1, Preliminary preparation
SoC learning chapter - realizing hello FPGA printing
Prepare the hardware that should be ready
2, Add PIO peripherals
1, Gold reference project
1. Open the gold reference project
2. Open Platform Designer
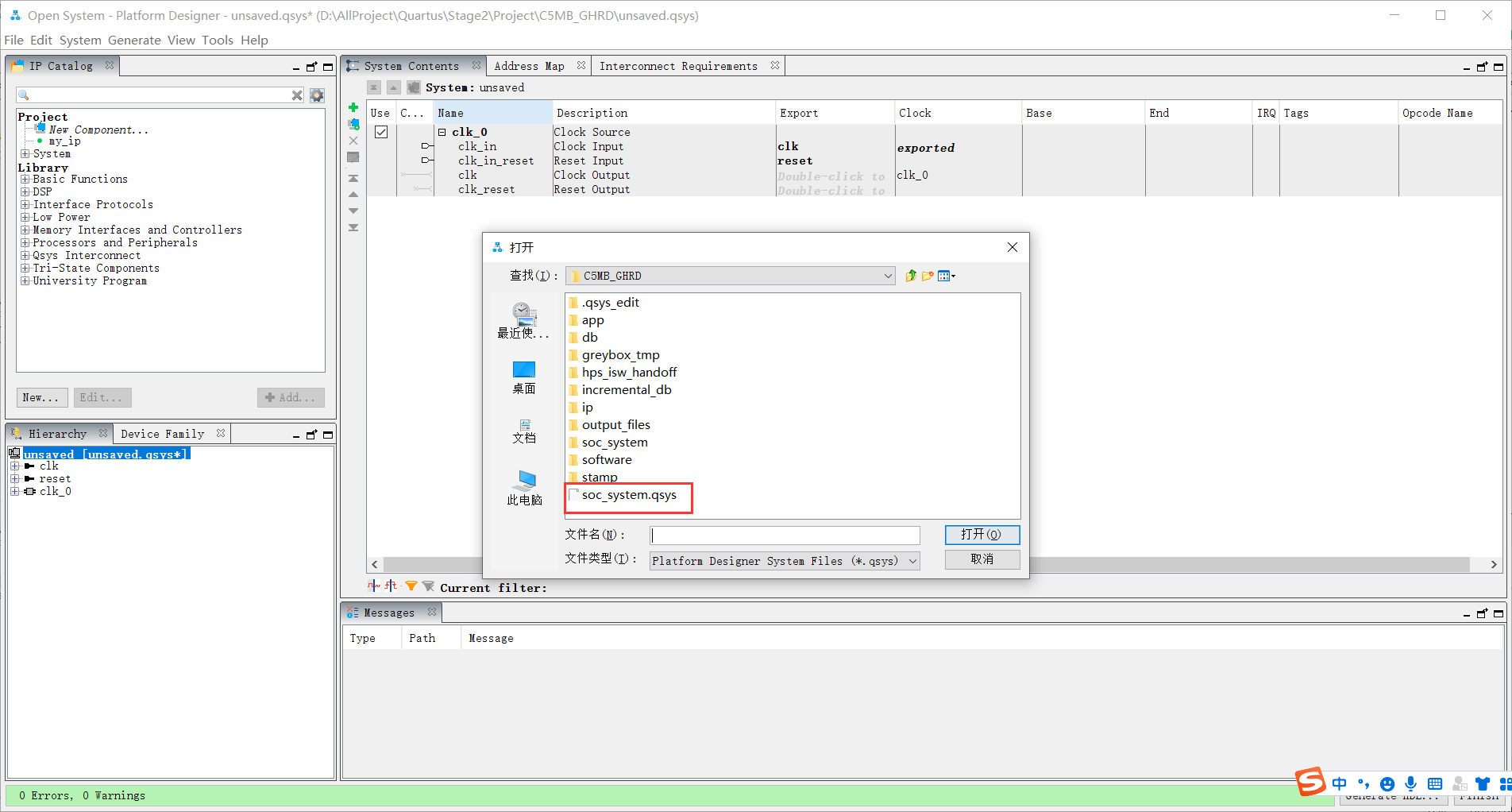
3. Open the corresponding qsys file
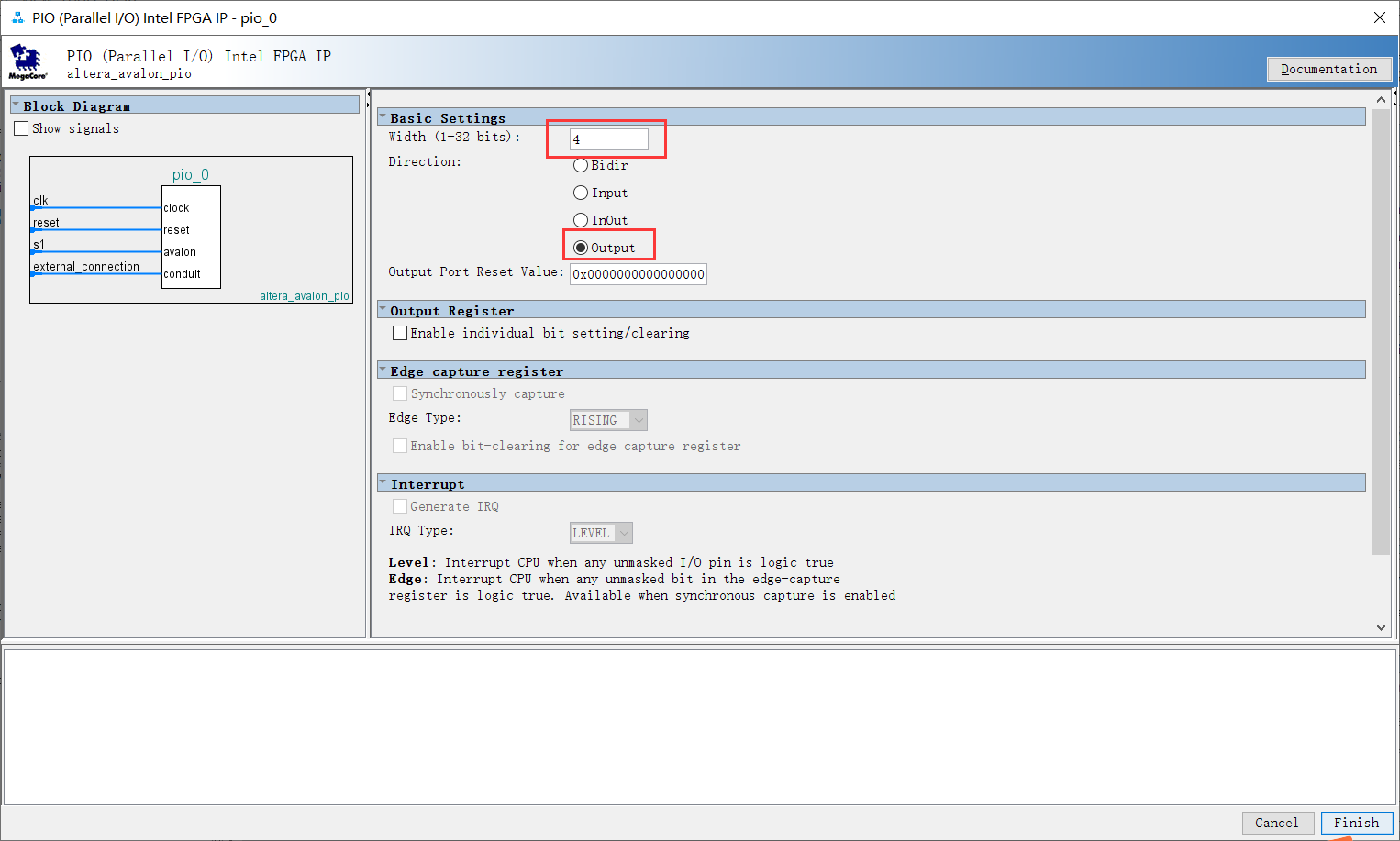
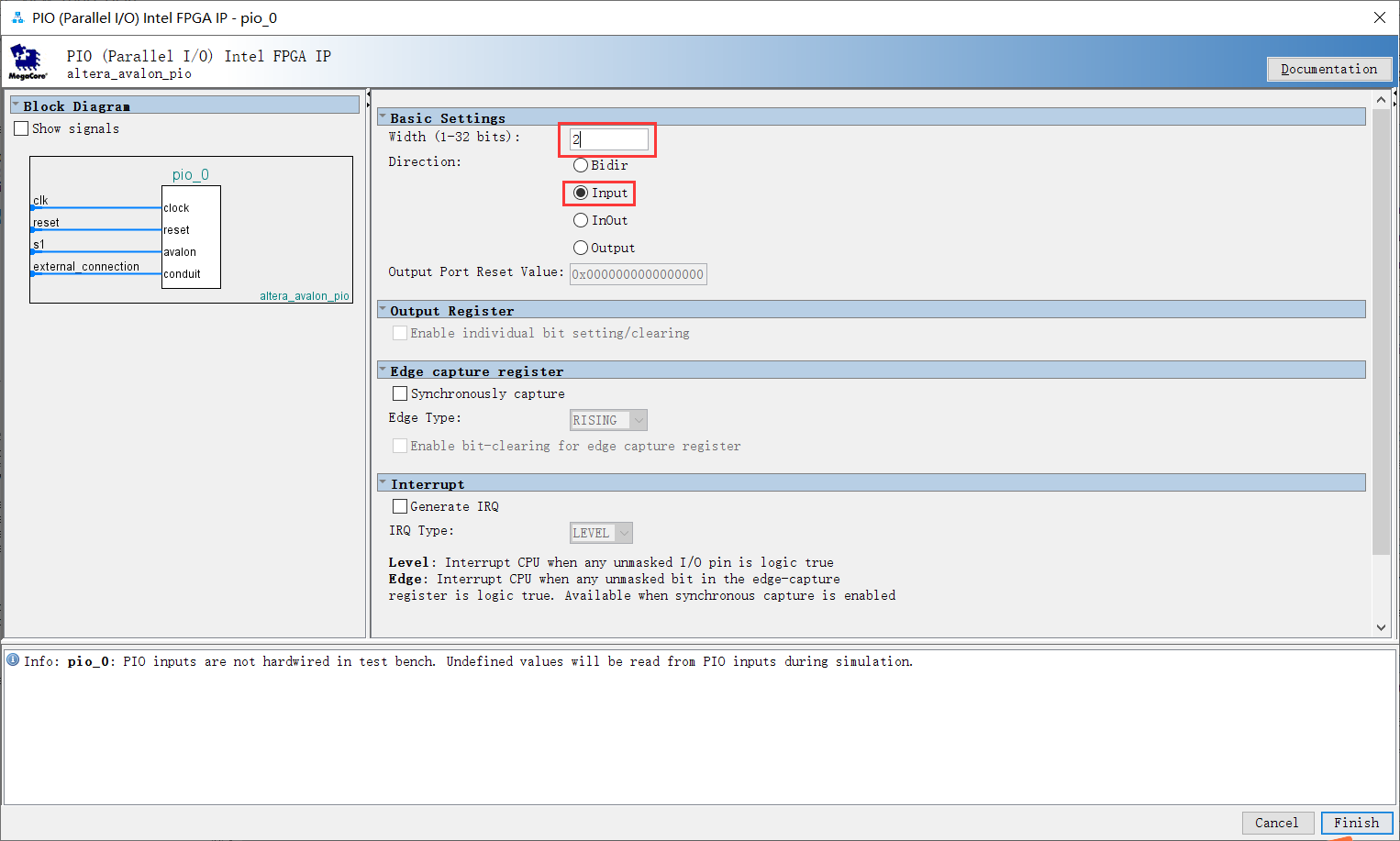
4. Add PIO_LED and PIO_KEY
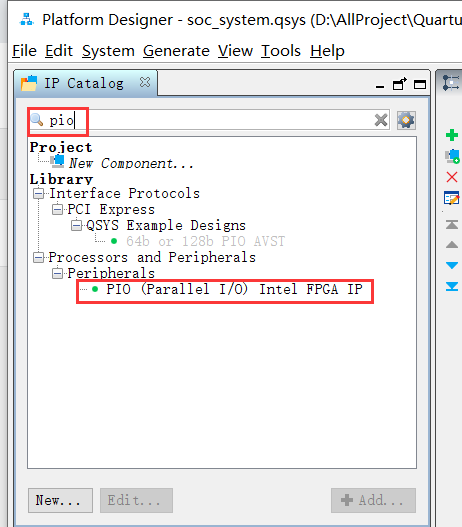
| name | Bit width | Input and output |
|---|---|---|
| PIO_LED | 4-bit wide | output |
| name | Bit width | Input and output |
|---|---|---|
| PIO_KEY | 2-bit width | input |
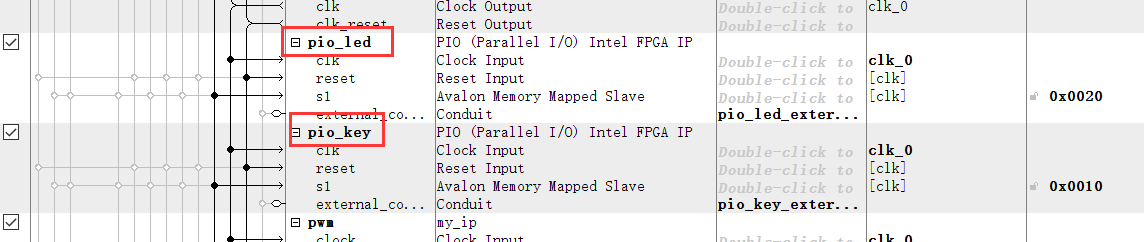
Add to soc system
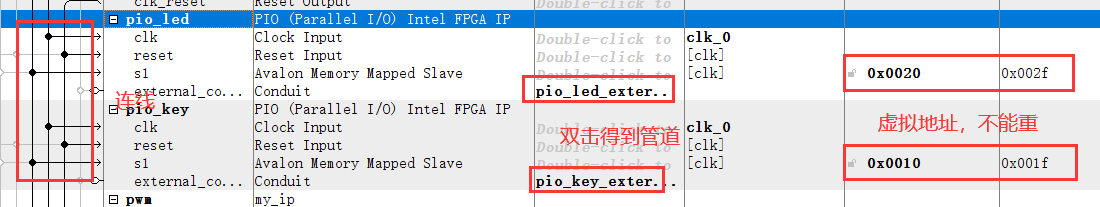
2, Configure PIO peripherals
Connect, double-click, reset address
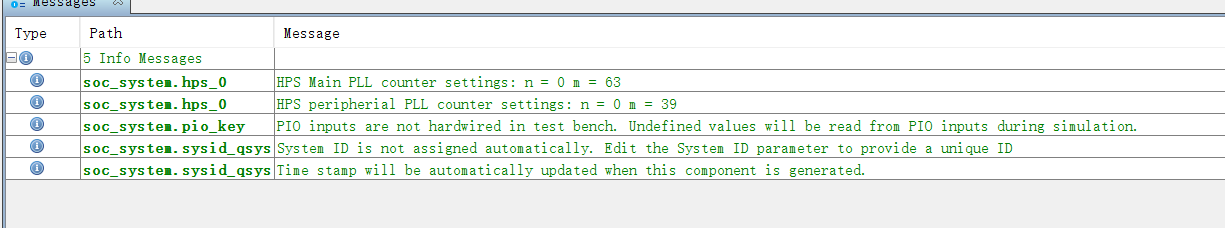
Wait until there is no error green below
3, Generation generation
1.Generate HDL
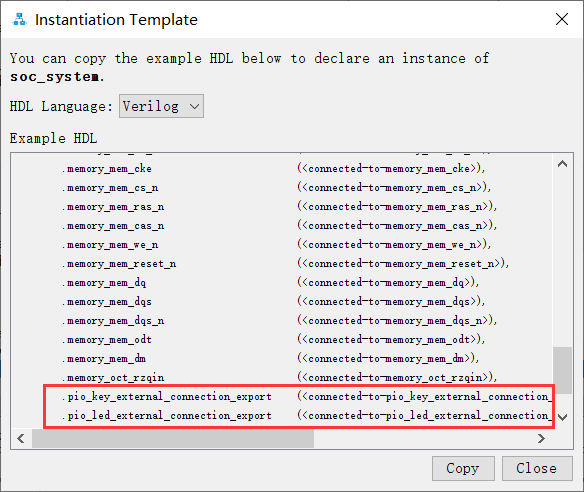
2. Show instance template generates an instance template
Copy the added peripheral instantiation template
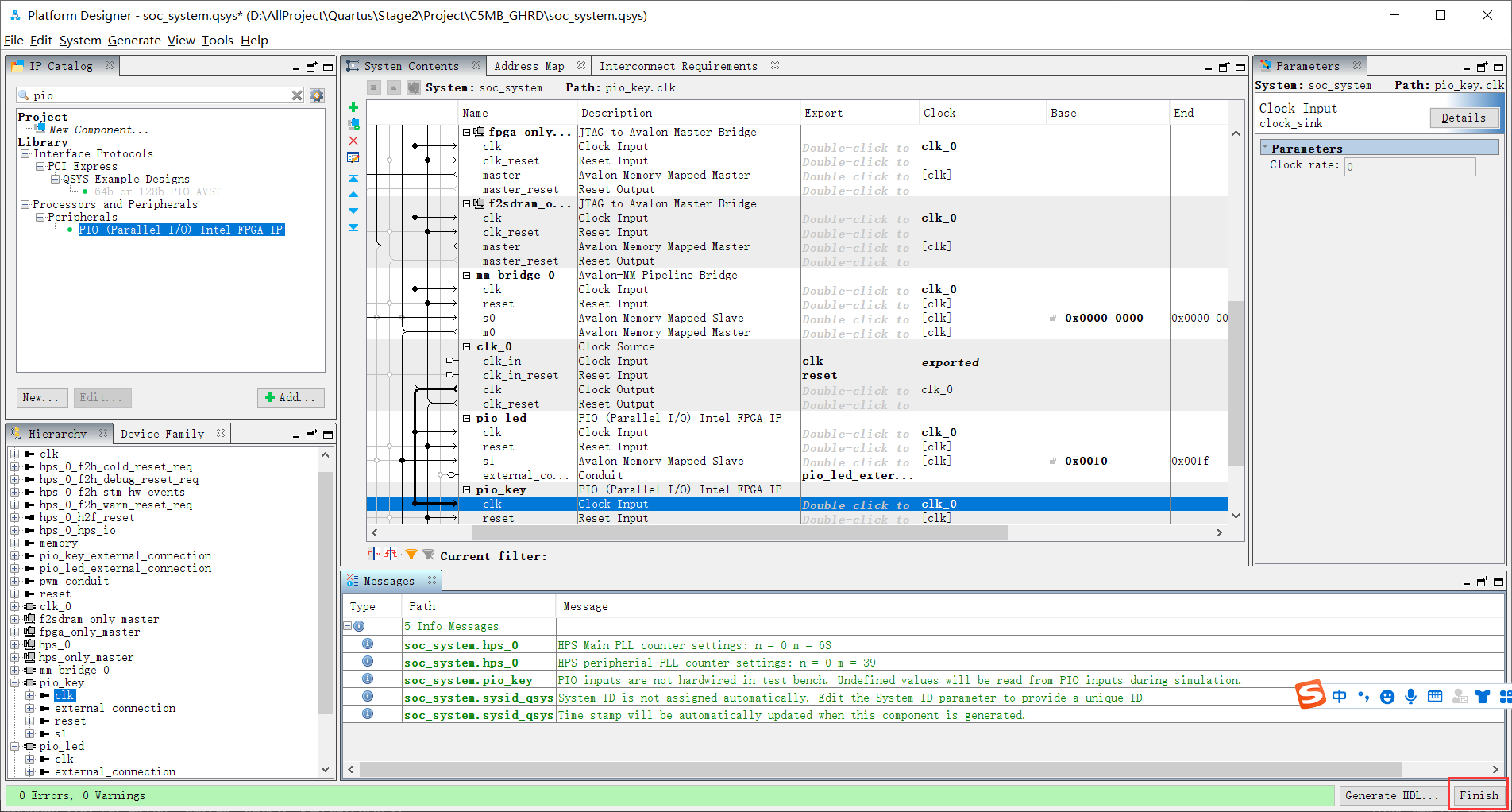
3.Finish Platform Designer
4, Gold reference engineering code modification
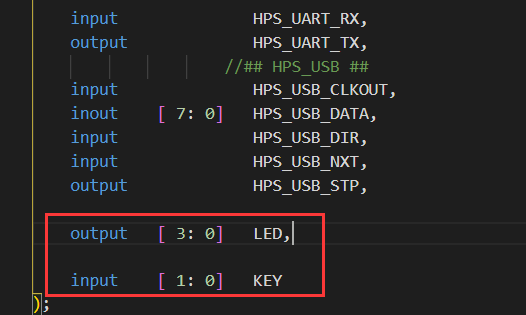
1. Add peripheral port
output [ 3: 0] LED,
input [ 1: 0] KEY
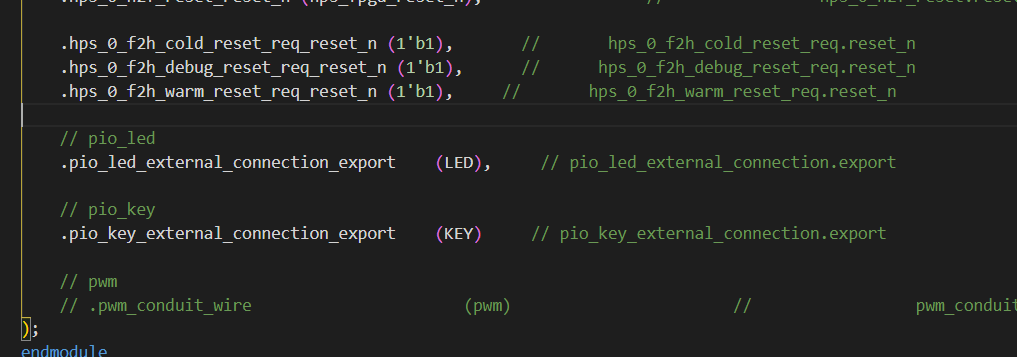
// pio_led .pio_led_external_connection_export (LED), // pio_led_external_connection.export // pio_key .pio_key_external_connection_export (KEY) // pio_key_external_connection.export
Complete code
module C5MB_top(
/ FPGA /
input FPGA_CLK1_50,
/ HPS /
output [14: 0] HPS_DDR3_ADDR,
output [ 2: 0] HPS_DDR3_BA,
output HPS_DDR3_CAS_n,
output [ 0: 0] HPS_DDR3_CKE,
output HPS_DDR3_CK_n,
output HPS_DDR3_CK_p,
output [ 0: 0] HPS_DDR3_CS_n,
output [ 3: 0] HPS_DDR3_DM,
inout [31: 0] HPS_DDR3_DQ,
inout [ 3: 0] HPS_DDR3_DQS_n,
inout [ 3: 0] HPS_DDR3_DQS_p,
output [ 0: 0] HPS_DDR3_ODT,
output HPS_DDR3_RAS_n,
output HPS_DDR3_RESET_n,
input HPS_DDR3_RZQ,
output HPS_DDR3_WE_n,
output HPS_ENET_GTX_CLK,
inout HPS_ENET_INT_n, //hps_gpio_GPIO35
output HPS_ENET_MDC,
inout HPS_ENET_MDIO,
input HPS_ENET_RX_CLK,
input [ 3: 0] HPS_ENET_RX_DATA,
input HPS_ENET_RX_DV,
output [ 3: 0] HPS_ENET_TX_DATA,
output HPS_ENET_TX_EN,
inout HPS_EMMC_SEL, //hps_io_gpio_inst_GPIO44
output HPS_SDMMC_CLK,
inout HPS_SDMMC_CMD,
inout [ 7: 0] HPS_SDMMC_DATA,
output HPS_EMMC_RST_n,
input HPS_UART_RX,
output HPS_UART_TX,
//## HPS_USB ##
input HPS_USB_CLKOUT,
inout [ 7: 0] HPS_USB_DATA,
input HPS_USB_DIR,
input HPS_USB_NXT,
output HPS_USB_STP,
output [ 3: 0] LED,
input [ 1: 0] KEY
);
//=======================================================
// REG/WIRE declarations
//=======================================================
wire hps_fpga_reset_n;
wire fpga_clk_50;
wire fpga_clk_100;
// wire pwm;
// assign LED = {4{pwm}};
pll pll_inst (
.refclk (FPGA_CLK1_50), // refclk.clk
.rst (~hps_fpga_reset_n), // reset.reset
.outclk_0 (fpga_clk_50), // outclk0.clk
.outclk_1 (fpga_clk_100)
);
//=======================================================
// Structural coding
//=======================================================
soc_system u0 (
.clk_clk (fpga_clk_50), // clk.clk
.reset_reset_n (hps_fpga_reset_n), // reset.reset_n
//HPS ddr3
.memory_mem_a (HPS_DDR3_ADDR), // memory.mem_a
.memory_mem_ba (HPS_DDR3_BA), // .mem_ba
.memory_mem_ck (HPS_DDR3_CK_p), // .mem_ck
.memory_mem_ck_n (HPS_DDR3_CK_n), // .mem_ck_n
.memory_mem_cke (HPS_DDR3_CKE), // .mem_cke
.memory_mem_cs_n (HPS_DDR3_CS_n), // .mem_cs_n
.memory_mem_ras_n (HPS_DDR3_RAS_n), // .mem_ras_n
.memory_mem_cas_n (HPS_DDR3_CAS_n), // .mem_cas_n
.memory_mem_we_n (HPS_DDR3_WE_n), // .mem_we_n
.memory_mem_reset_n (HPS_DDR3_RESET_n), // .mem_reset_n
.memory_mem_dq (HPS_DDR3_DQ), // .mem_dq
.memory_mem_dqs (HPS_DDR3_DQS_p), // .mem_dqs
.memory_mem_dqs_n (HPS_DDR3_DQS_n), // .mem_dqs_n
.memory_mem_odt (HPS_DDR3_ODT), // .mem_odt
.memory_mem_dm (HPS_DDR3_DM), // .mem_dm
.memory_oct_rzqin (HPS_DDR3_RZQ), // .oct_rzqin
//HPS ethernet
.hps_0_hps_io_hps_io_emac1_inst_TX_CLK (HPS_ENET_GTX_CLK), // hps_0_hps_io.hps_io_emac1_inst_TX_CLK
.hps_0_hps_io_hps_io_emac1_inst_TXD0 (HPS_ENET_TX_DATA[0]), // .hps_io_emac1_inst_TXD0
.hps_0_hps_io_hps_io_emac1_inst_TXD1 (HPS_ENET_TX_DATA[1]), // .hps_io_emac1_inst_TXD1
.hps_0_hps_io_hps_io_emac1_inst_TXD2 (HPS_ENET_TX_DATA[2]), // .hps_io_emac1_inst_TXD2
.hps_0_hps_io_hps_io_emac1_inst_TXD3 (HPS_ENET_TX_DATA[3]), // .hps_io_emac1_inst_TXD3
.hps_0_hps_io_hps_io_emac1_inst_RXD0 (HPS_ENET_RX_DATA[0]), // .hps_io_emac1_inst_RXD0
.hps_0_hps_io_hps_io_emac1_inst_MDIO (HPS_ENET_MDIO), // .hps_io_emac1_inst_MDIO
.hps_0_hps_io_hps_io_emac1_inst_MDC (HPS_ENET_MDC), // .hps_io_emac1_inst_MDC
.hps_0_hps_io_hps_io_emac1_inst_RX_CTL (HPS_ENET_RX_DV), // .hps_io_emac1_inst_RX_CTL
.hps_0_hps_io_hps_io_emac1_inst_TX_CTL (HPS_ENET_TX_EN), // .hps_io_emac1_inst_TX_CTL
.hps_0_hps_io_hps_io_emac1_inst_RX_CLK (HPS_ENET_RX_CLK), // .hps_io_emac1_inst_RX_CLK
.hps_0_hps_io_hps_io_emac1_inst_RXD1 (HPS_ENET_RX_DATA[1]), // .hps_io_emac1_inst_RXD1
.hps_0_hps_io_hps_io_emac1_inst_RXD2 (HPS_ENET_RX_DATA[2]), // .hps_io_emac1_inst_RXD2
.hps_0_hps_io_hps_io_emac1_inst_RXD3 (HPS_ENET_RX_DATA[3]), // .hps_io_emac1_inst_RXD3
//HPS SD card
.hps_0_hps_io_hps_io_sdio_inst_CMD (HPS_SDMMC_CMD), // .hps_io_sdio_inst_CMD
.hps_0_hps_io_hps_io_sdio_inst_D0 (HPS_SDMMC_DATA[0]), // .hps_io_sdio_inst_D0
.hps_0_hps_io_hps_io_sdio_inst_D1 (HPS_SDMMC_DATA[1]), // .hps_io_sdio_inst_D1
.hps_0_hps_io_hps_io_sdio_inst_CLK (HPS_SDMMC_CLK), // .hps_io_sdio_inst_CLK
.hps_0_hps_io_hps_io_sdio_inst_D2 (HPS_SDMMC_DATA[2]), // .hps_io_sdio_inst_D2
.hps_0_hps_io_hps_io_sdio_inst_D3 (HPS_SDMMC_DATA[3]), // .hps_io_sdio_inst_D3
.hps_0_hps_io_hps_io_sdio_inst_D4 (HPS_SDMMC_DATA[4]), // .hps_io_sdio_inst_D4
.hps_0_hps_io_hps_io_sdio_inst_D5 (HPS_SDMMC_DATA[5]), // .hps_io_sdio_inst_D5
.hps_0_hps_io_hps_io_sdio_inst_D6 (HPS_SDMMC_DATA[6]), // .hps_io_sdio_inst_D6
.hps_0_hps_io_hps_io_sdio_inst_D7 (HPS_SDMMC_DATA[7]), // .hps_io_sdio_inst_D7
.hps_0_hps_io_hps_io_sdio_inst_PWREN (HPS_EMMC_RST_n), // .hps_io_sdio_inst_PWREN
//HPS USB
.hps_0_hps_io_hps_io_usb1_inst_D0 (HPS_USB_DATA[0]), // .hps_io_usb1_inst_D0
.hps_0_hps_io_hps_io_usb1_inst_D1 (HPS_USB_DATA[1]), // .hps_io_usb1_inst_D1
.hps_0_hps_io_hps_io_usb1_inst_D2 (HPS_USB_DATA[2]), // .hps_io_usb1_inst_D2
.hps_0_hps_io_hps_io_usb1_inst_D3 (HPS_USB_DATA[3]), // .hps_io_usb1_inst_D3
.hps_0_hps_io_hps_io_usb1_inst_D4 (HPS_USB_DATA[4]), // .hps_io_usb1_inst_D4
.hps_0_hps_io_hps_io_usb1_inst_D5 (HPS_USB_DATA[5]), // .hps_io_usb1_inst_D5
.hps_0_hps_io_hps_io_usb1_inst_D6 (HPS_USB_DATA[6]), // .hps_io_usb1_inst_D6
.hps_0_hps_io_hps_io_usb1_inst_D7 (HPS_USB_DATA[7]), // .hps_io_usb1_inst_D7
.hps_0_hps_io_hps_io_usb1_inst_CLK (HPS_USB_CLKOUT), // .hps_io_usb1_inst_CLK
.hps_0_hps_io_hps_io_usb1_inst_STP (HPS_USB_STP), // .hps_io_usb1_inst_STP
.hps_0_hps_io_hps_io_usb1_inst_DIR (HPS_USB_DIR), // .hps_io_usb1_inst_DIR
.hps_0_hps_io_hps_io_usb1_inst_NXT (HPS_USB_NXT), // .hps_io_usb1_inst_NXT
//HPS UART
.hps_0_hps_io_hps_io_uart0_inst_RX (HPS_UART_RX), // .hps_io_uart0_inst_RX
.hps_0_hps_io_hps_io_uart0_inst_TX (HPS_UART_TX), // .hps_io_uart0_inst_TX
.hps_0_hps_io_hps_io_gpio_inst_GPIO35 (HPS_ENET_INT_n), // .hps_io_gpio_inst_GPIO35
.hps_0_hps_io_hps_io_gpio_inst_GPIO44 (HPS_EMMC_SEL), // .hps_io_gpio_inst_GPIO44
.hps_0_h2f_reset_reset_n (hps_fpga_reset_n), // hps_0_h2f_reset.reset_n
.hps_0_f2h_cold_reset_req_reset_n (1'b1), // hps_0_f2h_cold_reset_req.reset_n
.hps_0_f2h_debug_reset_req_reset_n (1'b1), // hps_0_f2h_debug_reset_req.reset_n
.hps_0_f2h_warm_reset_req_reset_n (1'b1), // hps_0_f2h_warm_reset_req.reset_n
// pio_led
.pio_led_external_connection_export (LED), // pio_led_external_connection.export
// pio_key
.pio_key_external_connection_export (KEY) // pio_key_external_connection.export
// pwm
// .pwm_conduit_wire (pwm) // pwm_conduit.wire
);
endmodule
5, Compile gold project
The average computer takes 6-8 minutes
3, Generate corresponding files and transfer them to sd card
1, dtb device tree file
Enter the directory of gold reference project
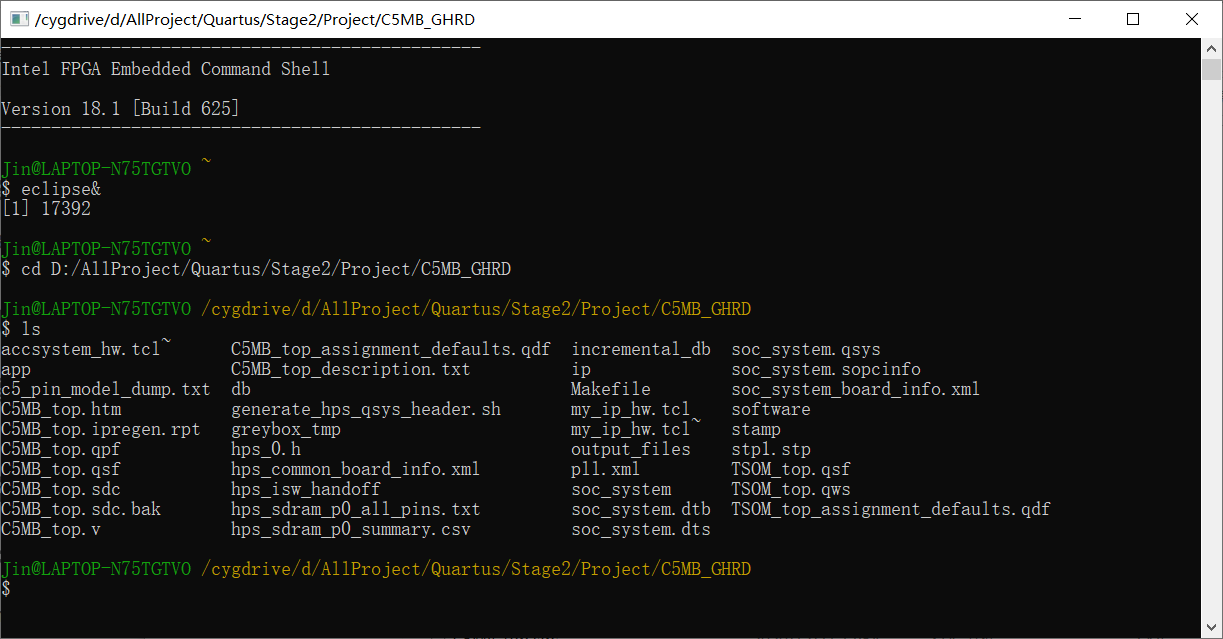
Generate dtb file
make dtb
If I have generated peripherals, I don't need to generate them. If I need to wait a few minutes for the first time
2, rbf file
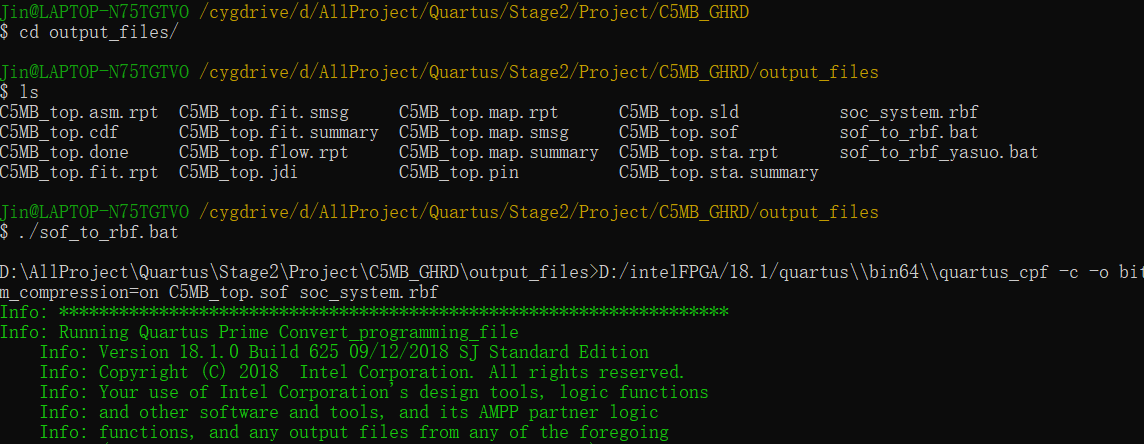
Enter to output_files / directory
Run sof_to_rbf.bat script file
cd output_files/ ./sof_to_rbf.bat
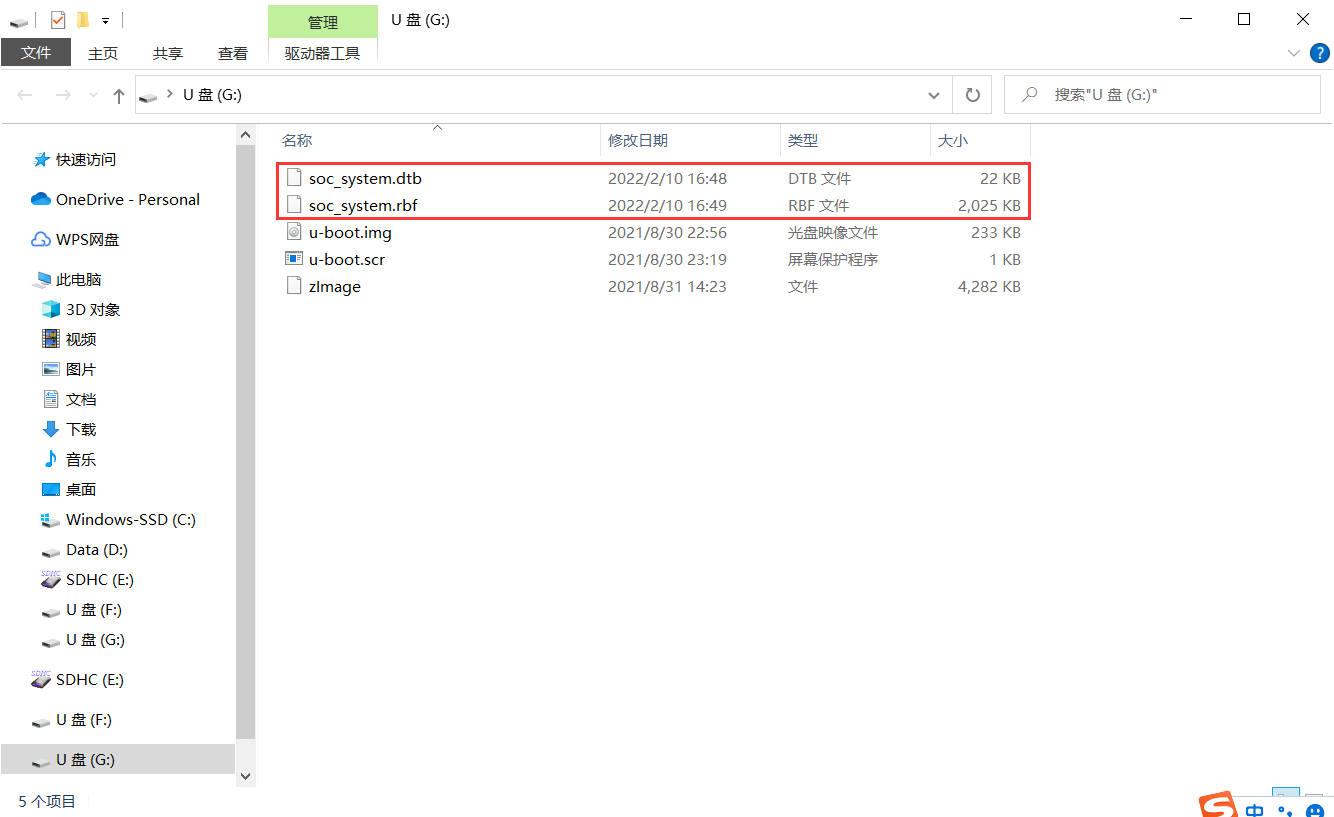
3, Replace dtb and rbf files in sd card
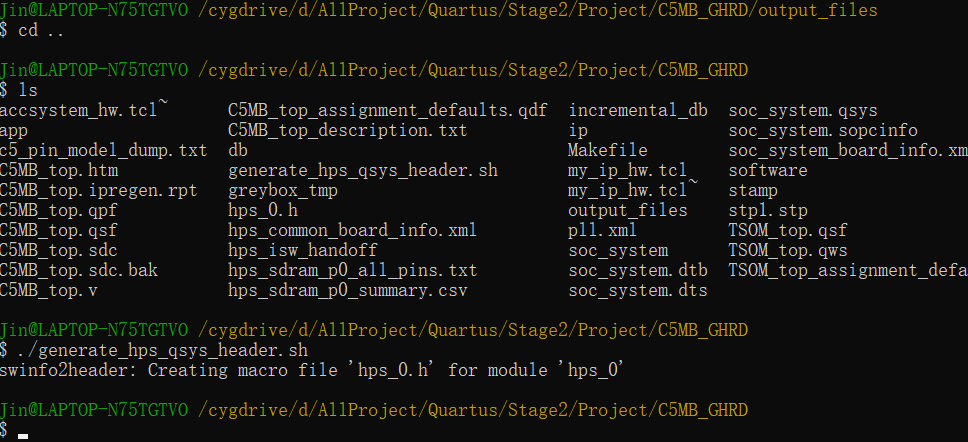
4, Generate hps_0.h
./generate_hps_qsys_header.sh
This hps_0.h is needed for the subsequent C language
3, C language implementation
1, Create and configure projects
1. Open SoC EDS Command Shell

2. Open eclipse
eclipse&
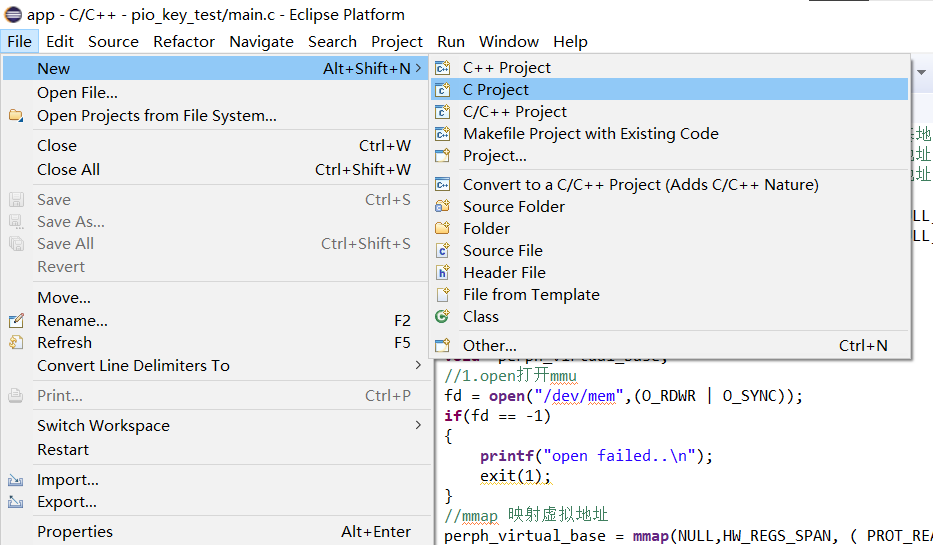
3. Create a new C Project
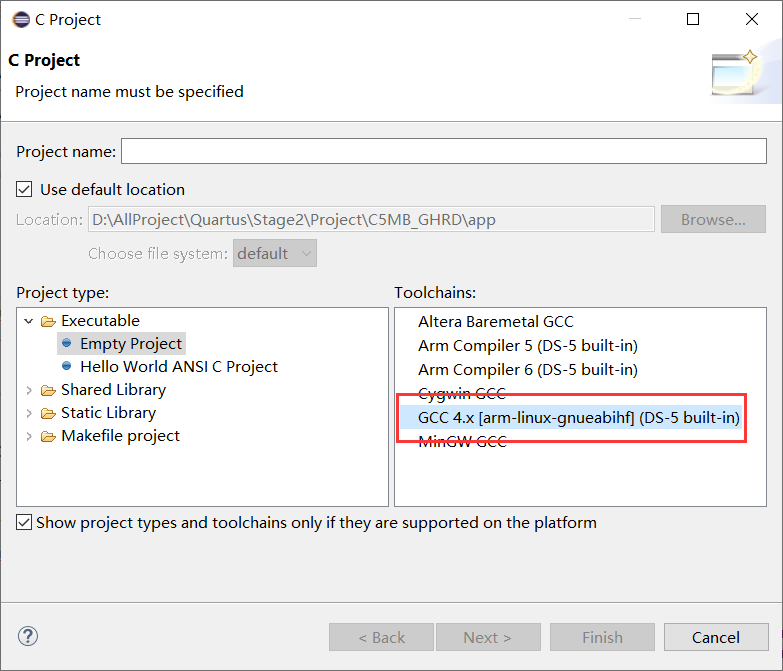
4. Select GCC compilation
5. Right click the created new project attribute
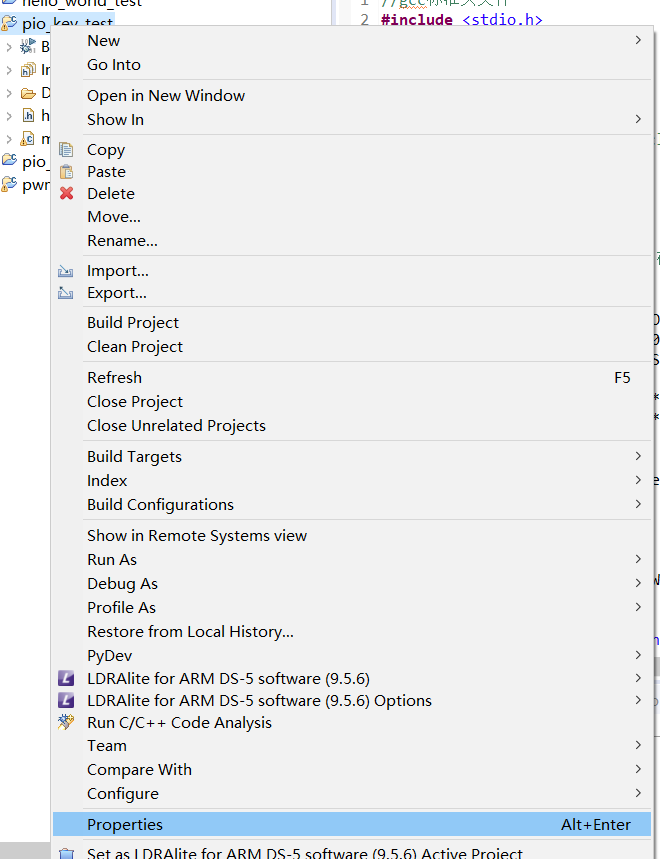
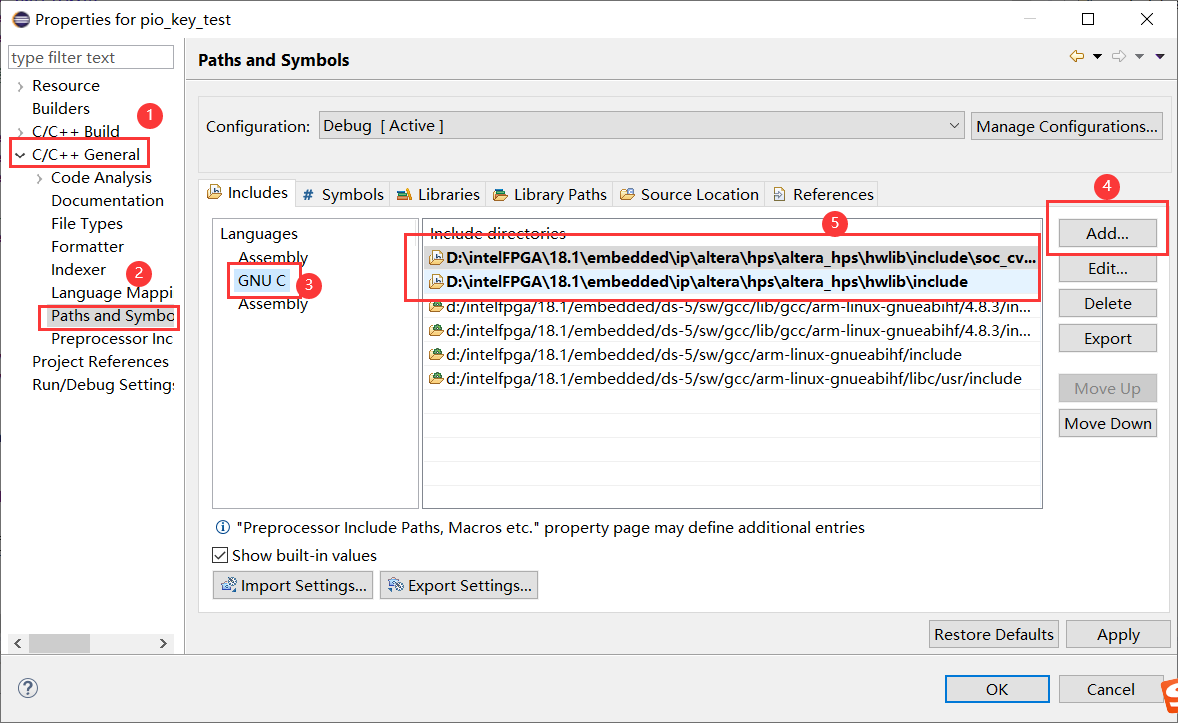
6. Add two additional libraries
D:\intelFPGA\18.1\embedded\ip\altera\hps\altera_hps\hwlib\include\soc_cv_av
D:\intelFPGA\18.1\embedded\ip\altera\hps\altera_hps\hwlib\include
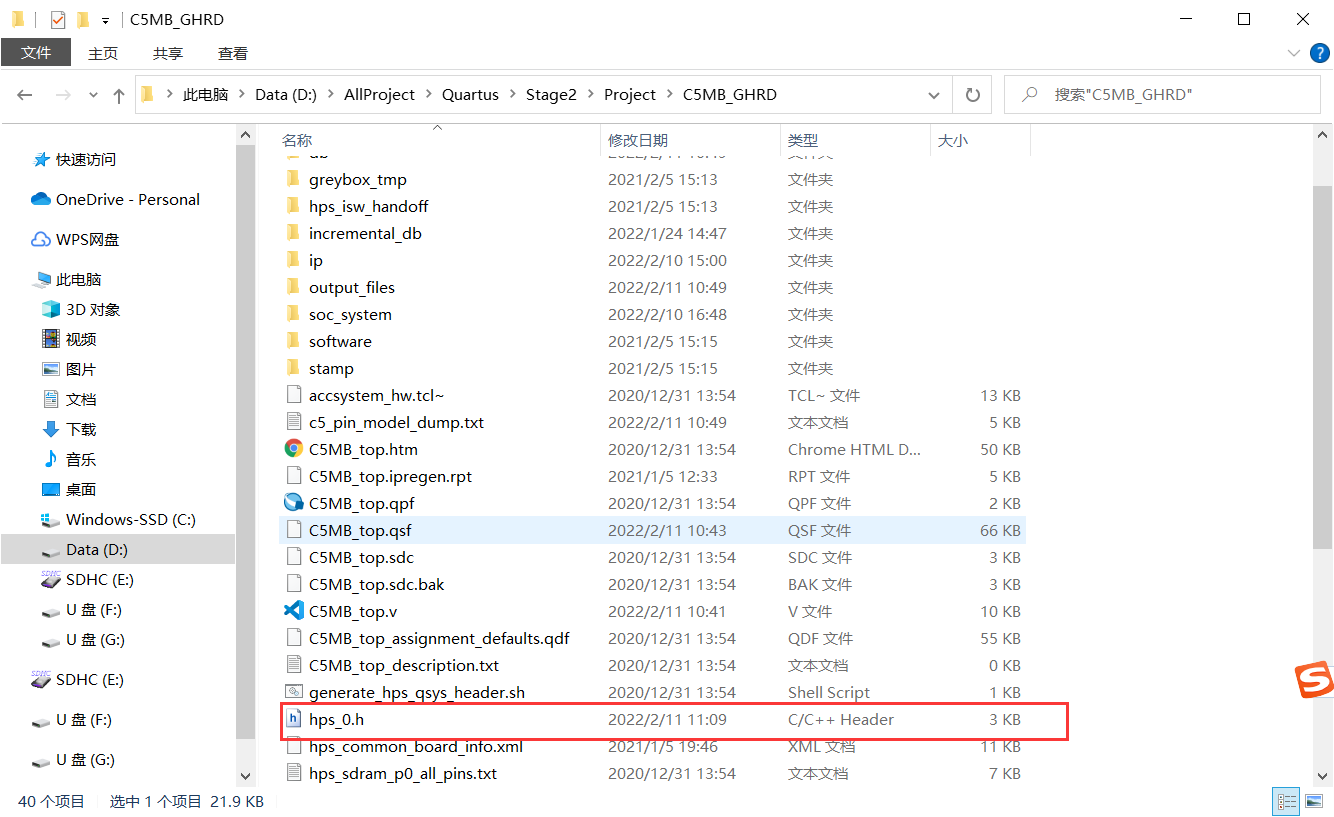
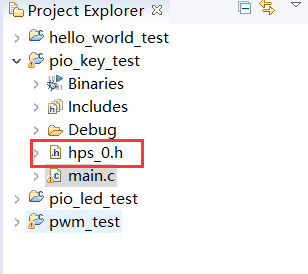
7. HPS of gold project_ 0. H file into the project
2, C language to achieve key lighting
1.New a new C file main c
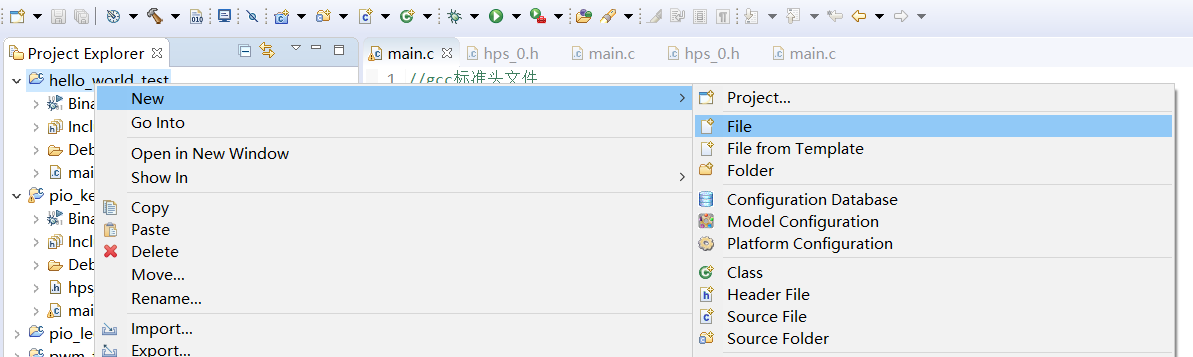
2. Write C language code
//gcc standard header file
#include <stdio.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <fcntl.h>
#include <sys/mman.h>
//Bottom definition header file provided by HPS manufacturer
#define soc_cv_av / / development platform Cyclone V series
#include "hwlib.h"
#include "socal/socal.h"
#include "socal/hps.h"
//Hardware description header file related to the user's specific HPS application system
#include "hps_0.h"
#define HW_ REGS_ Base (alt_stm_ofst) / / HPS peripheral address segment base address
#define HW_REGS_SPAN (0x04000000) // HPS peripheral address segment address space 64MB size
#define HW_REGS_MASK (HW_REGS_SPAN - 1) //HPS peripheral address segment address mask
static volatile unsigned long *led_pio_virtual_base = NULL;
static volatile unsigned long *key_pio_virtual_base = NULL;
//fpga initialization
int fpga_init(int *virtual_base)
{
int fd;
void *perph_virtual_base;
//1.open mmu
fd = open("/dev/mem",(O_RDWR | O_SYNC));
if(fd == -1)
{
printf("open failed..\n");
exit(1);
}
//mmap mapping virtual address
perph_virtual_base = mmap(NULL,HW_REGS_SPAN, ( PROT_READ | PROT_WRITE ),MAP_SHARED,fd,HW_REGS_BASE);
if(perph_virtual_base == MAP_SHARED)
{
printf("mmap() is failed..\n");
return 1;
}
//Interface
led_pio_virtual_base = perph_virtual_base + ((unsigned long)(ALT_LWFPGASLVS_OFST + PIO_LED_BASE) & (unsigned long)(HW_REGS_MASK));
key_pio_virtual_base = perph_virtual_base + ((unsigned long)(ALT_LWFPGASLVS_OFST + PIO_KEY_BASE) & (unsigned long)(HW_REGS_MASK));
//Save virtual address
*virtual_base = perph_virtual_base;
return fd;
}
int main()
{
int virtual_base;
int fd;
fd = fpga_init(&virtual_base);
unsigned int data;
while(1)
{
// data = ~(*(key_pio_virtual_base + 0));
// *(led_pio_virtual_base + 0) = ~(*(key_pio_virtual_base + 0));
// *(led_pio_virtual_base + 0) = data;
if(*(key_pio_virtual_base + 0) == 0x01)
{
*(led_pio_virtual_base + 0) = 0xf;
}
else if(*(key_pio_virtual_base + 0) == 0x02)
{
*(led_pio_virtual_base + 0) = 0x0;
}
}
if(munmap(virtual_base,HW_REGS_SPAN) != 0)
{
printf("munmap() is failed..\n");
close(fd);
return 1;
}
close(fd);
return 0;
}
After saving and compiling, a binary file will be generated
4, Connecting SoC FPGA
Put the binary file of C language into the opt file
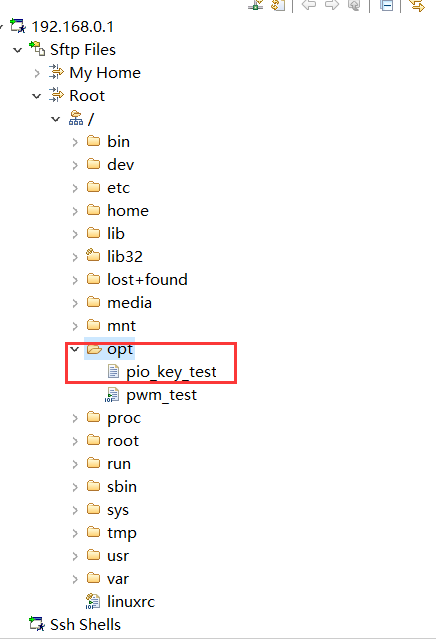
Permission is required to run the executable
cd opt/ chmod 777 pio_key_test ./pio_key_test
If the color turns green, you have permission
5, Execution effect
It's inconvenient to shoot here. It's just the effect of pressing the button to light the light
6, Summary
To realize the function of SoC is to add ip peripherals, calculate the virtual mapping address of peripherals, then assign a value to the base address through C language, and finally connect it to the board for execution. The basic steps are yes, but some contents of C language are not very understood.