2021SC@SDUSC
This article is an overview of the overall structure of paddedetection
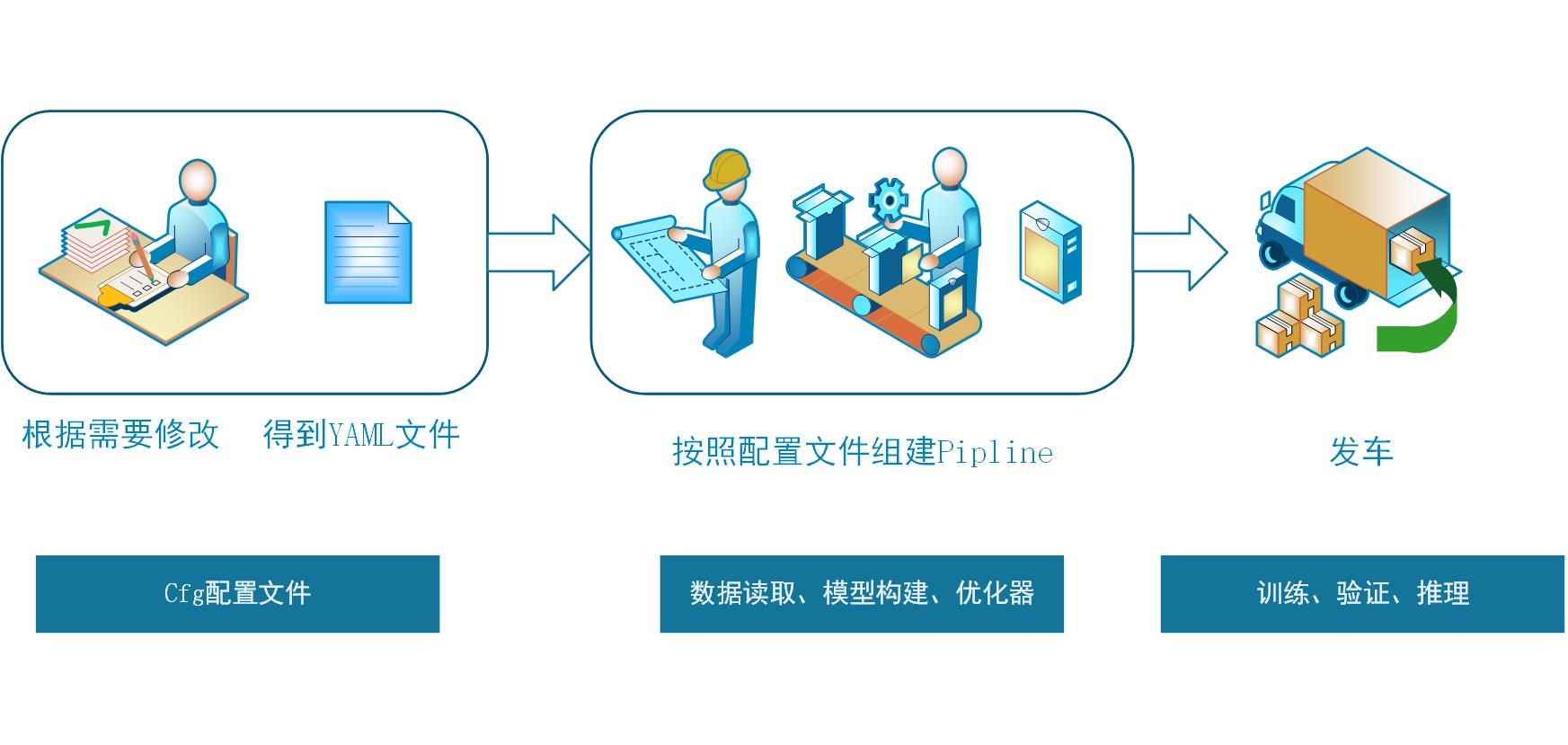
Structure diagram:

The core idea is to form a complete pipline through yaml file by combining the main module and pluggable module for train, eval, infer and export_model. yaml file is equivalent to design drawings. The program will design the structure we want according to our drawings.
Main functions of each folder for storing files:
'''
tree -f#Show full path
tree -d#Show all folders
└── PaddleDetection #home directory
├── configs #Store configuration files
│ ├──_base_ Configuration of each module
├── dataset #Save data sets, Download scripts of data sets, corresponding to each data set folder
│ ├── coco #80 class #object
│ ├── fddb #1 class #Face is usually used to evaluate face detection algorithms
│ ├── mot # Multi target tracking
│ ├── roadsign_voc #Lane line data category 4
│ ├── voc #20 class #object
│ └── wider_face #Class 1 face
├── deploy #Deployment related
│ ├── cpp #C + + deployment
│ │ ├── cmake #cmake file
│ │ ├── docs #Deployment document
│ │ ├── include #Library header file
│ │ ├── scripts #Dependency library configuration script, build script
│ │ └── src #Source code
│ └── python #python deployment
├── ppdet #Propeller object detection kit
│ ├── core #Core part
│ │ └── config #Configuration of instance and registration class
│ ├── data #data processing
│ │ ├── shared_queue #Shared queue (data multithreading)
│ │ ├── source #Various dataset classes
│ │ ├── tests #test
│ │ ├── tools #Tool (to coco data format)
│ │ └── transform #Data enhancement module
│ ├── ext_op #Add op
│ │ ├── src #op implementation source code
│ │ └── test #op test
│ ├── modeling #model structure
│ │ ├── architectures #network structure
│ │ ├── backbones #Backbone network
│ │ ├── heads #Head (RPN, loss)
│ │ ├── losses #Head (loss)
│ │ ├── mot #Multi target tracking
│ │ ├── necks #Neck (FPN)
│ │ ├── proposal_generator #Suggestion box generation (anchor, rpnhead)
│ │ ├── reid #Re identification
│ │ └── tests #test
│ ├── py_op #Some pre-processing and post-processing
│ └── utils #Utilities
└── tools #Training, testing, validation, and model export in the future
'''tools/train.py model training
train execution instance:
!python tools/train.py -c configs/yolov3_darknet53_270e_coco.yml --eval -o use_gpu=true
train.py process analysis:
- Start from the program entry (if# name = ='main ':)
- 1. Directly enter the main function
- Initialize training parameters:
- ①. parser = ArgsParser() # reads the parameters passed from the command line and loads the parameters of yaml file
- ②. Integrate the parameters together and check whether the parameter configuration is correct
- ③. Use GPU acceleration
- ④. Check whether the paddedet version is correct
- ⑤. Enter the run() function
- Configuration phase
- a. System variable configuration, initialization, obtaining the number of GPU s used, etc
- b. Create data reading class
- c. Create network structure class
- d. Create learning rate class
- e. Create optimizer class
- f. Initialize the model weight, load the pre training model, and integrate the model with the optimizer,
- g. Is it multi card, multi instance and multi model parallel training
- Start training
- g. Traverse the data, start cyclic training, and calculate a series of time (remaining time, average training time) according to the time stamp
- h. Model forward reasoning, back propagation, (multi card model parallel, loss merging)
- j. Output log after each iter
- k. Print the log regularly, save the model and optimizer parameters regularly, (eval on: optimal and timing)
- Until the end of the iteration
eval.py process analysis
- Start from the program entry (if# name = ='main ':)
- 1. Directly enter the main function
- Initialize training parameters:
- ①. parser = ArgsParser() # reads the parameters passed from the command line and loads the parameters of yaml file
- ②. Integrate the parameters together and check whether the parameter configuration is correct
- ③. Use GPU acceleration
- ④. Check whether the paddedet version is correct
- ⑤. Enter the run() function
- Configuration phase
- a. Create network structure class
- b. Initialize the model weight and load the pre training model
- c. Create data reading class
- Open evaluation
- d. Traverse the data, turn on forward reasoning, and collect the results
- e. Select Metric evaluation criteria
- f. Output log
- Output the results until the end of the iteration
infer.py process analysis
- Start from the program entry (if# name = ='main ':)
- 1. Directly enter the main function
- Initialize training parameters:
- ①. parser = ArgsParser() # reads the parameters passed from the command line and loads the parameters of yaml file
- ②. Integrate the parameters together and check whether the parameter configuration is correct
- ③. Use GPU acceleration
- ④. Check whether the paddedet version is correct
- ⑤. Enter the run() function
- Configuration phase
- a. Create network structure class
- b. Initialize the model weight and load the pre training model
- c. Create data reading class
- d. Select reasoning criteria
- Turn on reasoning
- e. Traverse the data, turn on forward reasoning, and collect the results
- f. Save reasoning results (box or mask)
- g. Save picture results using VisualDL
- Output the results until the end of the iteration
export_model.py process analysis
- Start from the program entry (if# name = ='main ':)
- 1. Directly enter the main function
- Initialize training parameters:
- ①. Set the cpu environment for execution, parser = ArgsParser() # read the parameters passed from the command line, and load the yaml file parameters
- ②. Convert the parameters in BN into reasoning parameters, integrate the parameters together, and check whether the parameter configuration is correct
- ③. Use GPU acceleration
- ④. Check whether the paddedet version is correct
- ⑤. Enter the run() function
- Configuration phase
- a. Create network structure class
- b. Initialize model weights
- g. Convert to static diagram and save the model