ROS project development process
Create workspace - > create function package - > create source code (Python / C + +) - > configure Compilation Rules - > compile and run
Workspace
src: source space
Build: build space [intermediate file]
Development: executable space
Install: install space
Detect environment variables
laniakea@laniakea-virtual-machine >>> echo $ROS_PACKAGE_PATH /home/laniakea/learn_GY0/catkin_ws/src:/opt/ros/melodic/share
Observe catkin_ lib folder in devel under WS
Place the compiled executable
. sh and bash setting script for environment variables
Placing function packs under src
Function package creation
catkin_create_pkg <package_name> [depend1] [depend2] [depend3]
Dependent-n: options on which the function pack depends
std_ Msgs: message interface defined in ROS standard
std_ Srvs: service interface defined in ROS standard
When you see a folder with cmakelists Txt and package XML, it must be a function package
<build_depend>message_generation</build_depend> <!-- Compile dependency --> <exec_depend>message_runtime</exec_depend> <!-- Run dependency -->
ROS Topic communication programming
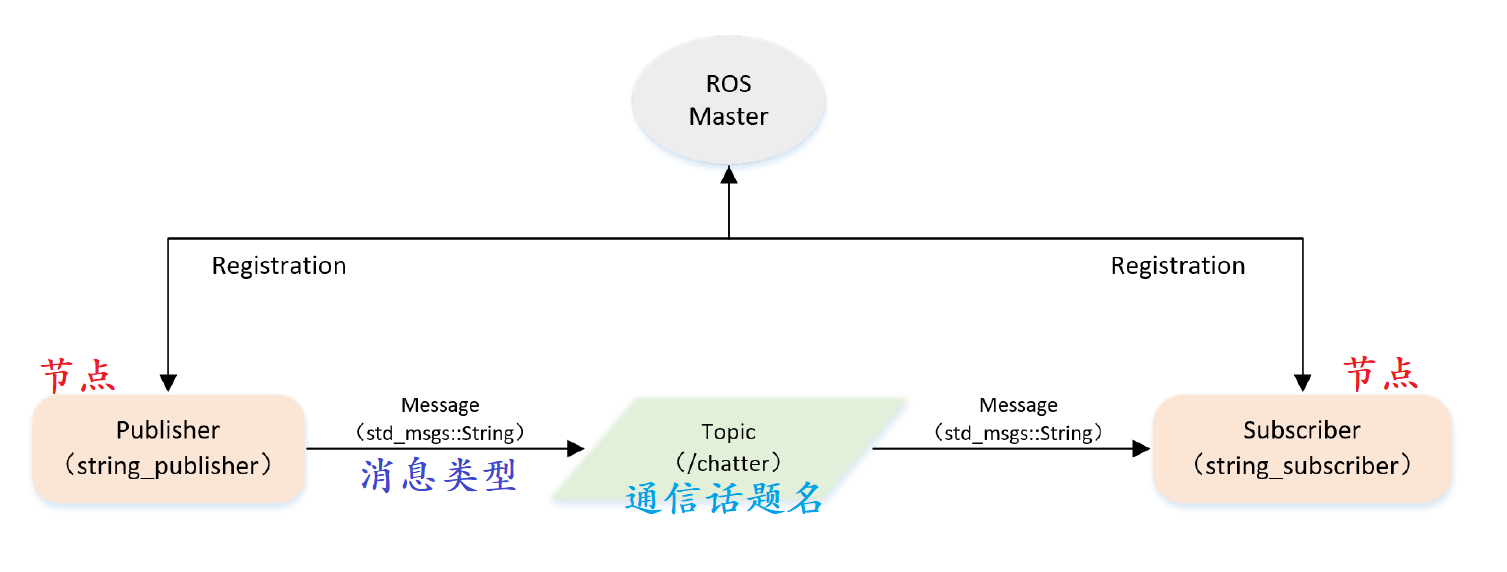
Publisher
- Initialize ROS node;
- Register the node information with the ROS Master, including the published topic name and the message type in the topic;
- Create message data;
- Circularly publish messages according to a certain frequency.
string_publisher.cpp
/**
* This routine will publish chatter topic, and the message type is String
*/
#include <sstream>
#include "ros/ros.h"
#include "std_msgs/String.h"
int main(int argc, char **argv)
{
// ROS node initialization
ros::init(argc, argv, "string_publisher");
// Create node handle
ros::NodeHandle n;
// Create a Publisher, publish topic named chatter, and the message type is std_msgs::String
// "chatter" topic name
// Buffer size
// Create Publisher from handle
ros::Publisher chatter_pub = n.advertise<std_msgs::String>("chatter", 1000);
// Set the frequency of the cycle
// 10 times per second at 10Hz
ros::Rate loop_rate(10);
int count = 0;
while (ros::ok())
{
// Initialize std_msgs::String type message
std_msgs::String msg;
std::stringstream ss;
ss << "hello world " << count;
msg.data = ss.str();
// Release news
ROS_INFO("%s", msg.data.c_str());
chatter_pub.publish(msg);
// Delay according to cycle frequency
loop_rate.sleep(); // 100ms
// If the above program is executed for 10ms, it only sleeps for 90ms
++count;
}
return 0;
}
subscriber
- Initialize ROS node;
- Subscribe to topics needed;
- Loop waiting for topic message, received
- Enter the callback function after the message;
- Complete the message processing in the callback function.
string_subscriber.cpp
/**
* This routine will subscribe to chatter topic, and the message type is String
*/
#include "ros/ros.h"
#include "std_msgs/String.h"
// After receiving the subscribed message, it will enter the message callback function - > data processing
// const constant pointer
// std_msgs::String message type
void chatterCallback(const std_msgs::String::ConstPtr& msg)
{
// Print the received message
ROS_INFO("I heard: [%s]", msg->data.c_str());
}
int main(int argc, char **argv)
{
// Initialize ROS node
ros::init(argc, argv, "string_subscriber");
// Create node handle
ros::NodeHandle n;
// Create a Subscriber, subscribe to topic named chatter, and register the callback function chatterCallback
// The buffer of Subscriber is not necessarily the same as that of Publisher
// Because you don't know the sending frequency of Publisher, you need to query all the time, so you need a callback function
ros::Subscriber sub = n.subscribe("chatter", 1000, chatterCallback);
// Loop waiting callback function
ros::spin();
return 0;
}
Configure cmakelists txt
- Set the code to be compiled and the generated executable file;
- Set up link library;
add_executable(string_publisher src/string_publisher.cpp)
add_executable(string_subscriber src/string_subscriber.cpp)
target_link_libraries(string_publisher ${catkin_LIBRARIES})
target_link_libraries(string_subscriber ${catkin_LIBRARIES})
Custom message interface
tree
.
├── CMakeLists.txt
├── include
│ └── learning_communication
├── msg # Store message definition file
│ └── PersonMsg.msg
├── package.xml
└── src
├── string_publisher.cpp
└── string_subscriber.cpp
4 directories, 5 files
PersonMsg.msg
string name
uint8 age
uint8 sex
uint8 unknown = 0
uint8 male = 1
uint8 female = 2
In package Add in XML
<build_depend>message_generation</build_depend> <exec_depend>message_runtime</exec_depend>
At cmakelists Txt
... # Find dependent packages find_package(catkin REQUIRED COMPONENTS roscpp rospy std_msgs std_srvs message_ generation # Dynamic message generation function package ) ... # Dynamically generate header file add_message_files(FILES PersonMsg.msg) generate_messages(DEPENDENCIES std_msgs) ... catkin_package( # INCLUDE_DIRS include # LIBRARIES learning_communication CATKIN_DEPENDS roscpp rospy std_msgs std_srvs message_runtime # DEPENDS system_lib )
A personmsg. Will be generated in devel H header file
person_publisher.cpp
/**
* This routine will subscribe to / person_info topic, custom message type, learning_communication::PersonMsg
*/
#include <ros/ros.h>
#include "learning_communication/PersonMsg.h"
// After receiving the subscribed message, it will enter the message callback function
void personInfoCallback(const learning_communication::PersonMsg::ConstPtr& msg)
{
// Print the received message
ROS_INFO("Subcribe Person Info: name:%s age:%d sex:%d",
msg->name.c_str(), msg->age, msg->sex);
}
int main(int argc, char **argv)
{
// Initialize ROS node
ros::init(argc, argv, "person_subscriber");
// Create node handle
ros::NodeHandle n;
// Create a Subscriber named / person_info topic, register the callback function personInfoCallback
ros::Subscriber person_info_sub = n.subscribe("/person_info", 10, personInfoCallback);
// Loop waiting callback function
ros::spin();
return 0;
}
person_subscriber.cpp
/**
* This routine will subscribe to / person_info topic, custom message type, learning_communication::PersonMsg
*/
#include <ros/ros.h>
#include "learning_communication/PersonMsg.h"
// After receiving the subscribed message, it will enter the message callback function
void personInfoCallback(const learning_communication::PersonMsg::ConstPtr& msg)
{
// Print the received message
ROS_INFO("Subcribe Person Info: name:%s age:%d sex:%d",
msg->name.c_str(), msg->age, msg->sex);
}
int main(int argc, char **argv)
{
// Initialize ROS node
ros::init(argc, argv, "person_subscriber");
// Create node handle
ros::NodeHandle n;
// Create a Subscriber named / person_info topic, register the callback function personInfoCallback
ros::Subscriber person_info_sub = n.subscribe("/person_info", 10, personInfoCallback);
// Loop waiting callback function
ros::spin();
return 0;
}
At cmakelists Txt
...
add_executable(person_publisher src/person_publisher.cpp)
add_executable(person_subscriber src/person_subscriber.cpp)
...
# Path to dynamically generate header file
add_dependencies(person_publisher ${PROJECT_NAME}_gencpp)
add_dependencies(person_subscriber ${PROJECT_NAME}_gencpp)
...
target_link_libraries(person_publisher ${catkin_LIBRARIES})
target_link_libraries(person_subscriber ${catkin_LIBRARIES})
ROS Service communication programming
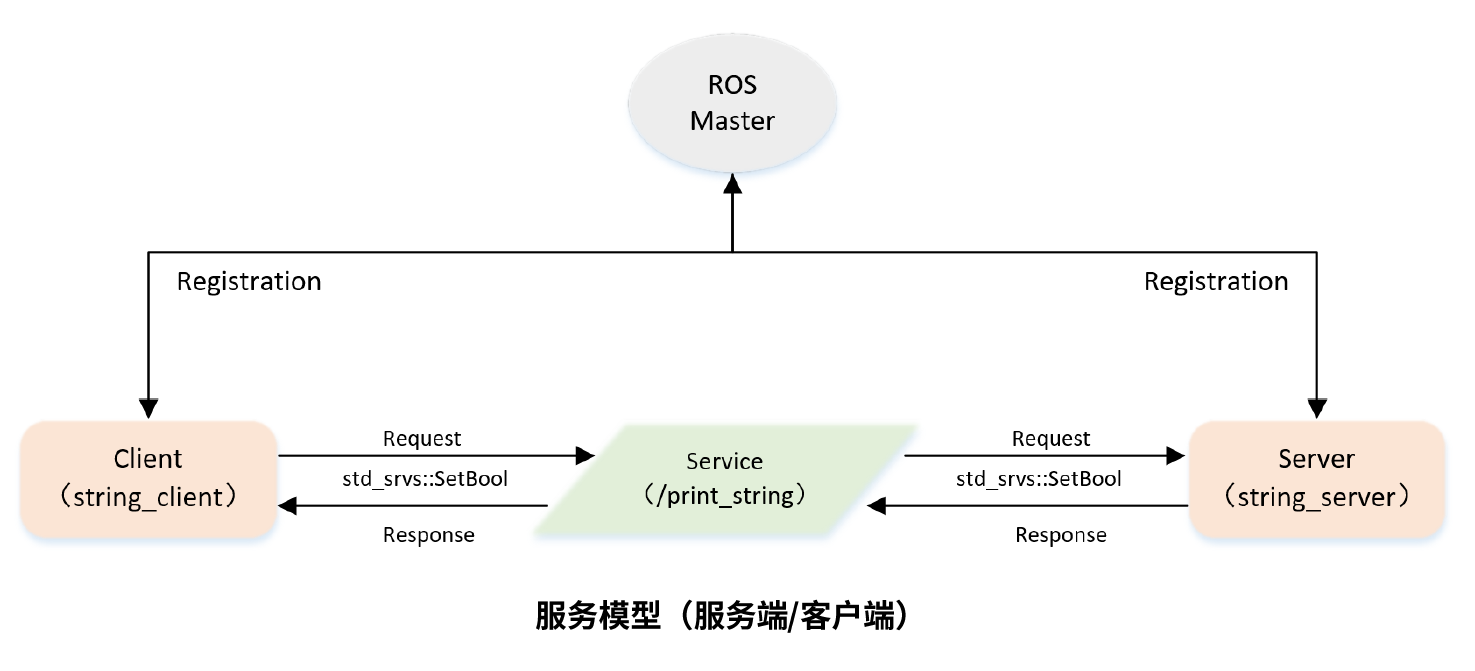
$rossrv show std_srvs/SetBool bool data # request send --- # Distinguish the contents of request and response # response feedback bool success string message
Implementation server
- Initialize ROS node;
- Create a Server instance;
- Wait for the service request circularly and enter the callback function;
- Complete the processing of the service function in the callback function and feed back the response data.
string_client.cpp
/**
* This routine will request print_string service, std_srvs::SetBool
*/
#include "ros/ros.h"
#Include "std_srvs / setbool. H" / / standard service interface definition in ROS
int main(int argc, char **argv)
{
// ROS node initialization
ros::init(argc, argv, "string_client");
// Create node handle
ros::NodeHandle n;
// Create a client, and the service message type is std_srvs::SetBool
ros::ServiceClient client = n.serviceClient<std_srvs::SetBool>("print_string");
// Create STD_ Srvs:: service message of type setbool
// Encapsulate the service message of the client
std_srvs::SetBool srv;
srv.request.data = true;
// Issue a service request and wait for the response result
// client.call(srv) blocks the function until the service gives a response
if (client.call(srv))
{
ROS_INFO("Response : [%s] %s", srv.response.success?"True":"False",
srv.response.message.c_str());
}
else
{
ROS_ERROR("Failed to call service print_string");
return 1;
}
return 0;
}
Implementation client
- Initialize ROS node;
- Create a Client instance;
- Publish service request data;
- Wait for the response result after Server processing.
string_server.cpp
/**
* This routine will provide print_string service, std_srvs::SetBool
*/
#include "ros/ros.h"
#include "std_srvs/SetBool.h"
// service callback function, input parameter req, output parameter res
bool print(std_srvs::SetBool::Request &req,
std_srvs::SetBool::Response &res)
{
// Print string
if(req.data)
{
ROS_INFO("Hello ROS!");
res.success = true;
res.message = "Print Successully";
}
else
{
res.success = false;
res.message = "Print Failed";
}
return true;
}
int main(int argc, char **argv)
{
// ROS node initialization
ros::init(argc, argv, "string_server");
// Create node handle
ros::NodeHandle n;response
// Create a file called print_string server, register the callback function print()
// Once a service enters (a node sends a service request), it enters the print callback function
ros::ServiceServer service = n.advertiseService("print_string", print);
// Loop waiting callback function
ROS_INFO("Ready to print hello string.");
ros::spin();
return 0;
}
At cmakelists Txt
...
add_executable(string_client src/string_client.cpp)
add_executable(string_server src/string_server.cpp)
...
target_link_libraries(string_client ${catkin_LIBRARIES})
target_link_libraries(string_server ${catkin_LIBRARIES})
Custom service
In learning_ Create srv folder under communication folder
Customization file personsrv srv
string name uint8 age uint8 sex uint8 unknown = 0 uint8 male = 1 uint8 female = 2 --- string result
person_client1
/**
* This routine will request / show_person service, service data type learning_communication::PersonSrv
*/
#include <ros/ros.h>
#include "learning_communication/PersonSrv.h"
int main(int argc, char** argv)
{
// Initialize ROS node
ros::init(argc, argv, "person_client");
// Create node handle
ros::NodeHandle node;
// After discovering the / spawn service, create a service client and connect to the service named / spawn
ros::service::waitForService("/show_person");
ros::ServiceClient person_client = node.serviceClient<learning_communication::PersonSrv>("/show_person");
// Initialize learning_ Request data of communication:: person
learning_communication::PersonSrv srv;
srv.request.name = "Tom";
srv.request.age = 20;
// In the srv file --- the above will generate the request namespace, and the following will generate the response namespace
srv.request.sex = learning_communication::PersonSrv::Request::male;
// Request service call
ROS_INFO("Call service to show person[name:%s, age:%d, sex:%d]",
srv.request.name.c_str(), srv.request.age, srv.request.sex);
// call(srv) sends a service request
// Wait for the result of the server response
person_client.call(srv);
// Display service call results
ROS_INFO("Show person result : %s", srv.response.result.c_str());
return 0;
};
person_server1
/**
* This routine will execute / show_person service, service data type learning_communication::PersonSrv
*/
#include <ros/ros.h>
#include "learning_communication/PersonSrv.h"
// service callback function, input parameter req, output parameter res
bool personCallback(learning_communication::PersonSrv::Request &req,
learning_communication::PersonSrv::Response &res)
{
// Display request data
ROS_INFO("Person: name:%s age:%d sex:%d", req.name.c_str(), req.age, req.sex);
// Set feedback data
res.result = "OK";
return true;
}
int main(int argc, char **argv)
{
// ROS node initialization
ros::init(argc, argv, "person_server");
// Create node handle
ros::NodeHandle n;
// Create a file named / show_ The server of person registers the callback function personCallback
ros::ServiceServer person_service = n.advertiseService("/show_person", personCallback);
// Loop waiting callback function
ROS_INFO("Ready to show person informtion.");
ros::spin();
return 0;
}
add_service_files(
FILES
PersonSrv.srv
)
...
add_dependencies(person_client1 ${PROJECT_NAME}_gencpp)
add_dependencies(person_server1 ${PROJECT_NAME}_gencpp)
...
target_link_libraries(person_client1 ${catkin_LIBRARIES})
target_link_libraries(person_server1 ${catkin_LIBRARIES})