Original website: RabbitMQ--SpringBoot -- Integration / use / usage / instance / example / actual combat_ CSDN blog
Other web sites
Spring AMQP 2.1.2.RELEASE Chinese document - 1. Preface | Docs4dev
RabbitMQ: @ RabbitListener and @ RabbitHandler and message serialization - short book
Several postures of springboot + rabbit MQ
RabbitMQ and SpringBoot integration practice - brief book
annotation
Other web sites
RabbitMQ: @ RabbitListener and @ RabbitHandler and message serialization - short book
@RabbitListener
Used in methods
When the supervisor hears a message in the queue, it will receive and process it. If it does not exist, an error will be reported.
@Component
public class Receiver {
//You can also listen to multiple queues: @ RabbitListener(queues = {"hello", "hi"})
@RabbitListener(queues = "hello")
public void process(String hello) {
System.out.println ("Receiver : " + hello);
}
}@The bindings property of the RabbitListener declares Binding (an error will be reported if the Queue, Exchange and RouteKey required for the Binding do not exist in RabbitMQ)
@RabbitListener(bindings = @QueueBinding(
exchange = @Exchange(value = "topic.exchange",durable = "true",type = "topic"),
value = @Queue(value = "consumer_queue",durable = "true"),
key = "key.#"
))
public void processMessage1(Message message) {
System.out.println(message);
}Used on classes
- To be used with @ RabbitHandler annotation
- @The RabbitListener label on the class indicates that when a message is received, it will be handed over to the method of @ RabbitHandler for processing. The specific method to use for processing is determined according to the parameter type after MessageConverter conversion.
@Component
@RabbitListener(queues = "consumer_queue")
public class Receiver {
@RabbitHandler
public void processMessage1(String message) {
System.out.println(message);
}
@RabbitHandler
public void processMessage2(byte[] message) {
System.out.println(new String(message));
}
}@Payload and @ Headers
Other web sites
Spring AMQP 2.1.2.RELEASE Chinese document - 3. Reference | Docs4dev
RabbitMQ (III) RabbitMQ advanced integrated application - blind scavenger - blog Park
brief introduction
@Headers must be received through Map.
//@Header("amqp_receivedRoutingKey") String rk directly obtains a key in the header
Get the body and headers information in the message
@RabbitListener(queues = "debug")
public void processMessage1(@Payload String body, @Headers Map<String,Object> headers) {
System.out.println("body: "+body);
System.out.println("Headers: "+headers);
}Get a single Header property
@RabbitListener(queues = "debug")
public void processMessage1(@Payload String body, @Header String token) {
System.out.println("body: "+body);
System.out.println("token: "+token);
}binding
Other web sites
SpringBoot integration rabbitmq
brief introduction
1. There are two ways to create switch / queue / binding instances
Switch (the following two methods are equivalent):
ExchangeBuilder.topicExchange(EXCHANGE_TOPIC_WELCOME).durable(true).build(); new TopicExchange(EXCHANGE_TOPIC_WELCOME, true, false)
Queue (the following two methods are equivalent):
QueueBuilder.durable("Hi").build();
new Queue(QUEUE_HI, true)Binding (the following two methods are equivalent):
Note: the first parameter is not a string.
BindingBuilder.bind(helloQueue).to(welcomExchange).with("hello.#")
new Binding("Queue@hello", Binding.DestinationType.QUEUE,
"Exchange@topic.welcome", "hello.#", null)The degree of recommendation decreases in turn.
Method 1: configure by configuration class (concise)
package com.example.config;
import org.springframework.amqp.core.*;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
@Configuration
public class RabbitRouterConfig {
public static final String QUEUE_HELLO = "Queue@hello";
public static final String QUEUE_HI = "Queue@hi";
public static final String EXCHANGE_TOPIC_WELCOME = "Exchange@topic.welcome";
public static final String ROUTINGKEY_HELLOS = "hello.#";
@Autowired
AmqpAdmin amqpAdmin;
@Bean
Object initBindingTest() {
amqpAdmin.declareExchange(new TopicExchange(EXCHANGE_TOPIC_WELCOME, true, false));
amqpAdmin.declareQueue(new Queue(QUEUE_HI, true));
amqpAdmin.declareQueue(new Queue(QUEUE_HELLO, true));
amqpAdmin.declareBinding(new Binding(QUEUE_HELLO, Binding.DestinationType.QUEUE,
EXCHANGE_TOPIC_WELCOME, ROUTINGKEY_HELLOS, null));
return new Object();
}
}amqpAdmin.declareBinding
A Binding object is required as a parameter
- Exchange: exchange name
- Type: exchanger type. The BuiltinExchangeType enumeration class has the following 4 types of switches: DIRECT("direct"), FANOUT("fanout"), TOPIC("topic"), HEADERS("headers")
- durable: sets whether to persist. true: persistent, false: non persistent. Persistence can save the switch to disk, and relevant messages will not be lost when the server is restarted.
- autoDelete: sets whether to delete automatically. true: automatically delete; false: not automatically delete. The premise of automatic deletion is that at least one queue or switch is bound to this switch, and then all queues or switches bound to this switch are unbound from this switch.
- internal: set whether it is built-in. true: built-in switch, false: non built-in switch. Built in switch, the client cannot directly send messages to this switch, and can only route to the switch through the switch.
- arguments: other structured parameters. Such as backup switch: alternate exchange, timeout. Example configuration timeout method:
Map<String, Object> params = new HashMap();
params.put("x-message-ttl", 2000);
amqpAdmin.declareBinding(new Binding(QUEUE_HELLO, Binding.DestinationType.QUEUE,
EXCHANGE_TOPIC_WELCOME, ROUTINGKEY_HELLOS, params));Method 2: configure by configuration class (cumbersome)
Applicable when there are few queues and switches
package com.lly.order.message;
import org.springframework.amqp.core.*;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
@Configuration
public class RabbitMqConfig {
public final static String QUEUE_DIRECT = "Queue@direct";
public final static String QUEUE_TOPIC_ONE = "Queue@topic_one";
public final static String TOPIC_QUEUE_TWO = "Queue@topic_two";
public final static String QUEUE_FANOUT_ONE = "Queue@fanout_one";
public final static String QUEUE_FANOUT_TWO = "Queue@fanout_two";
public final static String EXCHANGE_TOPIC = "Exchange@topic";
public final static String EXCHANGE_FANOUT = "Exchange@fanout";
public final static String ROUTINGKEY_TOPIC_ONE = "hello.key";
public final static String ROUTINGKEY_TOPIC_TWO = "*.key";
// direct mode queue
@Bean
public Queue directQueue() {
return new Queue(QUEUE_DIRECT, true);
}
// topic subscriber mode queue
@Bean
public Queue topicQueueOne() {
return new Queue(QUEUE_TOPIC_ONE, true);
}
@Bean
public Queue topicQueueTwo() {
return new Queue(TOPIC_QUEUE_TWO, true);
}
// fanout broadcaster mode queue
@Bean
public Queue fanoutQueueOne() {
return new Queue(QUEUE_FANOUT_ONE, true);
}
@Bean
public Queue fanoutQueueTwo() {
return new Queue(QUEUE_FANOUT_TWO, true);
}
// topic exchanger
@Bean
public TopicExchange topExchange() {
return new TopicExchange(EXCHANGE_TOPIC);
}
// fanout exchanger
@Bean
public FanoutExchange fanoutExchange() {
return new FanoutExchange(EXCHANGE_FANOUT);
}
// Subscriber mode binding
@Bean
public Binding topicExchangeBingingOne() {
return BindingBuilder.bind(topicQueueOne()).to(topExchange()).with(ROUTINGKEY_TOPIC_ONE);
}
@Bean
public Binding topicExchangeBingingTwo() {
return BindingBuilder.bind(topicQueueTwo()).to(topicExchange()).with(ROUTINGKEY_TOPIC_TWO);
}
// Broadcast mode binding
@Bean
public Binding fanoutExchangeBingingOne() {
return BindingBuilder.bind(fanoutQueueOne()).to(fanoutExchange());
}
@Bean
public Binding fanoutExchangeBingingTwo() {
return BindingBuilder.bind(fanoutQueueTwo()).to(fanoutExchange());
}
}Method 3: configure by code
@Component
public class Receiver {
@RabbitListener(queues = "hello")
public void process(String hello) {
System.out.println ("Receiver : " + hello);
}
@RabbitListener(bindings = @QueueBinding(
exchange = @Exchange(value = "Exchange@topic.Hello",durable = "true",type = "topic"),
value = @Queue(value = "Queue@Hello",durable = "true"),
key = "key.#"
))
public void processMessage1(Message message) {
System.out.println(message);
}
}Method 4: configure through MQ web page
Add switch: http://localhost:15672/#/exchanges // For example: Exchange@topic.Hello
Add queue: http://localhost:15672/#/queues // For example: Queue@Hello
Add routing key to switch: http://localhost:15672/#/exchanges =>Click switch name = > binding = > Add queue and route
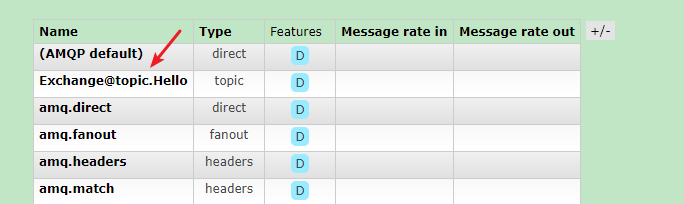
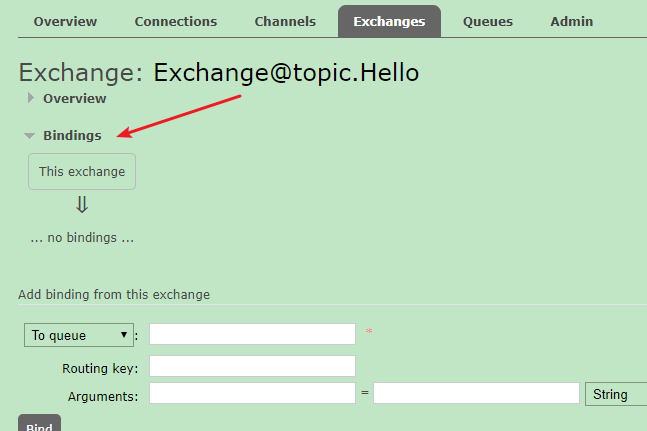
to configure
RabbitTemplate configuration
| example | effect |
| rabbitTemplate.setConfirmCallback(rabbitConfirmCallback); | Set the confirm callback function. |
| rabbitTemplate.setReturnCallback(rabbitReturnCallback); | Set the return callback function. |
| rabbitTemplate.setMandatory(true); | When mandatory is set to true, if exchange cannot find a suitable queue to store the message according to its own type and message routingKey, the broker will call the basic.return method to return the message to the producer. When the mandatory is set to false, the broker will directly discard the message when the above situation occurs. |
| rabbitTemplate.setUsePublisherConnection(true); | Use a separate sending connection to avoid the same blocking of consumers due to the blocking of producers for various reasons |
example
Operation RabbitMQ
Start RabbitMQ
Command line run:
rabbitmq-server.bat
//For the first time, run rabbitmq-plugins.bat enable rabbitmq_management
Configure an administrator user
User name: admin Password: 123456
The permissions are configured as:/
See: RabbitMQ series - Overview_ feiying0canglang's blog - CSDN blog
code
rely on
<dependency> <groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId> <artifactId>spring-boot-starter-amqp</artifactId> </dependency>
application.yml
server:
# port: 9100
port: 9101
spring:
application:
# name: demo-rabbitmq-sender
name: demo-rabbitmq-receiver
rabbitmq:
host: localhost
port: 5672
username: admin
password: 123456
# virtualHost: /Queue configuration
package com.example.config;
import org.springframework.amqp.core.*;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
@Configuration
public class RabbitRouterConfig {
public static final String QUEUE_HELLO = "Queue@hello";
public static final String QUEUE_HI = "Queue@hi";
public static final String EXCHANGE_TOPIC_WELCOME = "Exchange@topic.welcome";
public static final String ROUTINGKEY_HELLOS = "hello.#";
@Autowired
AmqpAdmin amqpAdmin;
@Bean
Object initBindingTest() {
amqpAdmin.declareExchange(new TopicExchange(EXCHANGE_TOPIC_WELCOME, true, false));
amqpAdmin.declareQueue(new Queue(QUEUE_HI, true));
amqpAdmin.declareQueue(new Queue(QUEUE_HELLO, true));
amqpAdmin.declareBinding(new Binding(QUEUE_HELLO, Binding.DestinationType.QUEUE,
EXCHANGE_TOPIC_WELCOME, ROUTINGKEY_HELLOS, null));
return new Object();
}
}Controller
package com.example.controller;
import com.example.config.RabbitConfig;
import com.example.mq.Sender;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.PostMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestController;
import java.time.LocalDateTime;
@RestController
public class HelloController {
@Autowired
private Sender sender;
@PostMapping("/hi")
public void hi() {
sender.send(RabbitConfig.QUEUE_HI, "hi1 message:" + LocalDateTime.now());
}
@PostMapping("/hello1")
public void hello1() {
sender.send("hello.a", "hello1 message:" + LocalDateTime.now());
}
@PostMapping("/hello2")
public void hello2() {
sender.send("Exchange@topic.welcome","hello.b", "hello2 message:" + LocalDateTime.now());
}
}
sender
package com.example.mq;
import org.springframework.amqp.core.AmqpTemplate;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
import java.util.Date;
@Component
public class Sender {
@Autowired
private AmqpTemplate rabbitTemplate;
public void send(String routingKey, String message) {
this.rabbitTemplate.convertAndSend(routingKey, message);
}
public void send(String exchange, String routingKey, String message) {
this.rabbitTemplate.convertAndSend(exchange, routingKey, message);
}
}receiver
package com.example.mq;
import com.example.config.RabbitRouterConfig;
import com.rabbitmq.client.Channel;
import org.springframework.amqp.core.Message;
import org.springframework.amqp.rabbit.annotation.RabbitListener;
import org.springframework.messaging.handler.annotation.Payload;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
@Component
public class Receiver {
@RabbitListener(queues = RabbitRouterConfig.QUEUE_HELLO)
public void hello(String hello) {
System.out.println ("Receiver(hello) : " + hello);
}
@RabbitListener(queues = RabbitRouterConfig.QUEUE_HI)
public void hi(String payload) {
System.out.println ("Receiver(hi) : " + payload);
throw new RuntimeException("Manual abnormality");
}
// @RabbitListener(queues = RabbitRouterConfig.QUEUE_HELLO)
// public void helloAll(@Payload String payload, Message message, Channel channel) {
// System.out.println("Receiver(hello): ");
// System.out.println("payload:" + payload);
// System.out.println("message:" + message);
// System.out.println("channel:" + channel);
// }
// @RabbitListener(queues = RabbitRouterConfig.QUEUE_HI)
// public void hiAll(@Payload String payload, Message message, Channel channel) {
// System.out.println("Receiver(hi): ");
// System.out.println("payload:" + payload);
// System.out.println("message:" + message);
// System.out.println("channel:" + channel);
// }
}
Basic test
Run sender
server:
port: 9100
# port: 9101
spring:
application:
name: demo-rabbitmq-sender
# name: demo-rabbitmq-receiver
rabbitmq:
host: localhost
port: 5672
username: admin
password: 123456
# virtualHost: /Run receiver
server:
# port: 9100
port: 9101
spring:
application:
# name: demo-rabbitmq-sender
name: demo-rabbitmq-receiver
rabbitmq:
host: localhost
port: 5672
username: admin
password: 123456
# virtualHost: /MQ page
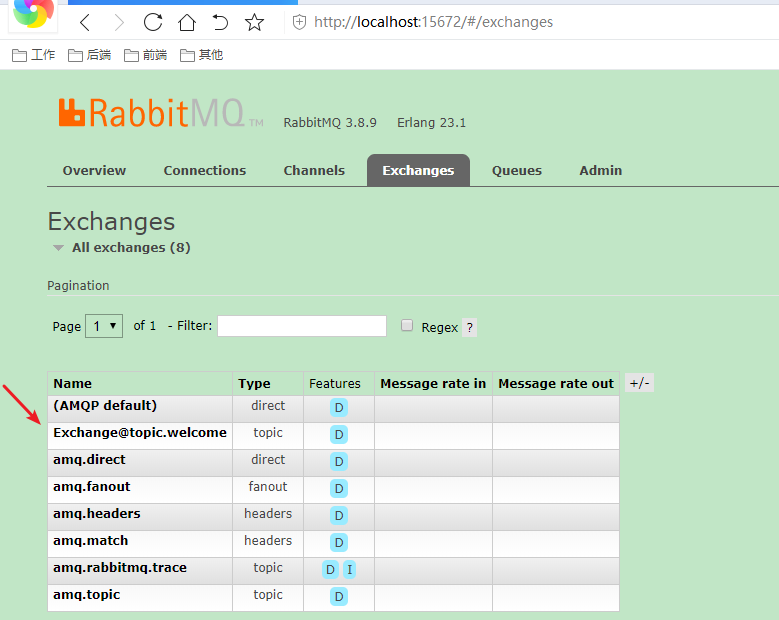
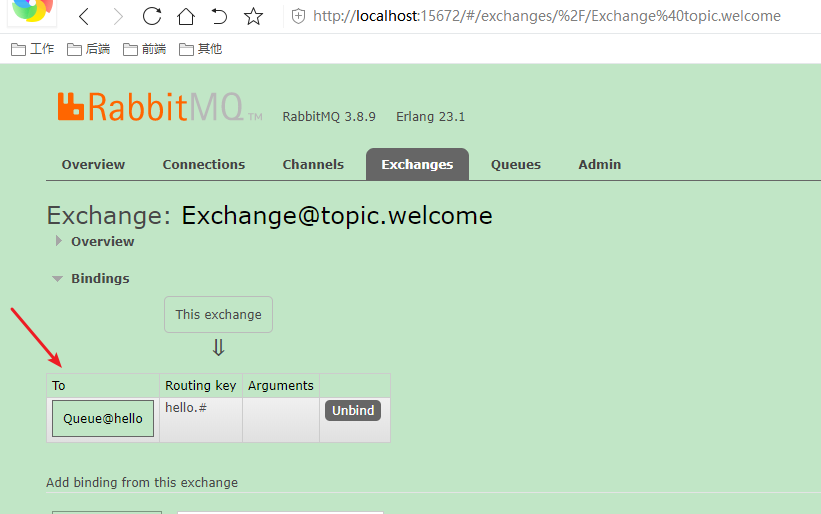
Test data only (payload)
postman access: Node Exporter
receiver print results
Receiver(hi) : hi message:2020-10-21T18:52:24.766
postman access: Node Exporter
receiver print result: no print
That is, if the queue has been bound to the switch, the switch and routing key must be specified.
postman access: Node Exporter
receiver print results
Receiver(hello) : hello2 message:2020-10-21T18:52:41.434
Test details
Test to get payload/message/channel
Use the second code of the receiver.
postman access: Node Exporter
receiver print results
Receiver(hi):
payload:hi1 message:2020-10-22T15:41:11.796
message:(Body:'hi1 message:2020-10-22T15:41:11.796' MessageProperties [headers={}, contentType=text/plain, contentEncoding=UTF-8, contentLength=0, receivedDeliveryMode=PERSISTENT, priority=0, redelivered=false, receivedExchange=, receivedRoutingKey=Queue@hi, deliveryTag=1, consumerTag=amq.ctag-K0Yka5vHxrq6JzNXlg3ncQ, consumerQueue=Queue@hi])
channel:Cached Rabbit Channel: AMQChannel(amqp://admin@127.0.0.1:5672/,1), conn: Proxy@4f4c88f9 Shared Rabbit Connection: SimpleConnection@7c52fc81 [delegate=amqp://admin@127.0.0.1:5672/, localPort= 62067]postman access: Node Exporter
receiver print result: no print
That is, if the queue has been bound to the switch, the switch and routing key must be specified.
postman access: Node Exporter
receiver print results
Receiver(hello):
payload:hello2 message:2020-10-22T15:42:13.126
message:(Body:'hello2 message:2020-10-22T15:42:13.126' MessageProperties [headers={}, contentType=text/plain, contentEncoding=UTF-8, contentLength=0, receivedDeliveryMode=PERSISTENT, priority=0, redelivered=false, receivedExchange=Exchange@topic.welcome, receivedRoutingKey=hello.b, deliveryTag=1, consumerTag=amq.ctag-yZryIR801zNV5f0f9mJd9g, consumerQueue=Queue@hello])
channel:Cached Rabbit Channel: AMQChannel(amqp://admin@127.0.0.1:5672/,2), conn: Proxy@4f4c88f9 Shared Rabbit Connection: SimpleConnection@7c52fc81 [delegate=amqp://admin@127.0.0.1:5672/, localPort= 62067]