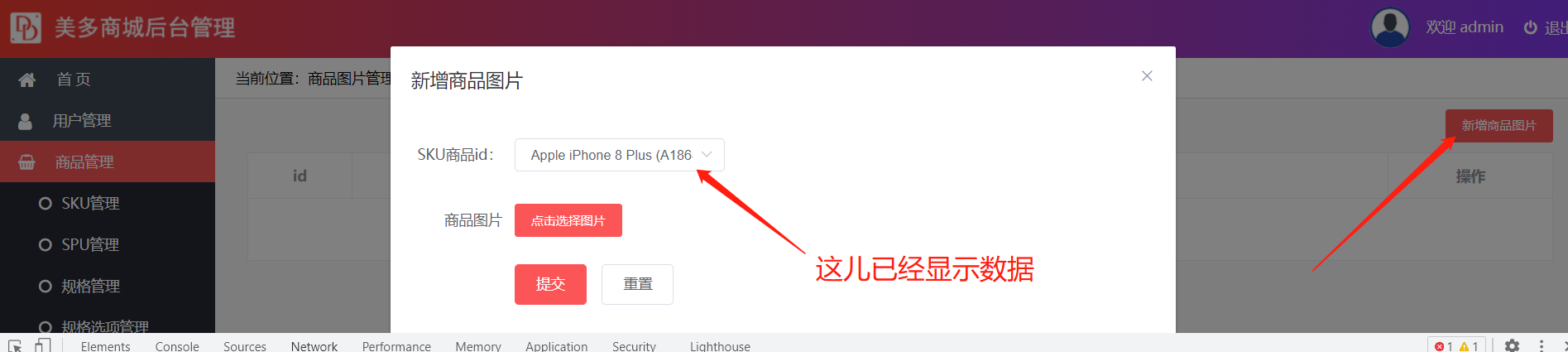
Save picture data
Before saving the data, we need to obtain the id of the sku associated with the picture
1. Get sku table id
Interface analysis
Request method: GET / meiduo_admin/skus/simple/
# -------Get the id of sku--------
url(r'skus/simple/$', images.ImageView.as_view({'get': 'simple'})),Request parameters: pass jwt token data through the request header.
Return data: JSON
[
{
"id": 1,
"name": "Apple MacBook Pro 13.3 Inch notebook Silver"
},
{
"id": 2,
"name": "Apple MacBook Pro 13.3 Inch notebook dark gray"
},
......
]
| Return value | type | Is it necessary | explain |
|---|---|---|---|
| Id | int | yes | sku item id |
| name | array | yes | Sku trade name |
Backend implementation
from rest_framework.permissions import IsAdminUser
from rest_framework.viewsets import ModelViewSet
from meiduo_admin.serializers.images import ImageSeriazlier, SKUSeriazlier
from goods.models import SKUImage, SKU
from meiduo_admin.utils import UserPageNum
from rest_framework.response import Response
class ImageView(ModelViewSet):
# Picture serializer
serializer_class = ImageSeriazlier
# Picture query set
queryset = SKUImage.objects.all()
# paging
pagination_class = UserPageNum
permission_classes = [IsAdminUser]
# Get sku product information
def simple(self, request):
# Query all sku items
data = SKU.objects.all()
# Serialization operation return
ser = SKUSeriazlier(data, many=True)
return Response(ser.data)
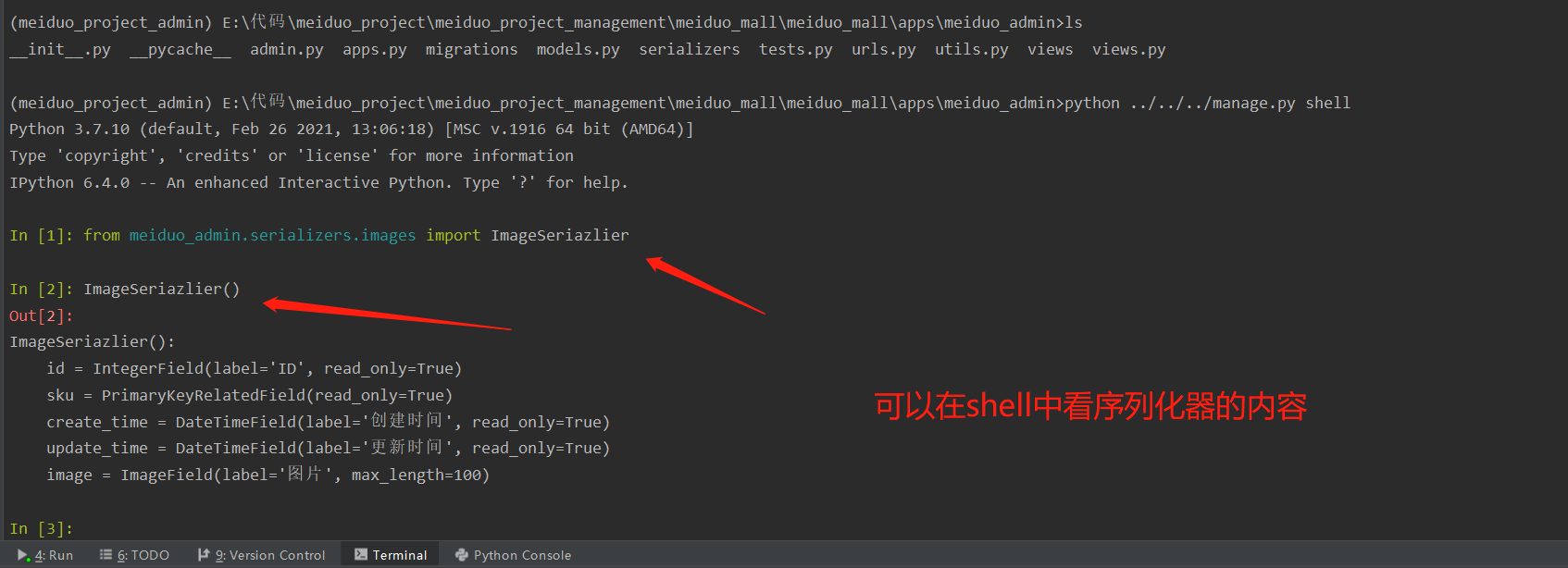
Definition of serializer
from goods.models import SKU
class SKUSeriazlier(serializers.ModelSerializer):
class Meta:
model=SKU
fields=('id','name')
2. Save picture data

Interface analysis
Request method: POST / meiduo_admin/skus/images/
# Picture query routing****************************
router = DefaultRouter()
router.register('skus/images', images.ImageView, base_name='images')
# print(router.urls)
urlpatterns += router.urlsRequest parameters: pass jwt token data through the request header.
Form submission data:
"sku": "SKU commodity id",
"image": "SKU Product picture"
| parameter | type | Is it necessary | explain |
|---|---|---|---|
| sku | str | yes | SKU item id |
| image | Fiel | yes | SKU product picture |
Return data: JSON
{
"id": "picture id",
"sku": "SKU commodity id",
"image": "Picture address"
}
| parameter | type | Is it necessary | explain |
|---|---|---|---|
| id | Int | yes | Picture id |
| sku | int | yes | SKU item id |
| image | str | yes | Picture address |
Backend implementation
While saving the picture, we also need to generate a new detail page asynchronously, which is why we need to define asynchronous tasks
[after the back-end personnel modify the picture, the speed of changing the picture on the static page may be slower, so to prevent blocking, asynchronous tasks should be used here]

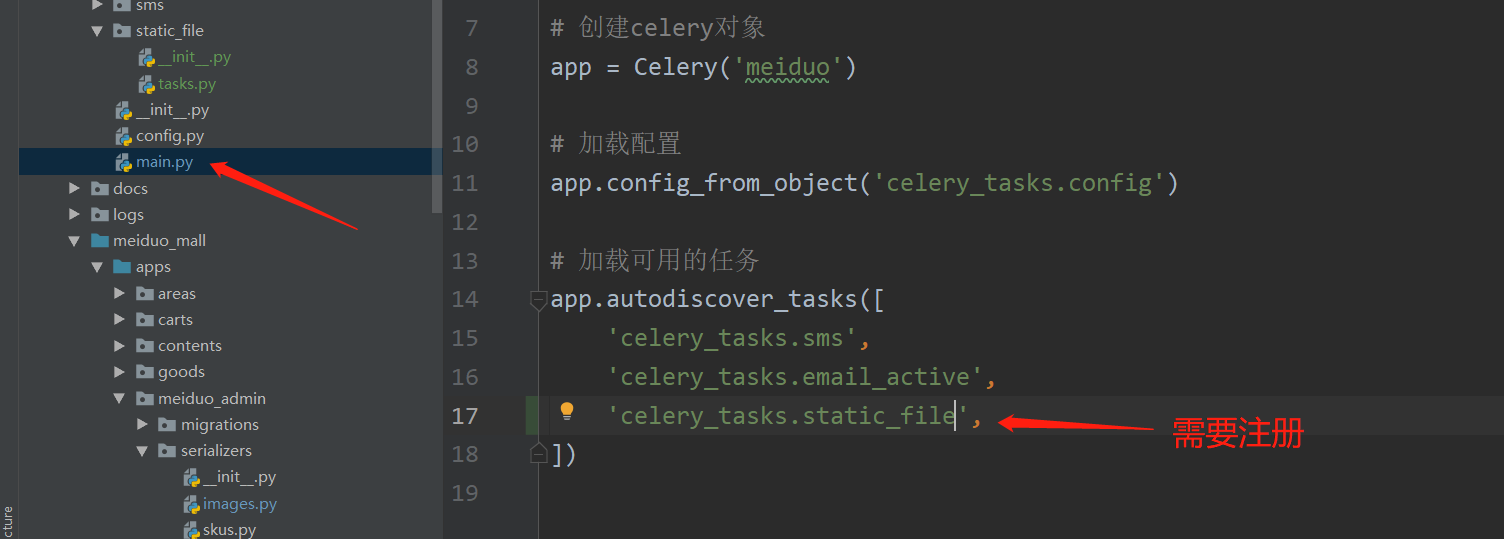
import os
from django.conf import settings
from django.shortcuts import render
from meiduo_mall.utils.categories import get_categories
from meiduo_mall.utils.breadcrumb import get_breadcrumb
from goods.models import SKU
from celery_tasks.main import app
@app.task(name='get_detail_html')
def get_detail_html(sku_id):
# Get current sku object
sku = SKU.objects.get(id=sku_id)
# Classified data
categories = get_categories()
# Get breadcrumbs navigation
breadcrumb = get_breadcrumb(sku.category)
# Get spu
spu = sku.spu
# Get specification information: SKU = = > SPU = = > specs
specs = spu.specs.order_by('id')
# Query all SKUs, such as all inventory items of Huawei P10
skus = spu.skus.order_by('id')
'''
{
option:sku_id
}
Note: in the tuple of the key, the index of the specification is fixed
Example data are as follows:
{
(1,3):1,
(2,3):2,
(1,4):3,
(2,4):4
}
'''
sku_options = {}
sku_option = []
for sku1 in skus:
infos = sku1.specs.order_by('spec_id')
option_key = []
for info in infos:
option_key.append(info.option_id)
# Get the specification information of the current product
if sku.id == sku1.id:
sku_option.append(info.option_id)
sku_options[tuple(option_key)] = sku1.id
# Traverse all specifications of the current spu
specs_list = []
for index, spec in enumerate(specs):
option_list = []
for option in spec.options.all():
# If the current item is blue or 64, the list is [2,3]
sku_option_temp = sku_option[:]
# Replace the element corresponding to the index: the index of the specification is fixed [1,3]
sku_option_temp[index] = option.id
# Add SKU for option_ ID attribute, which is used to output links in html
option.sku_id = sku_options.get(tuple(sku_option_temp), 0)
# Add option object
option_list.append(option)
# Add a list of options for the specification object
spec.option_list = option_list
# Reconstruct specification data
specs_list.append(spec)
context = {
'sku': sku,
'categories': categories,
'breadcrumb': breadcrumb,
'category_id': sku.category_id,
'spu': spu,
'specs': specs_list
}
response = render(None, 'detail.html', context)
file_name = os.path.join(settings.BASE_DIR, 'static/detail/%d.html' % sku.id)
# Write file
with open(file_name, 'w') as f1:
f1.write(response.content.decode())
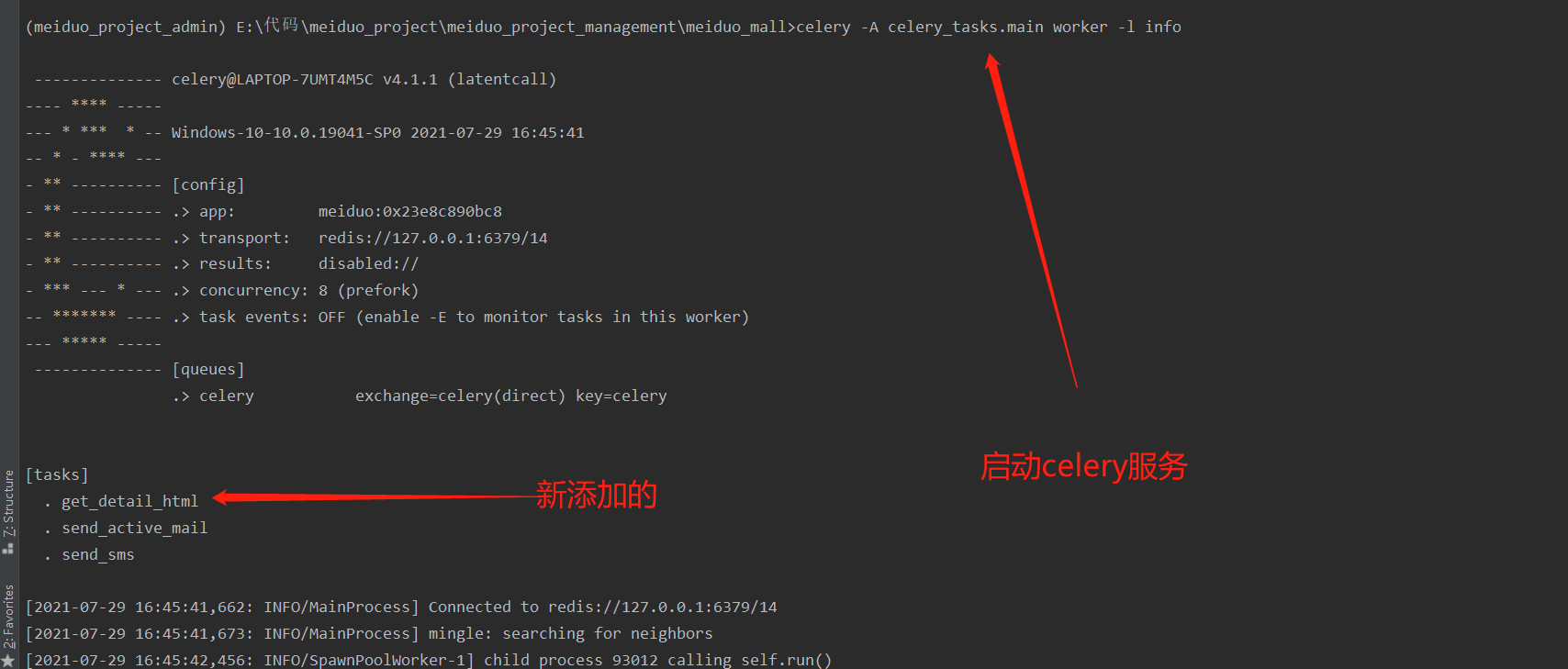
Code view
Configure the fastdfs file path in settings:
# Specify the fastdfs file path FASTDFS_PATH = os.path.join(BASE_DIR, 'utils/fdfs/client.conf')
images.py
from rest_framework.permissions import IsAdminUser
from rest_framework.viewsets import ModelViewSet
from meiduo_admin.serializers.images import ImageSerializer, SKUSerializer
from goods.models import SKUImage, SKU
from meiduo_admin.utils import UserPageNum
from rest_framework.response import Response
from fdfs_client.client import Fdfs_client
from django.conf import settings
from celery_tasks.static_file.tasks import get_detail_html
class ImageView(ModelViewSet):
# Picture serializer
serializer_class = ImageSerializer
# Picture query set
queryset = SKUImage.objects.all()
# paging
pagination_class = UserPageNum
# permission_classes = [IsAdminUser]
# Get sku product information
def simple(self, request):
# Query all sku items
data = SKU.objects.all()
# Serialization operation return
ser = SKUSerializer(data, many=True)
return Response(ser.data)
# Rewrite the saved business logic of the extension class
def create(self, request, *args, **kwargs):
# Create FastDFS connection object
client = Fdfs_client(settings.FASTDFS_PATH)
# Get the image file passed by the front end
data = request.FILES.get('image')
# Upload pictures to fastDFS
res = client.upload_by_buffer(data.read())
# Judge whether the upload is successful
if res['Status'] != 'Upload successed.':
return Response(status=403)
# Get the uploaded path
image_url = res['Remote file_id']
# Get sku_id
sku_id = request.data.get('sku')[0]
# Save picture
img = SKUImage.objects.create(sku_id=sku_id, image=image_url)
# Generate a new detail page
get_detail_html.delay(img.sku.id)
# Return results
return Response(
{
'id': img.id,
'sku': sku_id,
'image': img.image.url # The complete routing information is returned here
},
status=201 # The front end needs to accept 201 status
)
[the above create method can be encapsulated in the serializer, and the specific operations can be seen in the source code. In fact, after these codes are written in the serializer, these codes can be commented out directly, and these operations have been provided in the parent class method. There is no request attribute in the serializer, which can be replaced by self.context['request ']]
Modified code:
Serializer: [the create code in the view can be commented out]
from rest_framework import serializers
from goods.models import SKUImage
from goods.models import SKU
from rest_framework.response import Response
from fdfs_client.client import Fdfs_client
from django.conf import settings
from celery_tasks.static_file.tasks import get_detail_html
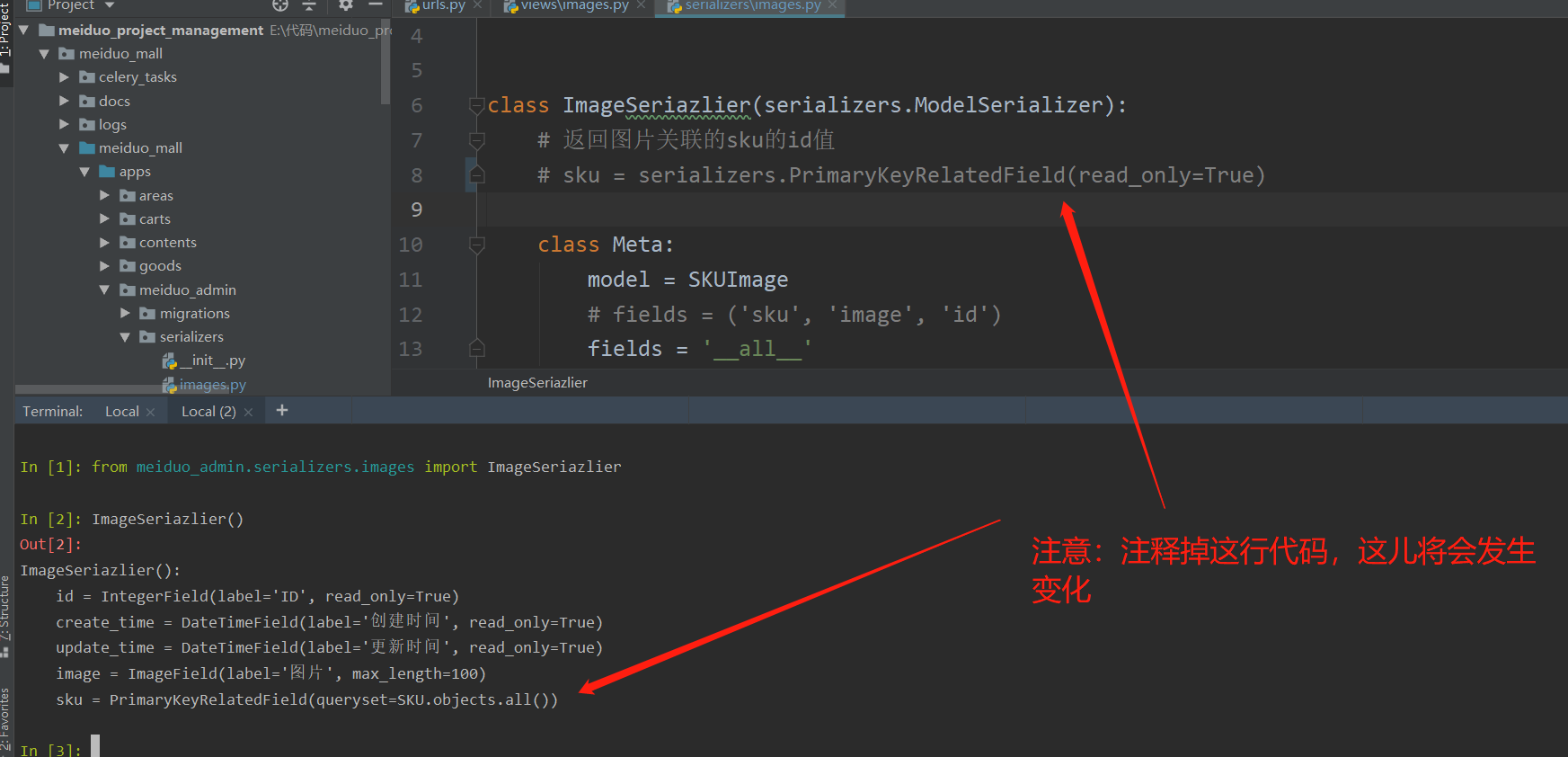
class ImageSerializer(serializers.ModelSerializer):
# Returns the id value of the sku associated with the picture
sku = serializers.PrimaryKeyRelatedField(read_only=True)
class Meta:
model = SKUImage
# fields = ('sku', 'image', 'id')
fields = '__all__'
def create(self, validated_data):
# Create FastDFS connection object
client = Fdfs_client(settings.FASTDFS_PATH)
# Get the image file from the front end
data = self.context['request'].FILES.get('image')
# data = request.data
# Upload pictures to fastDFS
res = client.upload_by_buffer(data.read())
# Judge whether the upload is successful
if res['Status'] != 'Upload successed.':
return Response(status=403)
# Get the uploaded path
image_url = res['Remote file_id']
# Get sku_id
sku_id = self.context['request'].data.get('sku')[0]
# Save picture
img = SKUImage.objects.create(sku_id=sku_id, image=image_url)
# Generate detail page and static page asynchronously
get_detail_html.delay(img.sku.id)
return imgNote: FDFS client may not be installed directly here. You can use the installation package file prepared in advance, PIP install FDFS client py master zip
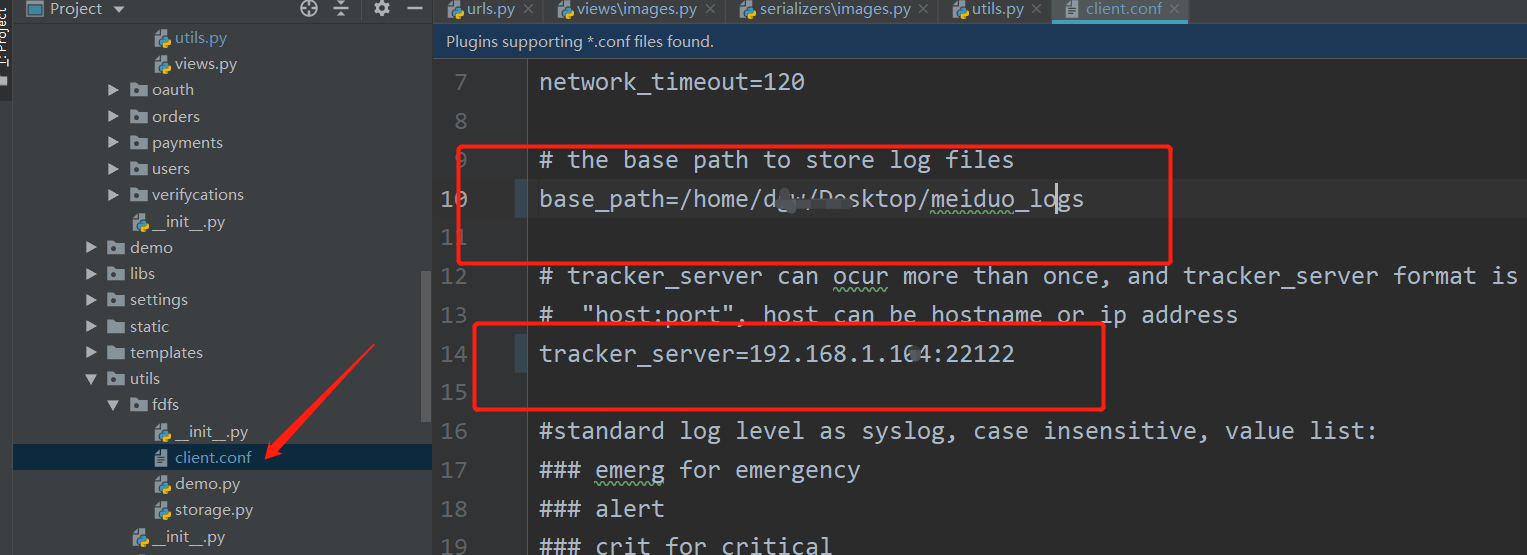
For the file upload and installation precautions of FastDFS client, check the blog:
https://blog.csdn.net/weixin_44799217/article/details/118463124