Shape Detection
Contour detection
contours, hierarchy = cv2.findContours(image,mode,method)
- The first parameter input image,
- The second parameter represents the retrieval mode of contour, which has four types:
1.cv2.RETR_EXTERNAL means that only the outer contour is detected
2.cv2. RETR_ The contour detected by list does not establish a hierarchical relationship
3.cv2.RETR_CCOMP establishes two levels of contours. The upper layer is the outer boundary and the inner layer is the boundary information of the inner hole. If there is a connected object in the inner hole, the boundary of the object is also on the top layer.
4.cv2.RETR_TREE establishes the outline of a hierarchical tree structure. - cv2.CHAIN_APPROX_NONE stores all contour points. The pixel position difference between two adjacent points does not exceed 1, that is, max (abs (x1-x2), abs (y2-y1)) = = 1
cv2.CHAIN_APPROX_SIMPLE compresses the elements in the horizontal, vertical and diagonal directions, and only retains the end coordinates of the direction. For example, a rectangular contour only needs 4 points to save the contour information
cv2.CHAIN_APPROX_TC89_L1,CV_CHAIN_APPROX_TC89_KCOS uses teh chinl chain approximation algorithm
Calculate contour area
contourArea(contour,oriented = False)
This function uses Green's formula to calculate the area of the contour. For contours with self intersection points, this function will almost certainly give wrong results.
1.contour: enter a two-dimensional vector and store it as vector(C + +) or Mat.
2.oriented: directional area sign.
- true: this function returns the value of a marked area depending on the direction of the contour (clockwise or counterclockwise).
- false: default value. Means to return an absolute value without direction.
Calculate contour length
cv2.arcLength(InputArray curve, bool closed)
- curve, the input 2D point set (contour vertex), which can be of type vector or Mat.
- Closed, used to indicate whether the curve is closed.
Multilateral fitting function
The main function is to polyline a continuous smooth curve and fit the polygon of the image contour points
cv2.approxPolyDP(InputArray curve, OutputArray approxCurve, double epsilon, bool closed)
- InputArray curve: generally, it is a point composed of contour points of the image
- OutputArray approxCurve: represents the set of polygon points to be output
- double epsilon: it mainly indicates the output accuracy, that is, the maximum distance between another contour point, 5, 6, 7, 8
- bool closed: indicates whether the output polygon is closed
Gets the smallest rectangular border
x,y,w,h = cv2.boundingRect(img)
def geContours(img):
countors,Hierarchy = cv2.findContours(img,cv2.RETR_EXTERNAL,cv2.CHAIN_APPROX_NONE)
for cnt in countors:
area = cv2.contourArea(cnt)
print(area)
if area>500:
cv2.drawContours(imgContour,cnt,-1,(255,0,0),3)
peri = cv2.arcLength(cnt,True)
print(peri)
approx = cv2.approxPolyDP(cnt,0.02*peri,True)
print(len(approx))
objCor = len(approx)
x,y,w,h = cv2.boundingRect(approx)
#Judge shape
if objCor == 3: objType = "Tri"
elif objCor == 4:
aspRatio = w/float(h)
if aspRatio >0.95 and aspRatio <1.05: objType= "Square"
else:objType="Rectangle"
elif objCor>4: objType= "circles"
else:objType="None"
cv2.rectangle(imgContour,(x,y),(x+w,y+h),(0,255,0),2)
cv2.putText(imgContour,objType,
(x+(w//2)-10,y+(h//2)-10),cv2.FONT_HERSHEY_COMPLEX,0.7,
(0,0,0),2)
module:
import cv2
import numpy as np
def stackImages(scale,imgArray):
'''
Image overlay module
'''
rows = len(imgArray)
cols = len(imgArray[0])
# &Output a matrix of rows * cols (imgArray)
print(rows,cols)
# &Determine whether imgaray [0] is a list
rowsAvailable = isinstance(imgArray[0], list)
# &What does imgaray [] [] mean?
# &Imgrarray [0] [0] refers to the picture of [0,0] (we divide the picture set into two-dimensional matrices, and the one in the first row and column is the first picture)
# &shape[1] is width, shape[0] is height, and shape[2] is height
width = imgArray[0][0].shape[1]
height = imgArray[0][0].shape[0]
if rowsAvailable:
for x in range (0, rows):
for y in range(0, cols):
# &Judge whether the shape of the image is consistent with that of the following image. If it is consistent, scale it in equal proportion; Otherwise, resize to be consistent first, and then zoom in and out
if imgArray[x][y].shape[:2] == imgArray[0][0].shape [:2]:
imgArray[x][y] = cv2.resize(imgArray[x][y], (0, 0), None, scale, scale)
else:
imgArray[x][y] = cv2.resize(imgArray[x][y], (imgArray[0][0].shape[1], imgArray[0][0].shape[0]), None, scale, scale)
# &If it is a grayscale image, it becomes an RGB image (in order to make the same image)
if len(imgArray[x][y].shape) == 2: imgArray[x][y]= cv2.cvtColor( imgArray[x][y], cv2.COLOR_GRAY2BGR)
# &Set zero matrix
imageBlank = np.zeros((height, width, 3), np.uint8)
hor = [imageBlank]*rows
hor_con = [imageBlank]*rows
for x in range(0, rows):
hor[x] = np.hstack(imgArray[x])
ver = np.vstack(hor)
# &If it is not a group of photos, it is only zoomed or grayscale converted to RGB
else:
for x in range(0, rows):
if imgArray[x].shape[:2] == imgArray[0].shape[:2]:
imgArray[x] = cv2.resize(imgArray[x], (0, 0), None, scale, scale)
else:
imgArray[x] = cv2.resize(imgArray[x], (imgArray[0].shape[1], imgArray[0].shape[0]), None,scale, scale)
if len(imgArray[x].shape) == 2: imgArray[x] = cv2.cvtColor(imgArray[x], cv2.COLOR_GRAY2BGR)
hor= np.hstack(imgArray)
ver = hor
return ver
def geContours(img):
countors,Hierarchy = cv2.findContours(img,cv2.RETR_EXTERNAL,cv2.CHAIN_APPROX_NONE)
for cnt in countors:
area = cv2.contourArea(cnt)
print(area)
if area>500:
cv2.drawContours(imgContour,cnt,-1,(255,0,0),3)
peri = cv2.arcLength(cnt,True)
print(peri)
approx = cv2.approxPolyDP(cnt,0.02*peri,True)
print(len(approx))
objCor = len(approx)
x,y,w,h = cv2.boundingRect(approx)
if objCor == 3: objType = "Tri"
elif objCor == 4:
aspRatio = w/float(h)
if aspRatio >0.95 and aspRatio <1.05: objType= "Square"
else:objType="Rectangle"
elif objCor>4: objType= "circles"
else:objType="None"
cv2.rectangle(imgContour,(x,y),(x+w,y+h),(0,255,0),2)
cv2.putText(imgContour,objType,
(x+(w//2)-10,y+(h//2)-10),cv2.FONT_HERSHEY_COMPLEX,0.7,
(0,0,0),2)
path = 'python/OpenCVTutorial/resources/shapes.png'
img = cv2.imread(path)
imgContour = img.copy()
imgGray = cv2.cvtColor(img,cv2.COLOR_RGB2GRAY)
imgBlur = cv2.GaussianBlur(imgGray,(7,7),1)
imgCanny = cv2.Canny(imgBlur,50,50)
geContours(imgCanny)
imgBlank = np.zeros_like(img)
imgStack = stackImages(0.4,([img,imgGray,imgBlur],
[imgCanny,imgContour,imgBlank]))
cv2.imshow("Stack",imgStack)
cv2.waitKey(0)
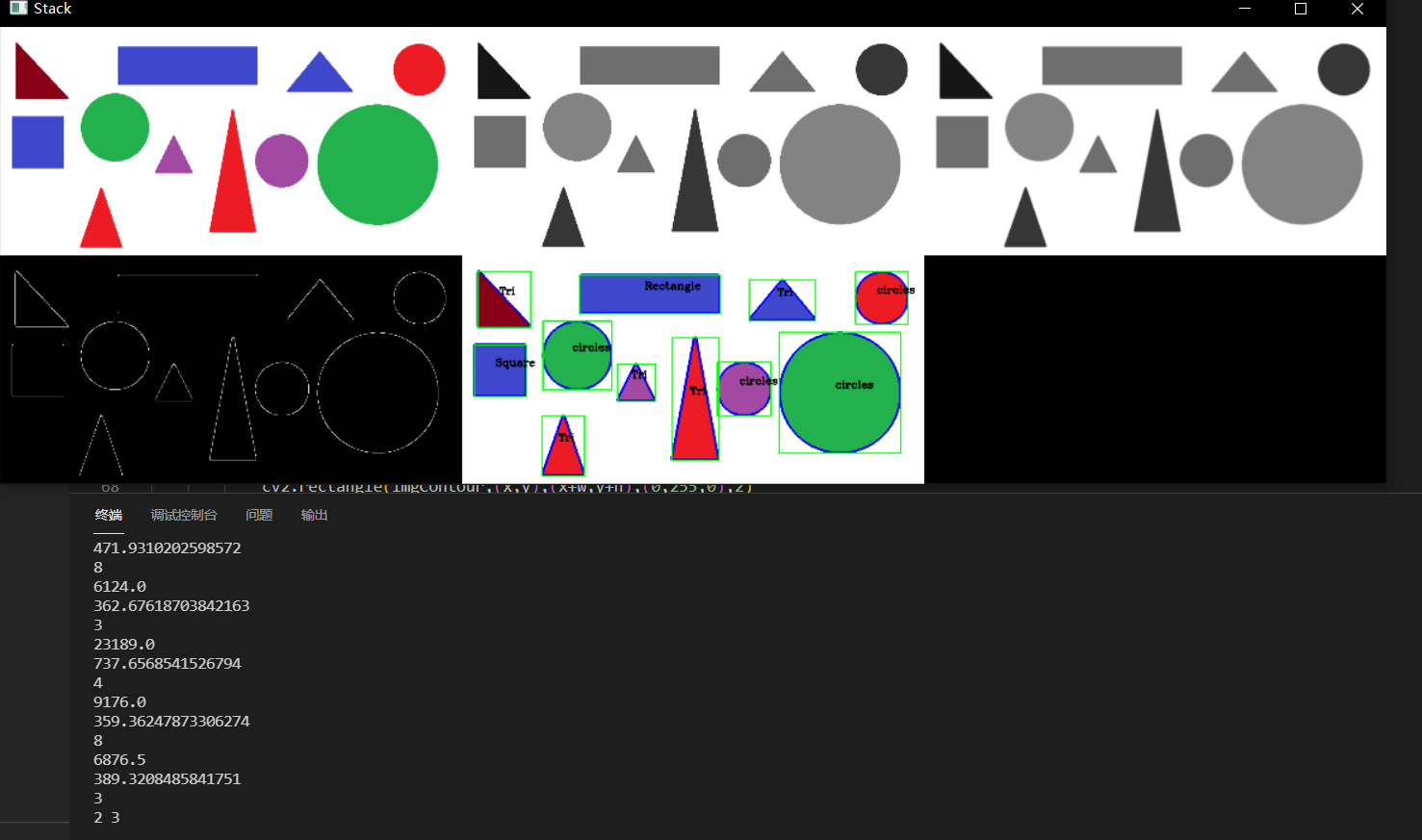
You can see that the last picture recognizes the shape