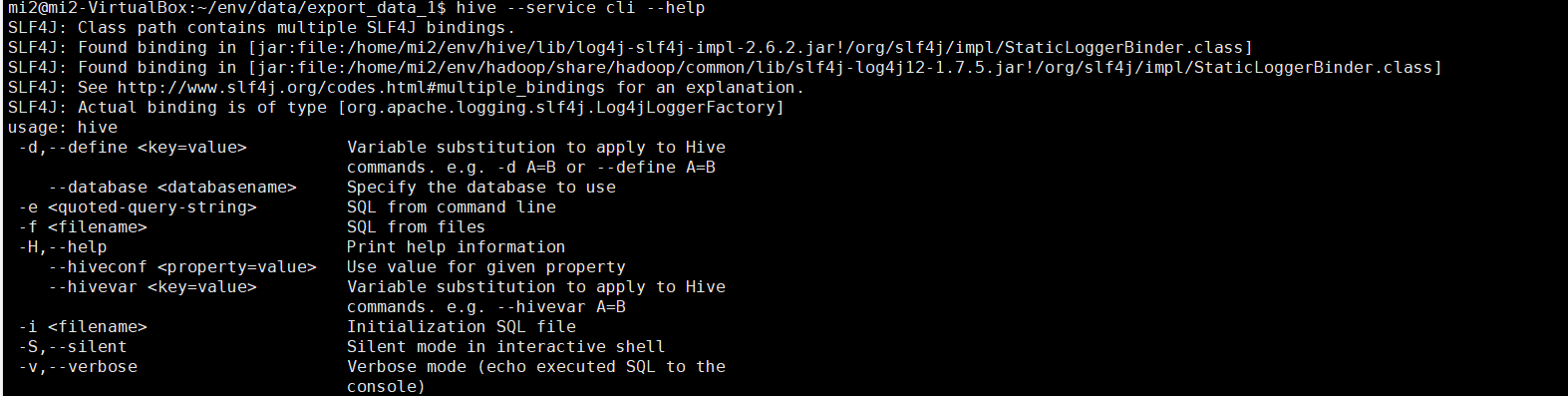
2.7 command line interface
2.7.1 CLI options

hive --help -- see cli Service usage help hive --service cli --help
2.7.2 variables and attributes

-- Display variables and attributes in all namespaces above set; -- Display variables and attributes in all the above namespaces, and Hadoop All properties defined in set -v;
-- New custom attribute
set foo = bar;
-- View custom attributes, equivalent to set hiveconf:foo;
set foo;
-- View custom properties
set hiveconf:foo;
-- Reference custom attribute
create table t3(i int, ${hiveconf:foo} string);
-- New custom variable
set hivevar:foo2 = bar2;
-- View custom variables
set hivevar:foo2;
-- View custom variables
set foo2;
-- Reference custom variable
create table t1(i int, ${foo2} string);
-- Reference custom variable
create table t2(i int, ${hivevar:foo2} string);
-- get into hive This configuration property is changed when the database is displayed. Note:=There should be no spaces on the left and right hive --hiveconf hive.cli.print.current.db=true; -- Modify configuration properties set hive.cli.print.current.db= false; -- Modify configuration properties set hiveconf:hive.cli.print.current.db = true;
-- View system variables (cannot be omitted) system:) set system:user.name; -- View environment variables (cannot be omitted) env:) set env:HOME;
2.7.7 viewing operation command history
$HOME/.hivehistory
2.7.8 execute shell command
-- Can only perform simple shell command
! /bin/echo ${hiveconf:foo};
2.7.9 using the dfs command of Hadoop in Hive
dfs -ls /;
2.7.10 how to comment in hive script
-- Hive notes
slightly
Specifically, read directly and check as you use. There is no need to waste time doing it manually
2.7.3 Hive Use once command in 2.7.4 Execute from file Hive query 2.7.5 hiverc file
Chapter 3 data type and file format
3.1 basic data type
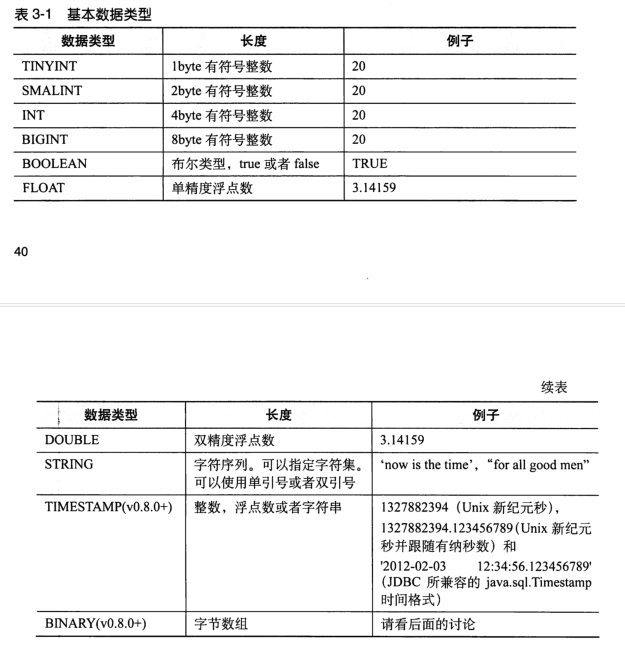
All these types are the implementation of Java interfaces. The specific behavior details of these types are completely consistent with the corresponding types in Java.
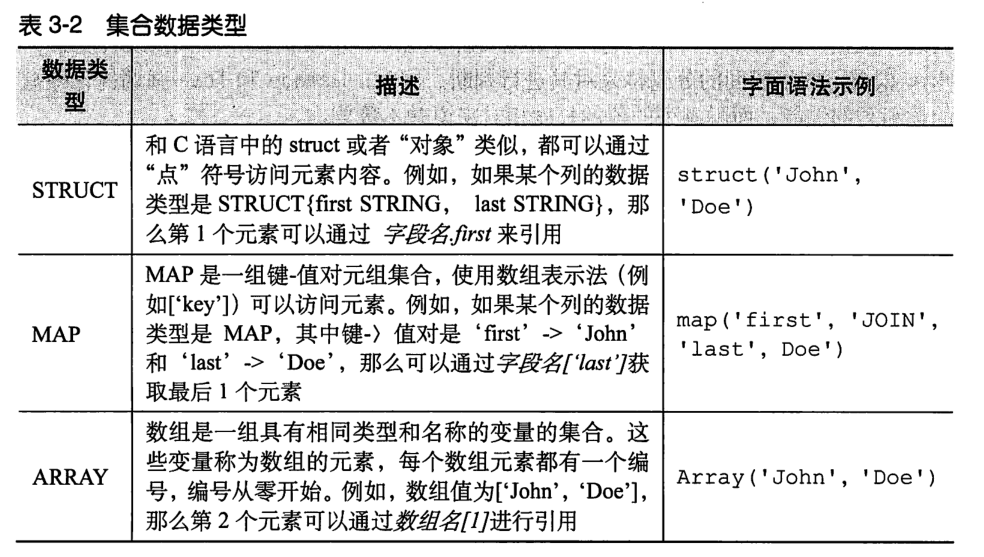
3.2 set data type


3.3 text file data coding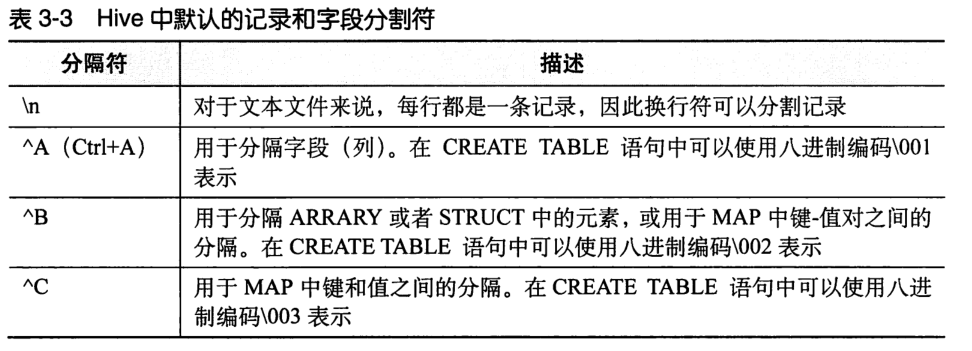
create table employees ( -- Put on hive The command line can be removed before execution Tab name string, salary float, subordinates array<string>, deductions map<string, float>, address struct<street:string, city:string, state:string, zip:int> ) row format delimited fields terminated by '\001' collection items terminated by '\002' map keys terminated by '\003' lines terminated by '\n' stored as textfile;
3.4 time reading mode

Chapter 4 HiveQL: data definition
4.1 database in hive
Hive database is essentially just a directory or namespace.
-- If it does not exist, it will be created. If it does exist, no error will be reported
create database if not exists mydb;
-- If it does not exist, it will be created. If it does exist, an error will be reported
create database mydb;
show databases like 'm.*';
use mydb;
show tables like 'e.*';
-- Specify the corresponding when creating the database hdfs Path( location),Add description information( comment),Add attribute( dbproperties)
-- Default database default The path to is a property hive.metastore.warehouse.dir Configured path
create database d4 comment 'about something' location '/d4' with dbproperties('creator' = 'Tom', 'date' = '2021-04-29');
-- Displays the current database
set hive.cli.print.current.db=true;
-- View current database
select current_database();
-- extended,Display attribute information
desc database extended d4;
-- Modify or add attribute information and cannot be deleted
alter database d4 set dbproperties('creator'= 'Jack');
-- If d1 No, no error will be reported; If d1 If there are more than 0 tables, an error will be reported
drop database if exists d1;
-- If d1 If it exists, delete all its tables first( cascade),Again d1 delete
drop database if exists d1 cascade;
4.3 creating tables
-- Create table
create table if not exists d4.employees (
-- Put on hive The command line can be removed before execution Tab
name string comment 'Employee name',
salary float comment 'Employee salary',
subordinates array<string> comment 'Names of subordinates',
deductions map<string, float> comment 'Keys are deductions names, values are percentages',
address struct<street:string, city:string, state:string, zip:int> comment 'Home address'
)
comment 'Description of the table'
tblproperties ('creator'='Tom', 'created_time'='2021-04-29');
-- View table information describe extended d4.employees; desc formatted d4.employees; -- Create a and table employees New table with the same structure employees3 create table if not exists d4.employees3 like d4.employees;
4.3.1 internal table
Deleting an internal table will delete data.
4.3.2 external table
When you delete an external table, the data will not be deleted, but the metadata information will be deleted.
-- Create external table create external table if not exists external_t1 (col string) row format delimited fields terminated by ',' location '/data/external_t1'; -- Create a structure and external_t1 Same external table external_t2 create external table if not exists external_t2 like external_t1 location '/path/to/data';
4.4 zoning table
create table if not exists d4.employees100 ( -- Put on hive The command line can be removed before execution Tab name string comment 'Employee name', salary float comment 'Employee salary', subordinates array<string> comment 'Names of subordinates', deductions map<string, float> comment 'Keys are deductions names, values are percentages', address struct<street:string, city:string, state:string, zip:int> comment 'Home address' ) partitioned by (country string, state string);
-- It is mandatory to specify the partition when querying, otherwise an error will be reported set hive.mapred.mode = strict; -- You do not need to specify a partition when querying set hive.mapred.mode = nonstrict; -- View partition show partitions employees100; show partitions employees100 partition(country='US'); -- View a partition information desc formatted employees100 partition(country='China', state = 'Beijing');
4.5 delete table
drop table if exists external_t1;
<!-- core-site.xml to configure trash Will delete the file, save the file trash,Delete after 1440 trash -->
<property>
<name>fs.trash.interval</name>
<value>1440</value>
<description>Number of minutes between trash checkpoints. If zero, the trash feature is disabled.</description>
</property>
4.6 modification table
-- rename table
alter table employees rename to emps;
-- Add partition,/d4/employees100/country=China/state=Beijing
alter table employees100 add if not exists partition(country = 'China', state = 'Beijing') ;
-- Add partition,/d4/employees100/jap/d
alter table employees100 add if not exists partition(country = 'JAP', state = 'D') location '/d4/employees100/jap/d'
-- Changing the partition path will not delete the old path data
alter table employees100 partition(country = 'US', state = 'NBA') set location '/d4/employees100/country=US/state=NBA';
-- delete a partition
alter table employees100 drop if exists partition(country = 'US', state = 'NBA');
-- Modify the column, the field itself in the first position after name Replace the statement with first
alter table employees100 change column salary pay float comment 'salary' after name;
-- Add column
alter table employees100 add columns(app_name string comment 'apps');
-- Delete and replace columns, delete all original columns (except partition columns), and use these new columns
alter table employees100 replace columns(
name string comment 'Employee name',
salary float comment 'Employee salary',
subordinates array<string> comment 'Names of subordinates',
deductions map<string, float> comment 'Keys are deductions names, values are percentages',
address struct<street:string, city:string, state:string, zip:int> comment 'Home address'
)
-- Modify table properties
alter table employees100 set tblproperties('prop' = 'prop');
-- Modify the storage properties of the table, such as the storage file type, omitted
-- Package a partition into one har Package, reduce the number of files and reduce NameNode Pressure, but does not save storage space
alter table employees100 archive partition (country="China",state="Beijing")
-- Put a partition har Restore package to original partition
alter table employees100 unarchive partition (country="China",state="Beijing")
-- Protect partitions from deletion
alter table employees100 partition (country="China",state="Beijing") enable no_drop
-- Protect partitions from being queried
alter table employees100 partition (country="China",state="Beijing") enable offline
-- Allow partition deletion and query
alter table employees100 partition (country="China",state="Beijing") disable no_drop
alter table employees100 partition (country="China",state="Beijing") disable offline
Chapter 5 HiveQL: data operation
-- Create table create table mydb.employees ( -- Put on hive The command line can be removed before execution Tab name string comment 'Employee name', salary float comment 'Employee salary', subordinates array<string> comment 'Names of subordinates', deductions map<string, float> comment 'Keys are deductions names, values are percentages', address struct<street:string, city:string, state:string, zip:int> comment 'Home address' ) row format delimited fields terminated by ',' collection items terminated by '#' map keys terminated by ':';
-- Data preparation,/home/mi2/env/data/data_type_t1.txt
Tom,5000.0,Tom_sub1#Tom_sub2#Tom_sub3,deduction1:120.0#deduction2:50.0#deduction3:200.0,Tom_street#Tom_city#Tom_state#123456
Jack,6000.0,Jack_sub1#Jack_sub2#Jack_sub3,deduction1:120.0#deduction2:50.0#deduction3:200.0,Jack_street#Jack_city#Jack_state#123456
Import data
-- Import data from local file to Hive surface load data local inpath '/home/mi2/env/data/data_type_t1.txt' overwrite into table employees;
-- explain: -- 1)local Indicates that the local file is loaded. If it is loaded hdfs Files are not needed local -- 2)overwrite It is overwrite write. If you add write, you don't need it overwrite -- 3)partition It's a partitioned table. If it's not a partitioned table, it won't be used partition load data local inpath '/home/mi2/env/data/data_type_t1.txt' overwrite into table employees partition (country = 'US', state = 'CA');
-- Insert data from query, overwrite write insert overwrite table employees select * from employees; -- Insert data from query, append write insert into table employees select * from employees; -- Insert data from query, overwrite and write to a partition insert overwrite table employees partition(country = 'US', state = 'CA') select * from employees;
-- Query different data and insert them into different partitions (static handwriting) from staged_employees select insert overwrite table employees partition(country = 'US', state = 'OR') select * where se.country = 'US' and se.state = 'OR' insert overwrite table employees partition(country = 'US', state = 'CA') select * where se.country = 'US' and se.state = 'CA' insert overwrite table employees partition(country = 'US', state = 'IL') select * where se.country = 'US' and se.state = 'IL'
-- Dynamically import partitions, country/state The value of is determined by select The last two columns of the statement are determined and matched according to the position insert overwrite table employees partition (country, state) select ...,se.country,se.state from staged_employees se; -- The dynamic and static import partitions are combined, and the name of the static partition must be in front of the name of the dynamic partition insert overwrite table employees partition (country = 'US', state) select ...,se.country,se.state from staged_employees se where se.country = 'US';
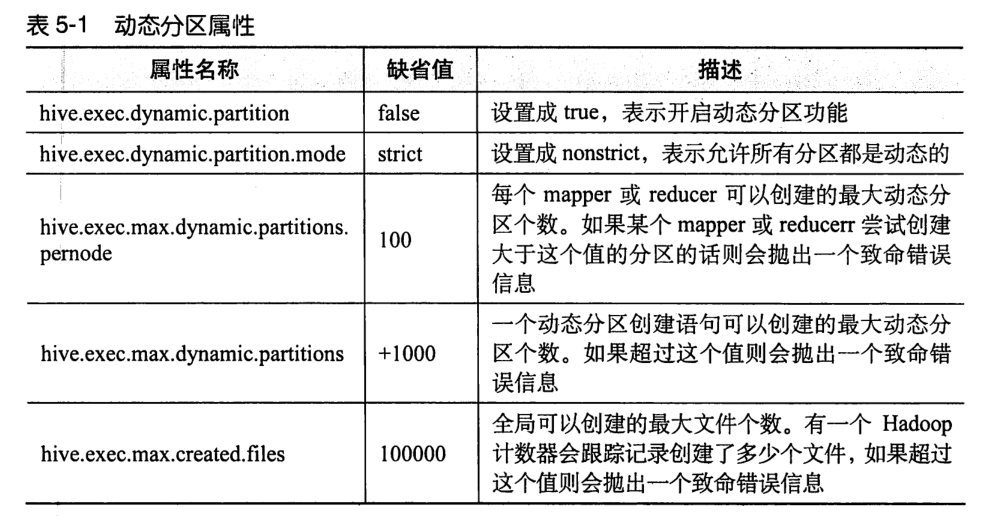
-- Can be in HiveQL Set configuration attribute value before set hive.exec.dynamic.partition=true; set hive.exec.dynamic.partition.mode=nonstrict; set hive.exec.max.dynamic.partitions.pernode=100;
Export data
-- overwrite/into Indicates overwrite write/Append write, local Represent local insert overwrite local directory '/home/mi2/env/data/export_data_1' select name, salary, address from employees;
Chapter 6 HiveQL: query
6.1 SELECT...FROM
select * from employees limit 1;
-- Query results
Tom 5000.0 ["Tom_sub1","Tom_sub2","Tom_sub3"] {"deduction1":120.0,"deduction2":50.0,"deduction3":200.0} {"street":"Tom_street","city":"Tom_city","state":"Tom_state","zip":123456}
select name, salary, subordinates[0], deductions['deduction1'], address.city from employees;
-- Query results
Tom 5000.0 Tom_sub1 120.0 Tom_city
Jack 6000.0 Jack_sub1 120.0 Jack_city
select upper(name), salary, deductions['deduction1'],round(salary - deductions['deduction1']) from employees;
-- Query results
TOM 5000.0 120.0 4880.0
JACK 6000.0 120.0 5880.0
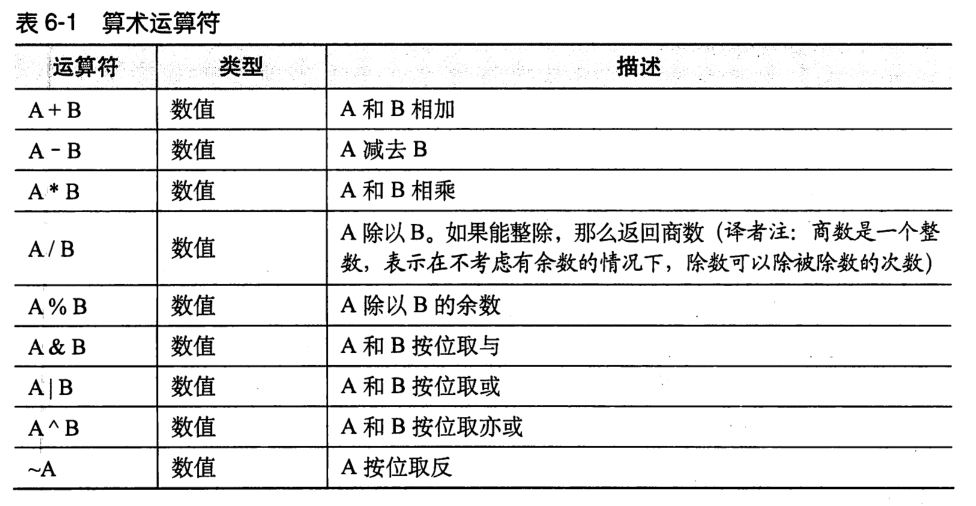
Arithmetic operator
Hive follows the rules of data types in the underlying Java.
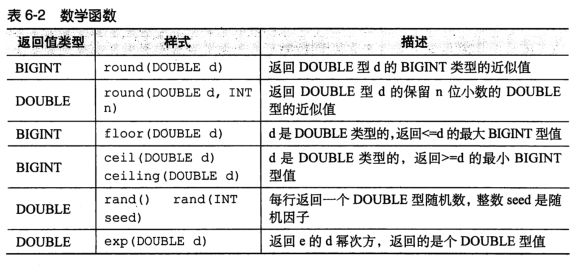
function
-- display Hive All functions show functions; -- View the description of a function desc function when; -- View the detailed description of a function desc function extended abs;
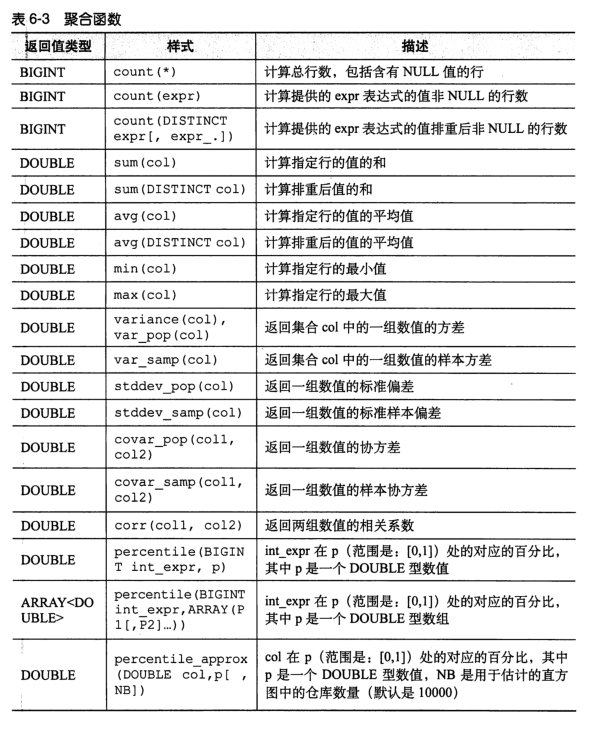
select name, explode(subordinates) from employees; -- Error report, only one column can be included explode(subordinates),Cannot contain other columns FAILED: SemanticException [Error 10081]: UDTF's are not supported outside the SELECT clause, nor nested in expressions -- Query with other columns select name, sub from employees lateral view explode(subordinates) subView as sub;
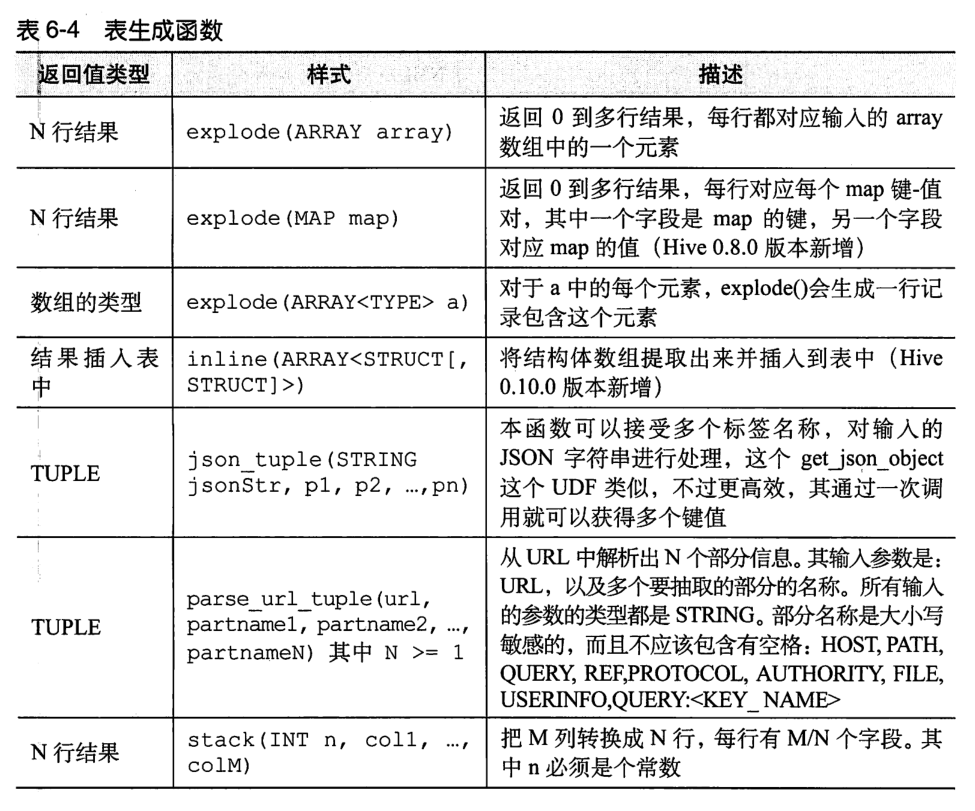
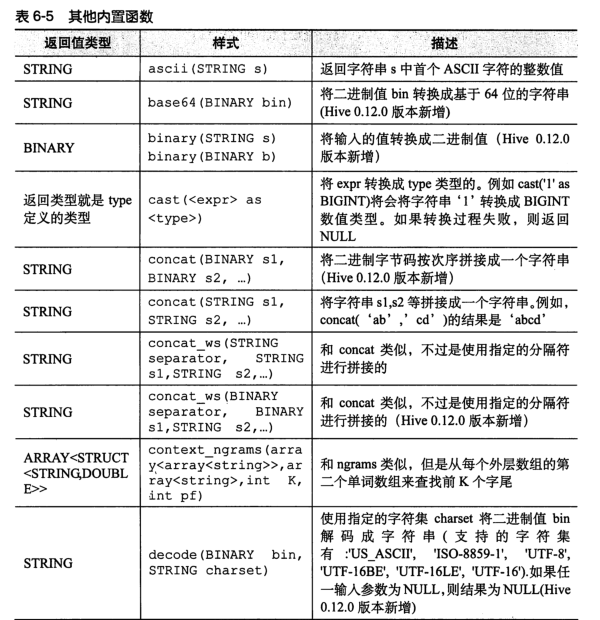
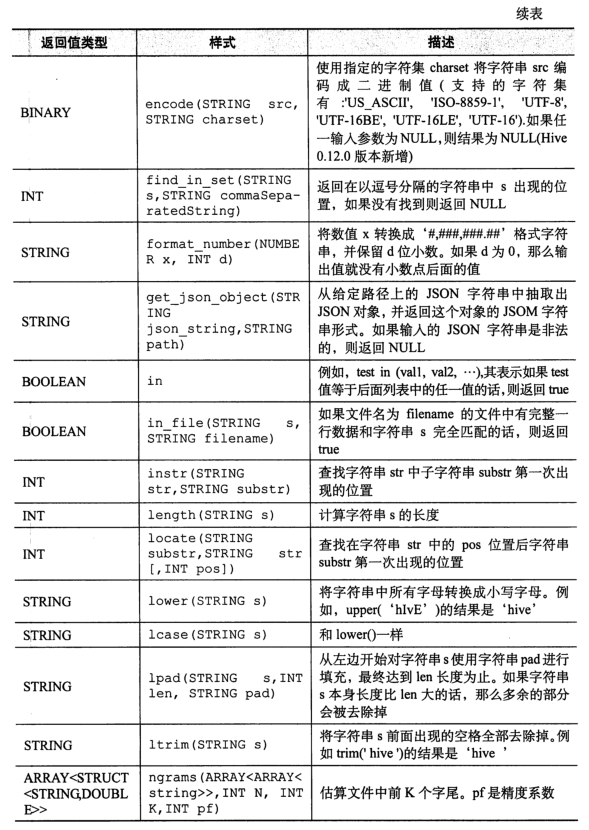
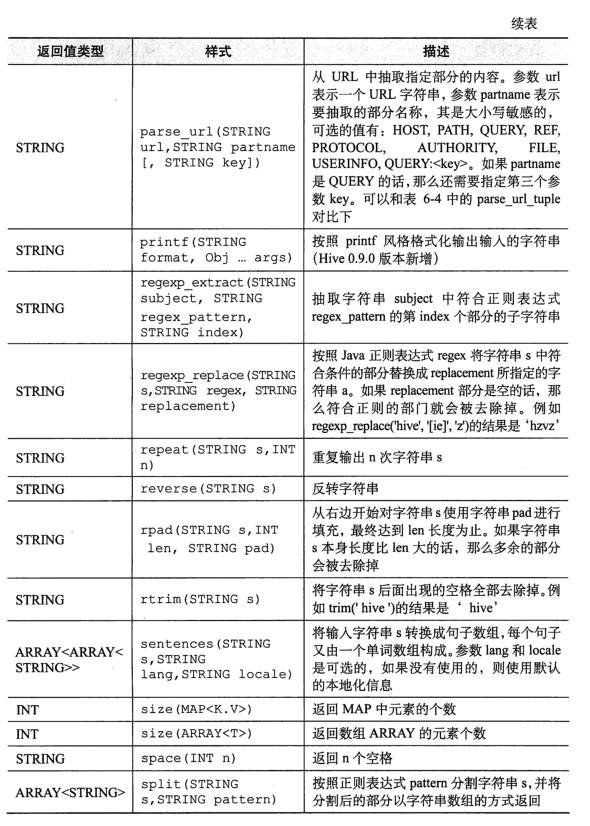
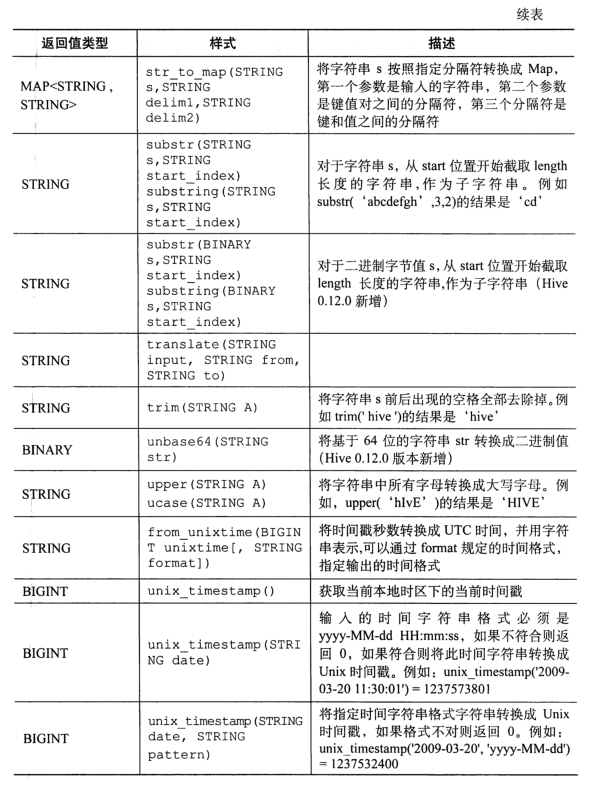
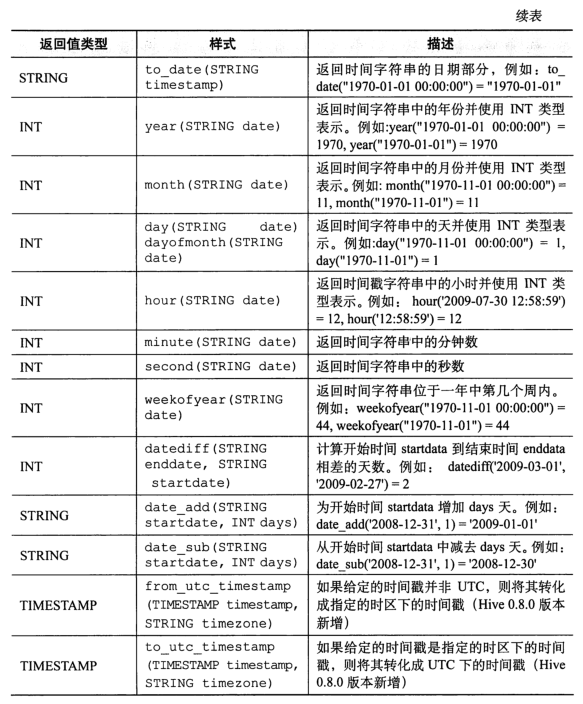
Note: user defined functions need to write JAVA classes and achieve JAR package entry (Chapter 13).
nested queries
select t.name from (select * from mydb.employees) t;
CASE...WHEN...THEN
select name, salary, case when salary < 3000.0 then 'low' when salary >= 3000.0 and salary < 5000.0 then 'middle' when salary >= 5000.0 and salary < 7000.0 then 'high' else 'very high' end as bracket from employees;
Under what circumstances can Hive avoid MapReduce
-- The author found that whether the local mode is turned on or not( hive.exec.mode.local.auto),Simple query (no aggregation) and other operations, such as count)Not at all MapReduce select name, salary*1.1 from employees where salary < 10000.0;
6.2 WHERE statement
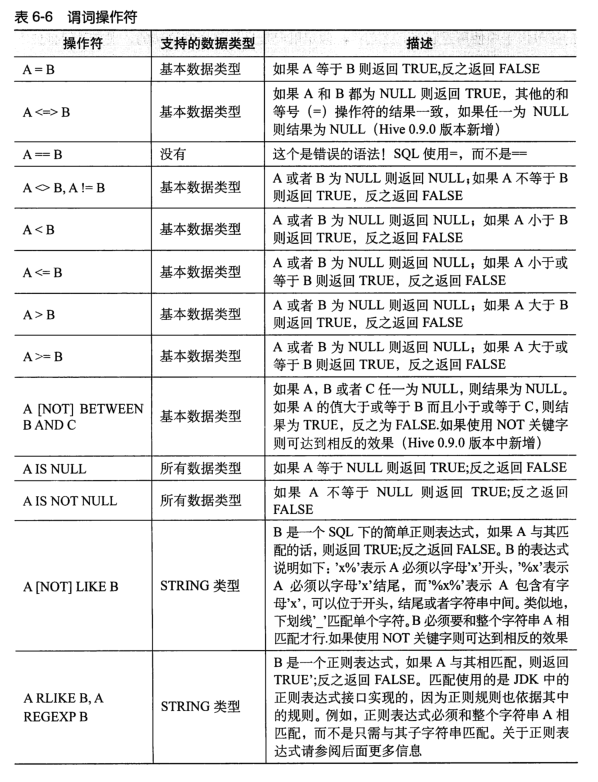
be careful 1)Floating point comparison error, try not to carry out floating-point comparison. If it is necessary to compare, it must be avoided float Automatic rotation double situation 2)LIKE only%and_Two matching characters, RLIKE/REGEXP After is a true regular expression
6.3 GROUP BY
select name, avg(salary) from employees where salary >= cast(5000.0 as float) group by name having avg(salary) >= cast(3000.0 as float);
6.4 JOIN
Only equivalent connection is supported (and mu lt iple equivalent conditions after on do not support or, only and), natural connection is not supported (columns with the same attribute should be removed after connection), and non equivalent connection is not supported (the condition after on is not =, but < and so on).
select e1.name, e1.salary from employees e1 join employees e2 on e1.name = e2.name where e1.name = 'Tom';
select e1.name, e1.salary from employees e1 join employees e2 on e1.salary < e2.salary -- I won't support it where e1.name = 'Tom';
be careful 1)Three or more tables join,If each on All use the same connection key, only one will be generated MapReduce job,Hive Assuming that the last table is the largest table, the user should ensure that the continuous query tables increase from left to right (if there is only one small table, it can be set) hive.auto.convert.join=true,Put the small table in memory and speed up! You can also set the small table size hive.mapjoin.smalltable.filesize). 2)line type [INNER] JOIN LEFT [OUTER] JOIN RIGHT [OUTER] JOIN FULL [OUTER] JOIN LEFT SEMI JOIN(Query results are displayed only in the left table) Cartesian product (e.g.: select * from a join b,set up hive.mapred.mode=strict (Cartesian product can be disabled)
6.5 ORDER BY and SORT BY
order by: Global sorting (potentially time consuming) sort by: Just each reducer Orderly
select name, salary from employees order by name asc, salary desc;
6.6 DISTRIBUTE BY with SORT BY
By default, the MapReduce computing framework will calculate the corresponding hash value according to the key entered by the map, and then distribute the key value pairs evenly to multiple reducers according to the hash value. distribute by col can distribute the same cols to the same reducer, and then sort by.
-- If distribute by and sort by After the same conditions, it is equivalent to cluster by(Cannot be in descending order!), Global sorting can be realized select name, salary from employees distribute by name sort by name asc, salary desc;
6.8 type conversion
Hive defaults to implicit type conversion. The underlying layer is Java. Narrow types automatically turn to wide types. Cast can be used for cast, and cast can be nested.
6.9 sampling query
slightly
6.10 UNION ALL
Merge two or more tables. Each table has the same column and the data type of the column is the same.
Chapter 7 HiveQL: Views

-- The view is read-only create view view_01 as select name, salary from employees;
-- In storage Hive Metadata MySQL database hive Query all views in select TBL_NAME from TBLS where TBL_TYPE = 'VIRTUAL_VIEW';
Chapter 8 HiveQL: index
Hive's index is actually an index table (hive's physical table), in which the value of the index column is stored. The value corresponds to the file path of HDFS and the offset of the value in the data file.

-- Create partition table employees10
create table mydb.employees10 (
-- Put on hive The command line can be removed before execution Tab
name string comment 'Employee name',
salary float comment 'Employee salary',
subordinates array<string> comment 'Names of subordinates',
deductions map<string, float> comment 'Keys are deductions names, values are percentages',
address struct<street:string, city:string, state:string, zip:int> comment 'Home address'
)
partitioned by (country string, city string)
row format delimited
fields terminated by ','
collection items terminated by '#'
map keys terminated by ':';
-- Import data
load data local inpath '/home/mi2/env/data/data_type_t1.txt' overwrite into table employees10 partition (country = 'US', city = 'CA');
-- Create index
create index employees10_index
on table employees10 (name)
as 'org.apache.hadoop.hive.ql.index.compact.CompactIndexHandler'
with deferred rebuild
idxproperties ('creator' = 'creator', 'ct' = '2021-04-30')
in table employees10_index_tb
comment 'Employees indexed by name';
-- View index
show formatted index on employees10;
-- Indexing (Books) is a dead trick, on One more after table)
alter index employees10_index on employees10 rebuild;
-- Delete index
drop index employees10_index on employees10;
Chapter 9 pattern design


