Addition, deletion and modification of DOM:
Add innerHTML + = appendChild() insertBefore()
Delete} innerHTML = 'remove() removeChild()
Modify replaceChild()
Query:
Know node - line breaks, text, comments, labels are all node lists
Tag: HTMLCollection
Array array
Array 2} Arguments
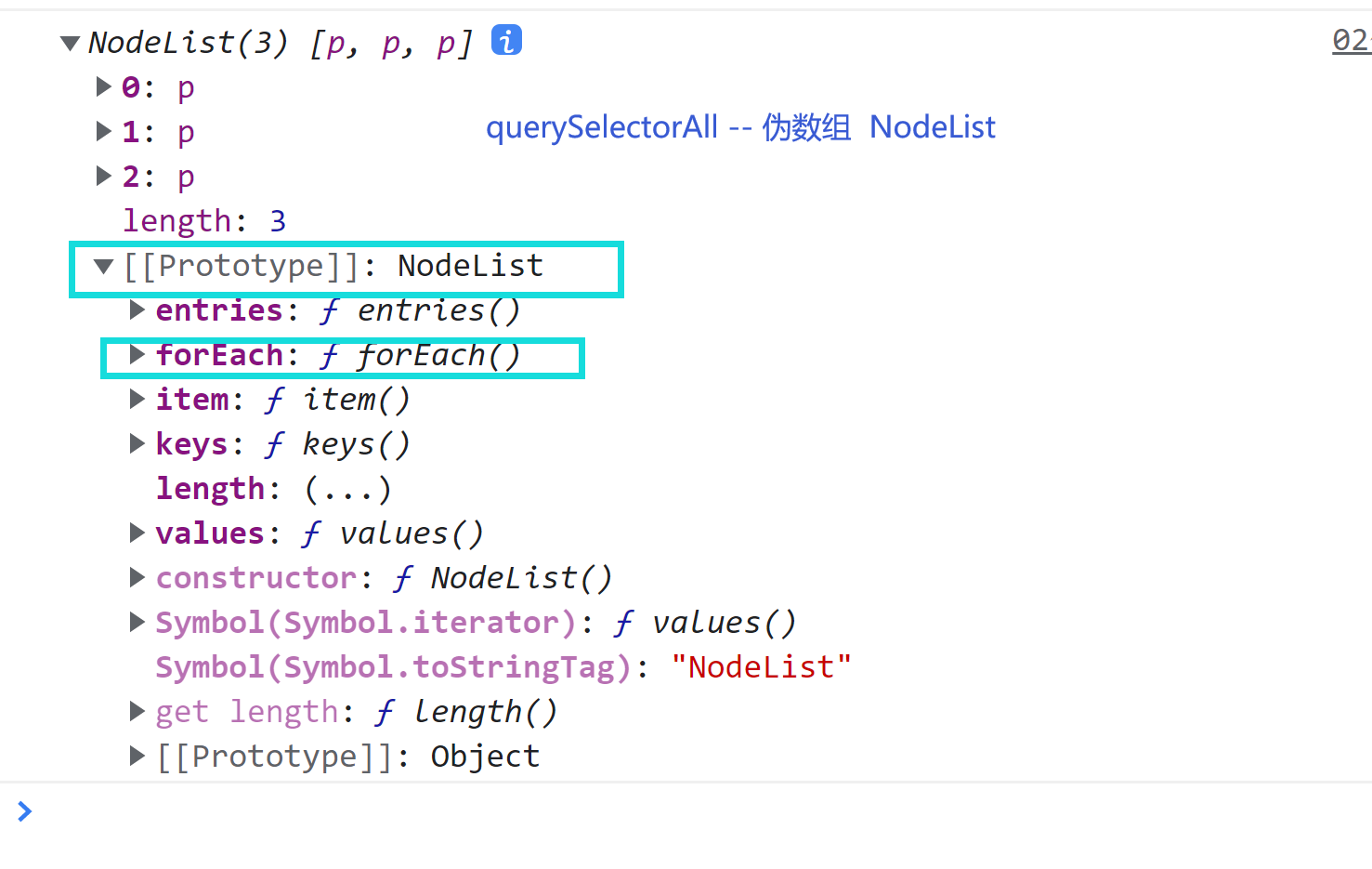
Array 3 # NodeList
Array 4} HTMLCollection
Each of the above arrays belongs to a different category, so it has different properties and methods
How to convert a pseudo array to a true array


var arr = new Array() ;
console.log(arr);
function fn() {
console.log(arguments);
}
fn()
var oPs = document.querySelectorAll('p') ;
console.log(oPs);
// oPs.push('a')
var oPs2 = document.getElementsByTagName('p') ;
console.log(oPs2);
// oPs2.pop()
var arr = [] ;
for(var i = 0 ; i < oPs.length ; i++) {
arr.push(oPs[i])
}
console.log(arr);
arr.push('a')
console.log(arr);
event
Event: something happened and was handled
Event: event source Event type = event handler
Event handlers are asynchronous
This anonymous function is called by the system after the event occurs
General event handling functions do not have a specific return value, but return can also be used
document.onclick = function () {
console.log(666);
return
console.log(777);
}The first parameter of the event handler function represents the event object
The event object is the whole process in which the user records what happened
document.onclick = function (a , b) {
console.log(a);
// The event handler function has only one parameter
console.log(b); // undefined
} document.onclick = function (e) {
// Most browsers support the first parameter of the event handler as an event object
// console.log(e);
// Older browsers can only use event to record event objects
// console.log(event);
e = e || event ;
// Target - which tag triggered the target
console.log(e.target);
// this points to the event source
console.log(this);
console.log(e.clientX);
}How to bind events
1 inline js ο nclick="fn()"
2. Event binding: odiv onclick = function(){}
3. Event monitoring: odiv Addeventlistener (type, event handler) --- will not be overwritten
Remove event
Both in-line js and ordinary event bindings can be removed in the way of overwriting by means of re assignment
The event listening method needs to be written as a named function before it can be removed (Note: when removing, it needs to be removed one by one) removeEventListener()
// onclick re assignment (any value is OK). It is generally recommended to write null
oDiv.onclick = null ;
function fn2() {
console.log(999);
}
function fn() {
console.log(666);
}
// Add event listener
function addEvent(ele , type , cb) {
if(window.addEventListener) {
ele.addEventListener(type , cb)
} else {
ele.attachEvent('on' + type , cb)
}
}
// Remove event listener
function removeEvent(ele , type , cb) {
if(window.removeEventListener) {
ele.removeEventListener(type , cb)
} else {
ele.detachEvent('on' + type , cb)
}
}Event flow:
Event bubbling: from the inside out
Event capture: from outside to inside
Mainly use event bubbling
How to implement event capture
The third parameter of addeventlistener (type, FN, true) indicates whether event capture is supported
What is an event flow:
Event flow describes the order in which events are received from the page
Interestingly, the development teams of Microsoft (ie) and Netscape (Netscape) have proposed two completely opposite concepts of event flow. The event flow of IE is event bubbling, while the event flow of Netscape is event capturing
Event capture: the idea of event capture flow is that less specific DOM nodes should receive events earlier, while the most specific nodes should receive events last
Event bubbling: the event flow proposed by IE is called event bubbling, that is, the event is received by the most specific element at the beginning, and then propagated upward level by level to less specific nodes
Ie proposes bubbling stream, while Netscape proposes capture stream. Later, under the unification of W3C organization, JS supports bubbling stream and capture stream. However, at present, lower versions of IE browsers can only support bubbling stream (IE6, IE7 and IE8 only support bubbling stream). Therefore, in order to be compatible with more browsers, it is recommended that you use bubbling stream.
Event flow includes three stages: event capture stage, target stage and event bubble stage
Prevent event bubbling
Using event objects
e.stopPropagation()
e.cancelBubble = true
oP.onclick = function (e) {
e = e || event ;
// Prevent event bubbling
// How mainstream browsers are written
// e.stopPropagation()
// Method for canceling event bubbling in low version IE
// e.cancelBubble = true ;
if(e.stopPropagation) {
e.stopPropagation()
} else {
e.cancelBubble = true ;
}
console.log('p');
}Event delegation
If there are too many event handlers on the page, performance will be affected
If you need to make every li have click events and bind events circularly - there will be many event handling functions on the page
Circular binding events cannot bind events to future objects
Solution: event delegation
The event of the child element will trigger the event of the parent element
Implementation of event delegation:
Find all the parent elements that need to bind events, bind events to the parent element, and then judge who triggered them according to the target
What is an event delegate
The same type event of the child element is delegated to the parent element
Why use event delegates
Reduce event handler
You can bind events to future objects
Principle of event delegation
Event bubbling --- events of the same type of child elements will trigger events of the same type of parent elements