react source code analysis 7.Fiber architecture
Video Explanation (efficient learning): Click to learn
Previous articles:
1. Introduction and interview questions
3.react source code architecture
4. Source directory structure and debugging
6.legacy and concurrent mode entry functions
20. Summary & answers to interview questions in Chapter 1
Fiber's deep understanding
The reconcile of react15 in the render phase cannot be interrupted, which may cause a jam when reconciling a large number of nodes, because the browser is handed over to js for execution all the time, and js is executed in a single thread. Therefore, after react16, there is a scheduler to schedule the time slice and give each task (work unit) a certain time. If it is not executed within this time, it is also necessary to hand over the execution right to the browser for drawing and rearrangement. Therefore, asynchronous and interruptible updates need a certain data structure to save the information of the work unit in memory. This data structure is Fiber.
So what can be done with the Fiber data structure,
- Work unit task decomposition: Fiber's most important function is to save the corresponding information (including priority) of native nodes or component nodes as work units. These nodes form a Fiber tree through the shape of pointers
- Incremental rendering: through the comparison between jsx object and current Fiber, the minimum difference patch is generated and applied to real nodes
- Pause, resume, and arrange priorities according to priority: the Fiber node saves priorities, which enables tasks to pause, resume, and arrange priorities by comparing the priorities of different nodes. It also provides a basis for the upper layer to realize batch update and suspend
- Save state: because Fiber can save state and updated information, it can update the state of function components, that is, hooks
Data structure of Fiber
The built-in properties of Fiber are as follows:
//ReactFiber.old.js
function FiberNode(
tag: WorkTag,
pendingProps: mixed,
key: null | string,
mode: TypeOfMode,
) {
//Save node information as a static data structure
this.tag = tag;//Type of corresponding component
this.key = key;//key attribute
this.elementType = null;//Element type
this.type = null;//func or class
this.stateNode = null;//Real dom node
//As the number of fibers, the architecture is connected into a fiber tree
this.return = null;//Point to parent node
this.child = null;//Point to child
this.sibling = null;//Point to sibling node
this.index = 0;
this.ref = null;
//Use as a unit of work to calculate state
this.pendingProps = pendingProps;
this.memoizedProps = null;
this.updateQueue = null;
this.memoizedState = null;
this.dependencies = null;
this.mode = mode;
//effect related
this.effectTag = NoEffect;
this.nextEffect = null;
this.firstEffect = null;
this.lastEffect = null;
//Priority related attributes
this.lanes = NoLanes;
this.childLanes = NoLanes;
//Pointers to current and workInProgress
this.alternate = null;
}Fiber dual cache
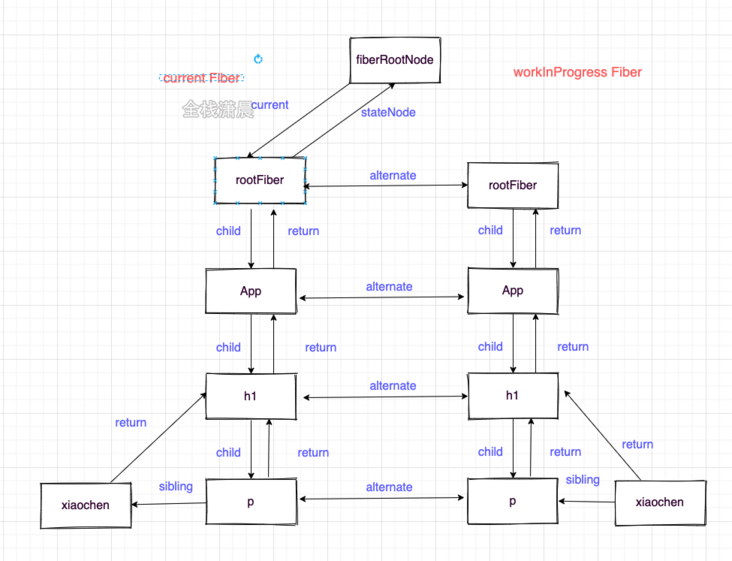
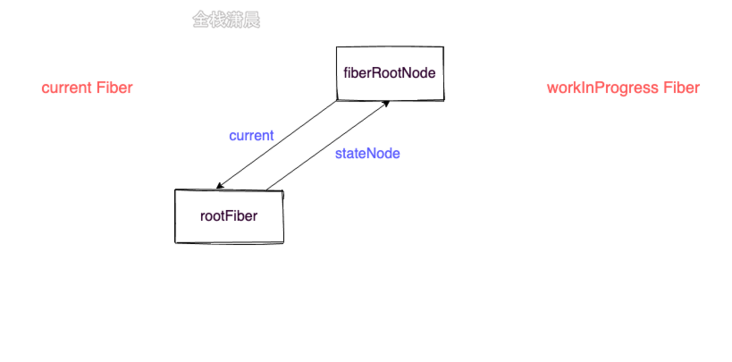
Now we know that Fiber can save the real dom, and the Fiber node corresponding to the real dom in memory will form a Fiber tree. This Fiber tree is called current Fiber in react, that is, the Fiber tree corresponding to the current dom tree, and the Fiber tree under construction is called workInProgress Fiber. The nodes of the two trees are connected through alternate
function App() {
return (
<>
<h1>
<p>count</p> xiaochen
</h1>
</>
)
}
ReactDOM.render(<App />, document.getElementById("root"));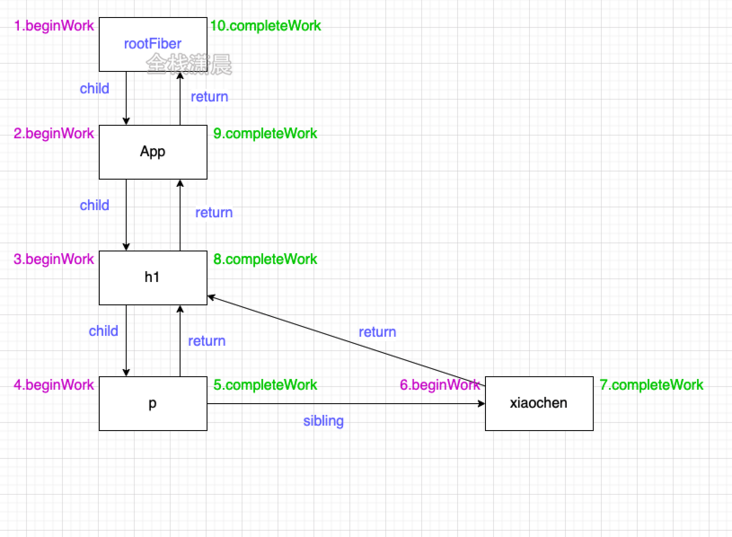
Building workInProgress Fiber occurs in createWorkInProgress, which can create or take Fiber
//ReactFiber.old.js
export function createWorkInProgress(current: Fiber, pendingProps: any): Fiber {
let workInProgress = current.alternate;
if (workInProgress === null) {//Distinguish between mount and update
workInProgress = createFiber(
current.tag,
pendingProps,
current.key,
current.mode,
);
workInProgress.elementType = current.elementType;
workInProgress.type = current.type;
workInProgress.stateNode = current.stateNode;
workInProgress.alternate = current;
current.alternate = workInProgress;
} else {
workInProgress.pendingProps = pendingProps;//Reuse attribute
workInProgress.type = current.type;
workInProgress.flags = NoFlags;
workInProgress.nextEffect = null;
workInProgress.firstEffect = null;
workInProgress.lastEffect = null;
//...
}
workInProgress.childLanes = current.childLanes;//Reuse attribute
workInProgress.lanes = current.lanes;
workInProgress.child = current.child;
workInProgress.memoizedProps = current.memoizedProps;
workInProgress.memoizedState = current.memoizedState;
workInProgress.updateQueue = current.updateQueue;
const currentDependencies = current.dependencies;
workInProgress.dependencies =
currentDependencies === null
? null
: {
lanes: currentDependencies.lanes,
firstContext: currentDependencies.firstContext,
};
workInProgress.sibling = current.sibling;
workInProgress.index = current.index;
workInProgress.ref = current.ref;
return workInProgress;
}- During mount: fiberRoot and rootFiber will be created, and then Fiber nodes will be created according to jsx objects, and the nodes will be connected into a current Fiber tree.
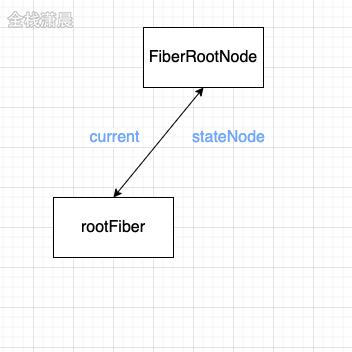
During update: jsx (render of ClassComponent or return value of FuncComponent) and current Fiber will be formed into a Fiber tree called workInProgress according to the new state (diff algorithm), and then the current of fiberRoot will point to the workInProgress tree. At this time, workInProgress will become current Fiber. fiberRoot: refers to the root node of the entire application. There is only one
fiberRoot: refers to the root node of the entire application. There is only one
rootFiber: ReactDOM.render or reactdom.unstable_ There can be multiple application nodes created by createroot.
We now know that there are two fiber trees, current Fiber and workInProgress Fiber. Fiber dual cache means that a new workInProgress Fiber is formed after reconciling (diff), and then the workInProgress Fiber is switched to current Fiber and applied to the real dom. The advantage of dual fiber is that the description of the view is formed in memory and finally applied to the dom, Reduced DOM operations.
Now let's take a look at the process diagram of Fiber dual cache creation:
When mount:
- At the beginning, only two nodes, fiberRoot and rootFiber, were created
- Then create workInProgress Fiber according to jsx:
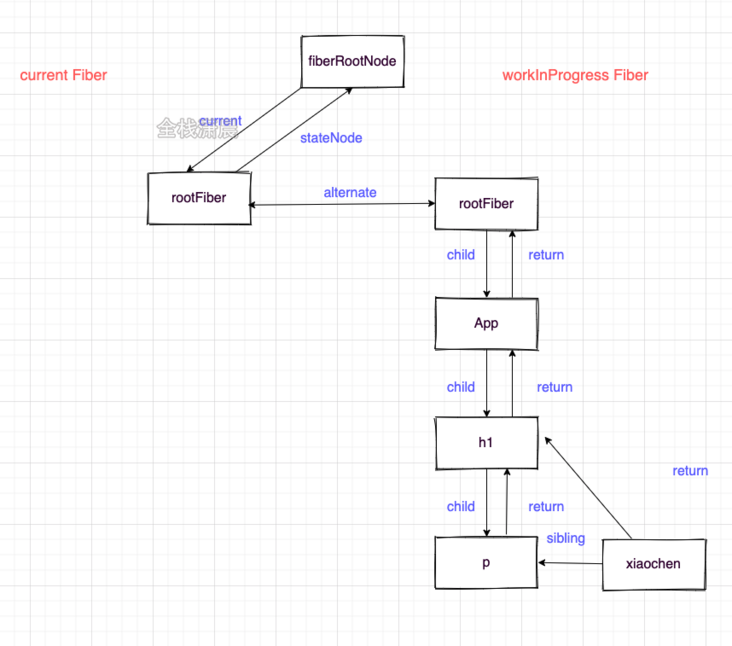
- Switch workInProgress Fiber to current Fiber
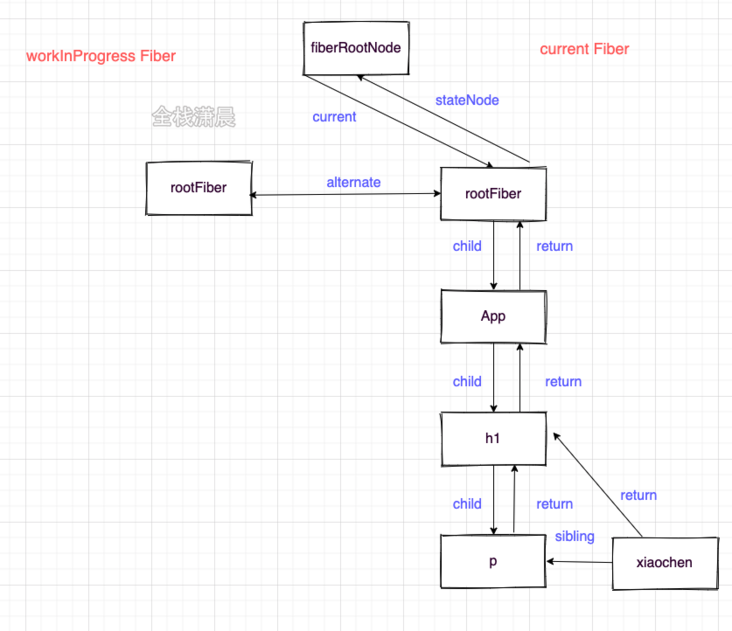
- At the beginning, only two nodes, fiberRoot and rootFiber, were created
update
- Create workInProgress Fiber based on current Fiber
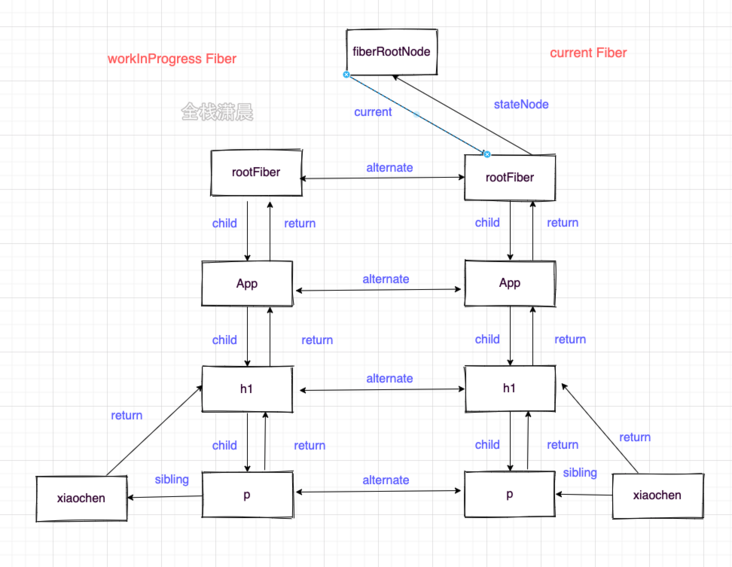
- Switch workInProgress Fiber to current Fiber
- Create workInProgress Fiber based on current Fiber