When Django is used for front-end and back-end separation development, it is usually combined with Django rest framework to create RESTful interface API. For framework introduction and version requirements, please refer to the official address: https://www.django-rest-framework.org

This article takes creating an API containing name and sex fields as an example to learn the use of Django rest framework.
It mainly includes the following five steps:
- Create Django project
- Create ORM model
- Load Django REST Framework
- Serialization model
- Create a view and url to load data
1. Create Django project
Create django_rest
django-admin startproject django_rest
Enter django_rest, create virtual environment env
virtualenv env
Activate the virtual environment and install django
source ./env/bin/activate
Install django
pip install django
Create rest_app
python manage.py startapp rest_app
Register app and add app to INSTALLED_APPS
#setting.py
INSTALLED_APPS = [
'django.contrib.admin',
'django.contrib.auth',
'django.contrib.contenttypes',
'django.contrib.sessions',
'django.contrib.messages',
'django.contrib.staticfiles',
'rest_app'
]
Create background admin account for management
$ python manage.py createsuperuser Username (leave blank to use 'root'):admin Email address: Password: Password (again): Superuser created successfully.
2. Create ORM model
We can use the default sqlite3 for the database. If necessary, we can change it in setting databases configuration in py.
Modify US / django_rest/models.py add our man model
#models.py
from django.db import models
# Create your models here.
class Man(models.Model):
name = models.CharField(max_length=64)
sex = models.CharField(max_length=64)
def __str__(self):
return self.name
Do database migration
python manage.py makemigrations python manage.py migrate
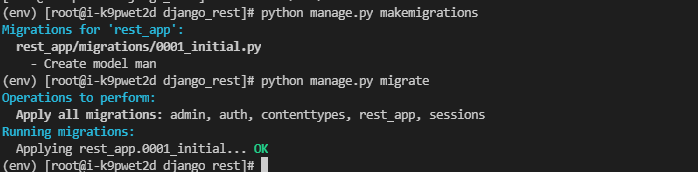
Register the Man model in our background so that you can add, delete, check and modify it through the background of django and write admin Py is as follows
#admin.py from django.contrib import admin from .models import Man # Register your models here. admin.site.register(Man) # Register Man to the background
Start django service
python manage.py runserver
visit http://127.0.0.1:8000/admin/ You can see the login interface and enter the password to log in
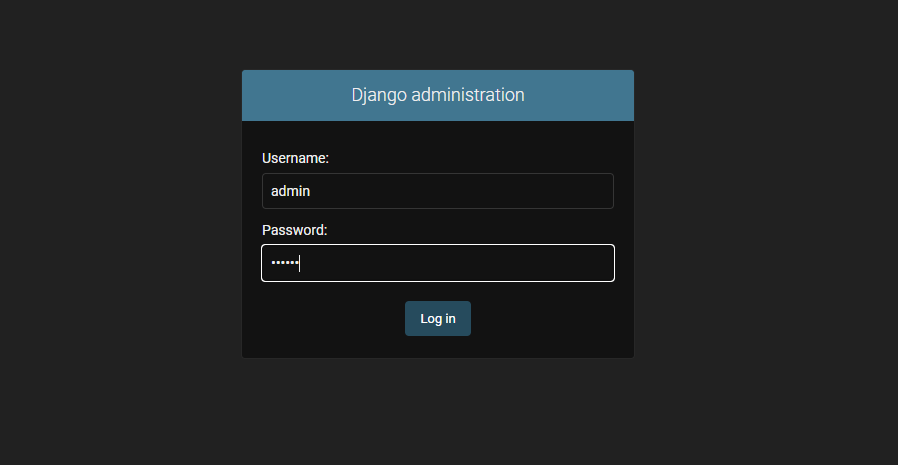
You can see our rest_ Model man object mans under app
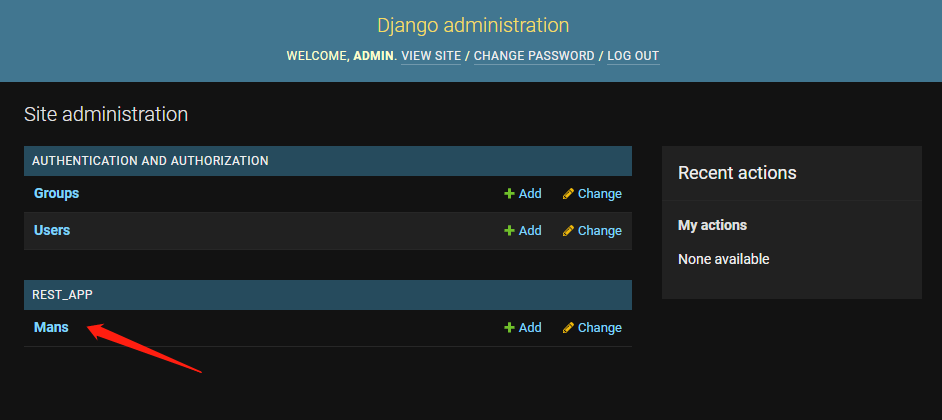
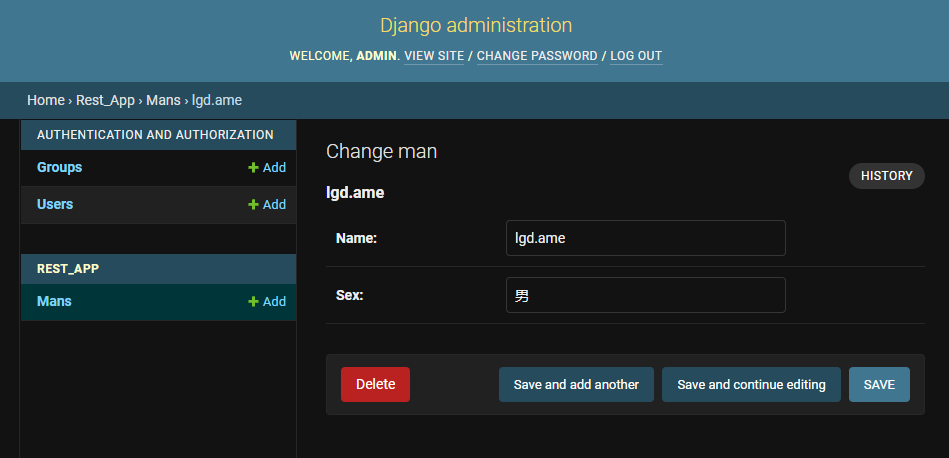
Let's add that man LGD ame
3. Load Django REST Framework
Setup Toolkit
pip install djangorestframework
Register rest_framework
#setting.py
INSTALLED_APPS = [
'django.contrib.admin',
'django.contrib.auth',
'django.contrib.contenttypes',
'django.contrib.sessions',
'django.contrib.messages',
'django.contrib.staticfiles',
'rest_app'
'rest_framework' #register
]
4. Serialization model
The serializer will convert (serialize) our model data into json format so that it can be requested. Similarly, when josn data is submitted, the serializer will convert the json data into a model for us to use.
We're at rest_ Create a file serializer under app py
We need to do three things:
- Import Man model
- Import sequence REST Framework serializer
- Create a new class to link the model to the serializer
from rest_framework import serializers
from .models import Man
class Manserializer(serializers.HyperlinkedModelSerializer):
class Meta:
model = Man
fields = ('name','sex')
5. Create a view and url to load data
We need to return the serialized data to the browser, so we need to do the following steps:
- Query the database through the impassable Man
- Pass the queried data to the serializer and convert it into json through the serializer
We're at rest_app/views.py write our view, ModelViewSet by rest_framework, including get and post methods
# views.py
from rest_framework import viewsets
from .serializers import ManSerializer
from .models import Man
class ManViewSet(viewsets.ModelViewSet):
queryset = Man.objects.all().order_by('name') #Query results to queryset
serializer_class = ManSerializer #Serialize results
In Django_ URLs. In the rest directory Py add api route
from django.contrib import admin
from django.urls import path, include
urlpatterns = [
path('admin/', admin.site.urls),
path('', include('rest_app.urls')),
]
At rest_ Create URLs in app directory Py add view route through rest_ The router in the framework ensures that our requests are to the correct dynamic resources.
from django.urls import include, path
from rest_framework import routers
from . import views
router = routers.DefaultRouter()
router.register(r'man', views.ManViewSet) #Route to ManViewSet view
# Wire up our API using automatic URL routing.
# Additionally, we include login URLs for the browsable API.
urlpatterns = [
path('', include(router.urls)), #Using router routing
path('api-auth/', include('rest_framework.urls', namespace='rest_framework'))
]
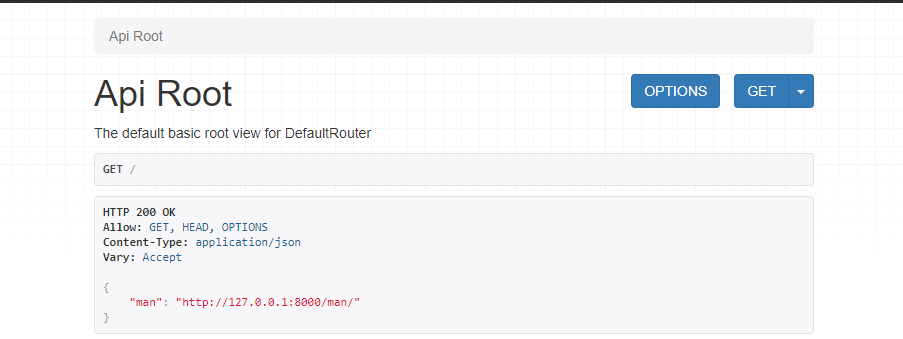
Finally, let's start the service and visit http://127.0.0.1:8000/ You can view our api information in the browser
python manage.py runserver
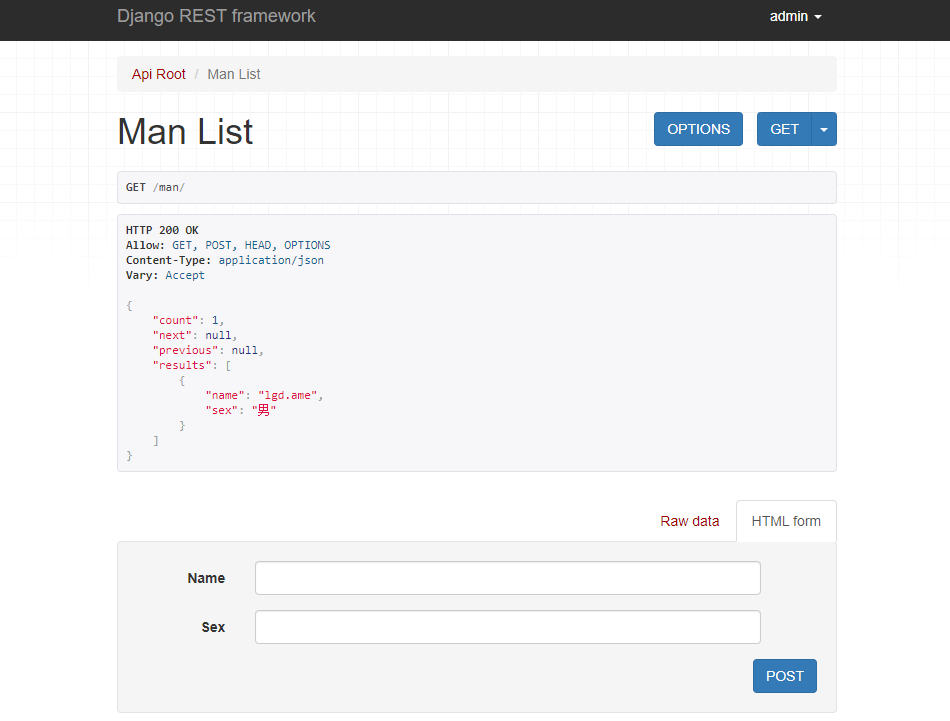
visit http://127.0.0.1:8000/man/ To view man resources
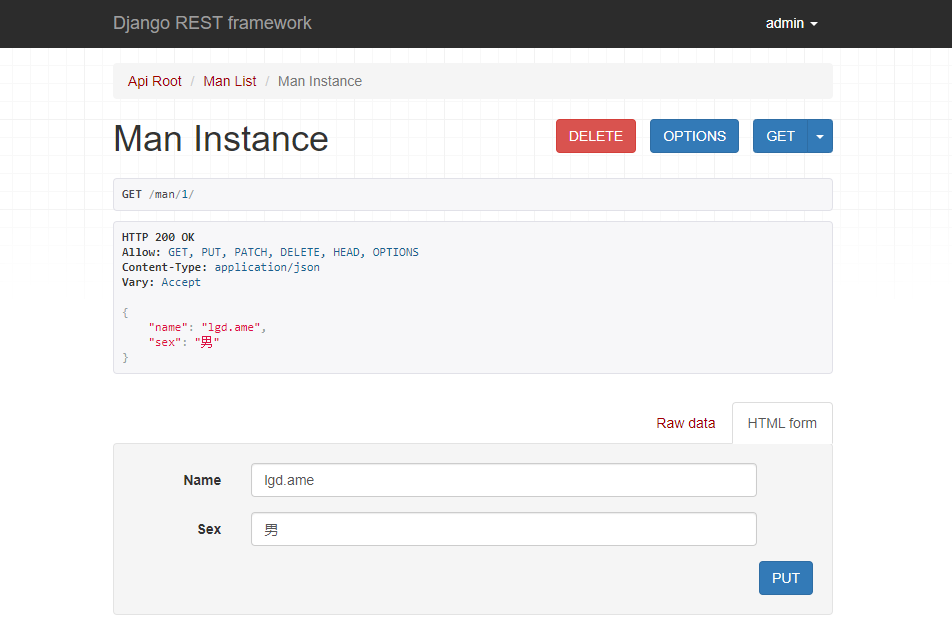
Access api resources by id http://127.0.0.1:8000/man/1/
In this way, we have created a basic restful style API. I think the key point is to understand the ModelViewSet and built-in router. It is difficult to know why without reading the source code.
If there are deficiencies in the article, please point them out in the comment area.
Welcome to collect, like and ask questions. Pay attention to the top water dispenser administrators. In addition to heating hot water, they sometimes do something else.