Vue.js - MVVM belief
Learning video address of station B: https://www.bilibili.com/video/BV1e7411M7GQ
- All based on ES6 (let, const, arrow function, promise, axios)
- MVVM model (React nactive is widely used in APP)
- Traditional js top and bottom gives you thinking, breaking the manual operation of DOM
1. Import vue.js
<script src="vue.js"></script>
2. new a Vue
<script> const myvue = new Vue(); console.log(myvue); </script>
console:
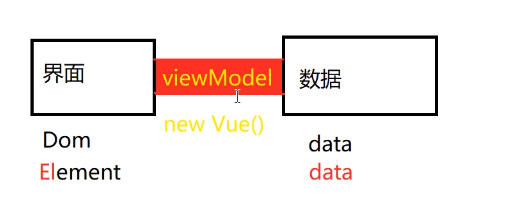
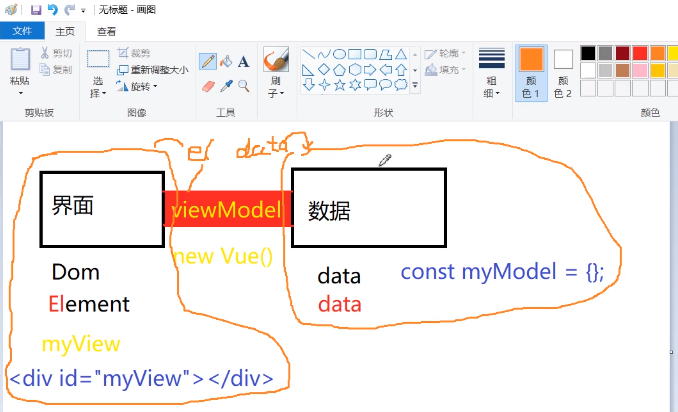
3. Pass an object to Vue, which has two parameters. The syntax is as follows:
<script> const myvue = new Vue({ //Interface: xxx, //Data: yyy }); console.log(myvue); </script>
Drawing understanding:
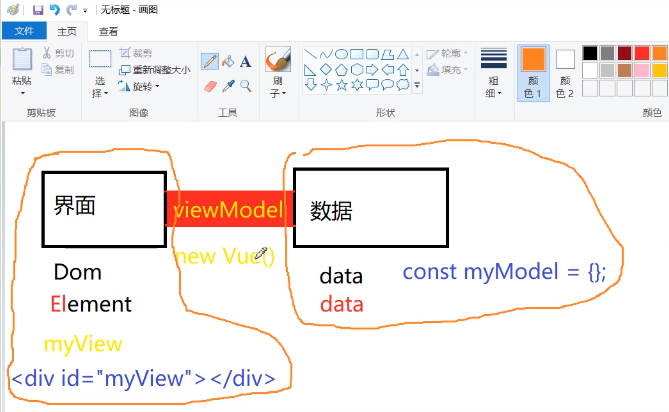
4. Gradually increase code
Interface:
<div id="myView"></div>
Data:
const myModel = {};
Integration code:
<body>
<div id="myView"></div>
</body>
<script>
const myModel = {};
const myvue = new Vue({
el: '#myView',
data: myModel
});
console.log(myvue);
</script>
The picture is as follows:
5.
<body>
<div id="myView">
{{name}}
</div>
</body>
<script>
//const Position is immutable, internal value is variable
//Single quotes are strings, not variables
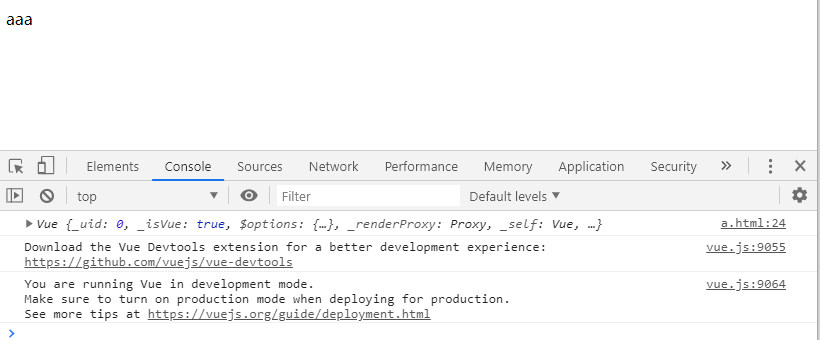
const myModel = { name: 'aaa' };
const myvue = new Vue({
el: '#myView',
data: myModel
});
console.log(myvue);
</script>
console:
6. MVVM+UI framework
MVVM's belief, interface as interface, data as data, realizes bidirectional data binding through viewmodel, and realizes the function of changing data interface as well
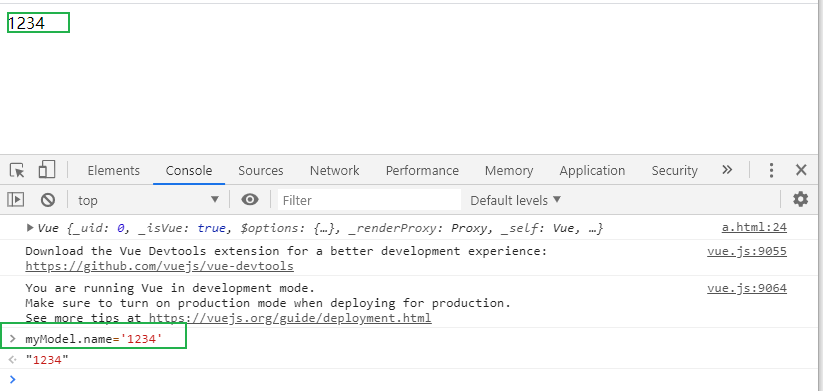
Amendment 1
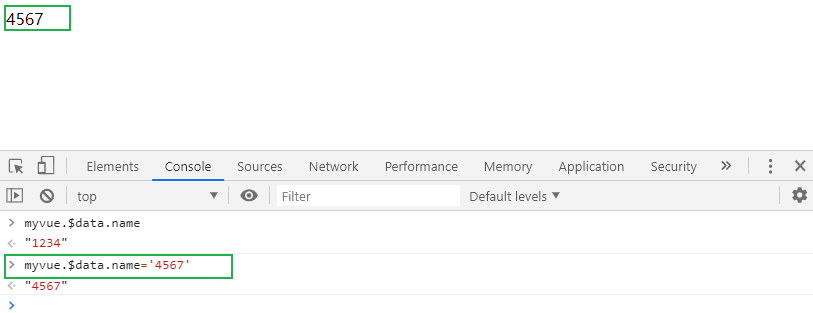
Amendment 2:
7. Interface display time
Old way of writing: manual DOM operation
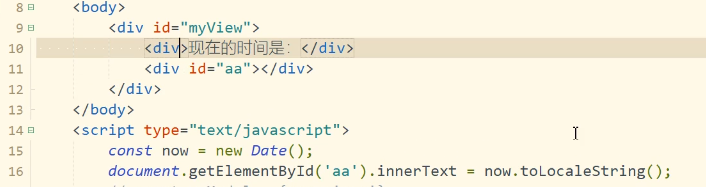
How to write MVVM:
<body>
<div id="myView">
//Now the time is: {now}}
</div>
</body>
<script>
const myModel = {
now: new Date().toLocaleString()
};
const myvue = new Vue({
el: '#myView',
data: myModel
});
console.log(myvue);
console:
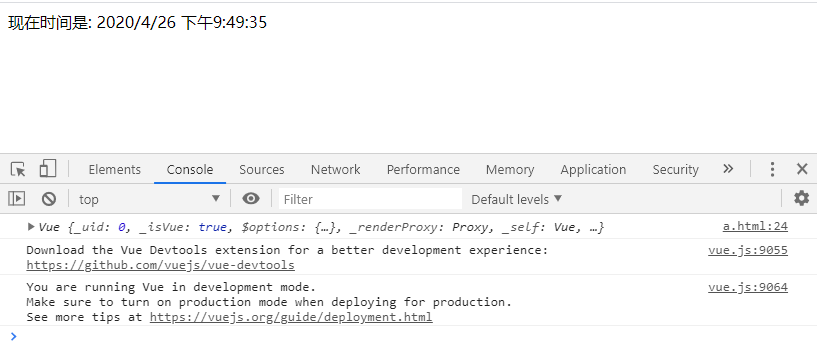
8. Get the latest time
<body> <div id="myView"> //Now the time is: {now}} </div> <div id="aa"> <button onclick="pp()">Get the latest time</button> </div> </body> <script> const myModel = { now: new Date().toLocaleString() }; const myvue = new Vue({ el: '#myView', data: myModel }); console.log(myvue); const pp = function () { myModel.now = new Date().toLocaleString(); }
console:
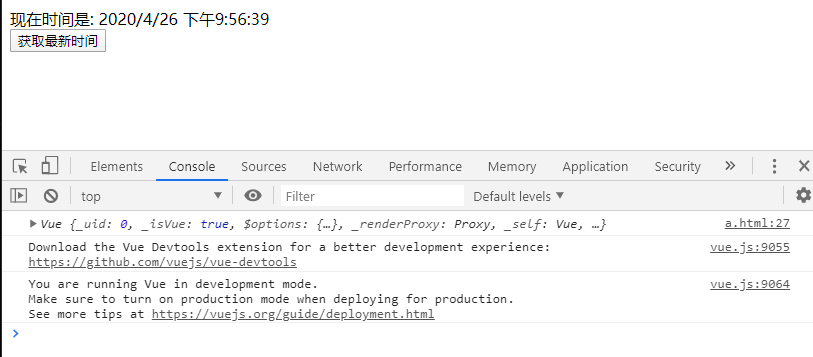
9. When clicking the button to implement pp(), the data level setInterval updates the code segment once a second, and the interface also responds to the update
const pp = function () { setInterval(() => { myModel.now = new Date().toLocaleString(); }, 1000); }
console: update every second

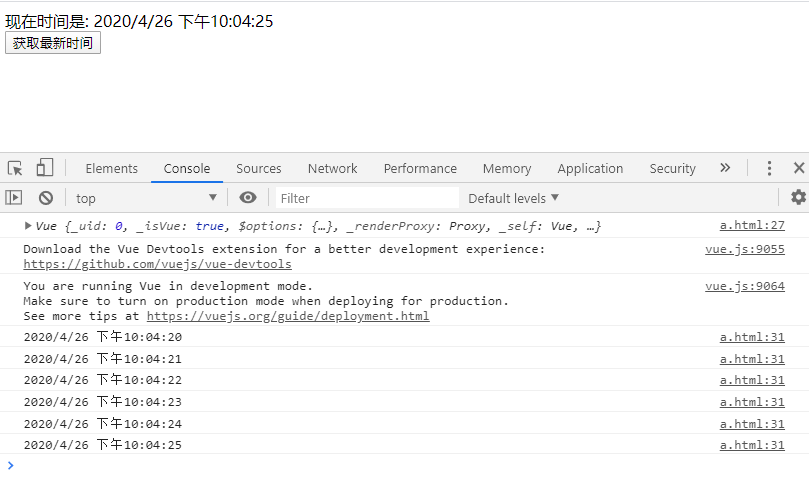
9. console print out
const pp = function () { setInterval(() => { myModel.now = new Date().toLocaleString(); }, 1000); }
10. v-for traversal
<div id="myView"> <ol> <li v-for="student in stuList">{{student.name}} </li> </ol> </div>
const myModel = { stuList: [ { name: 'Xiao Ming', sex: 'male' }, { name: 'lisa', sex: 'female' }, { name: 'jennie', sex: 'female' }] }
console:

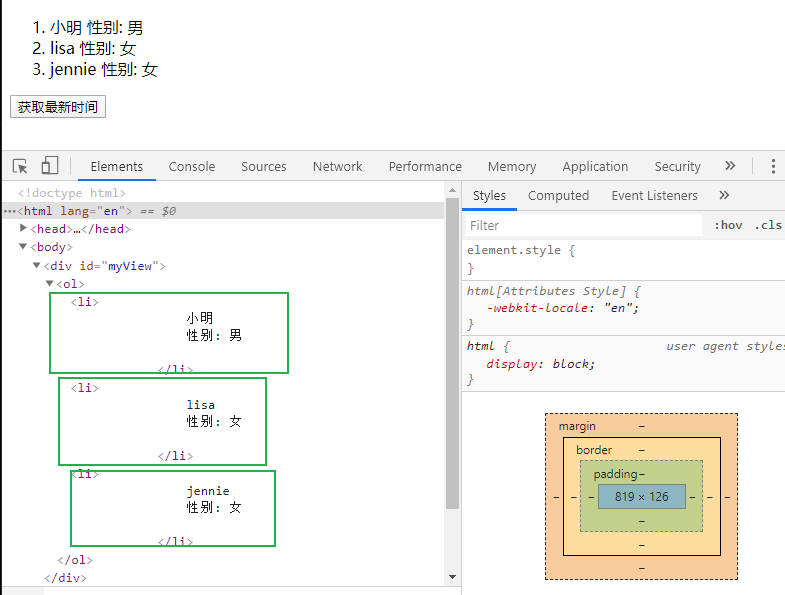
11.
<div id="myView"> <ol> <li v-for="student in stuList"> {{student.name}} //Gender: {{student.sex}}} </li> </ol> </div>
Virtual DOM: vue does the work of rendering
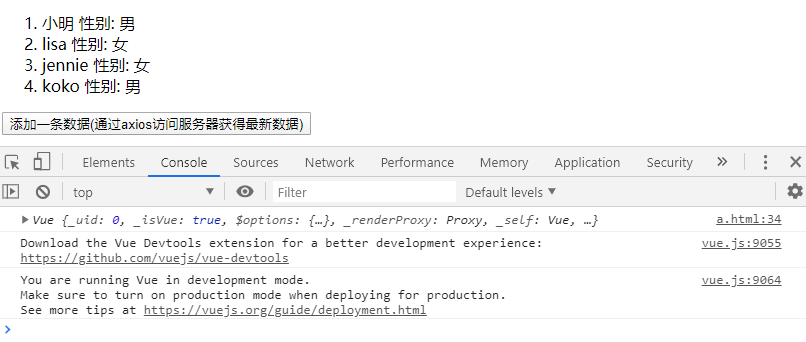
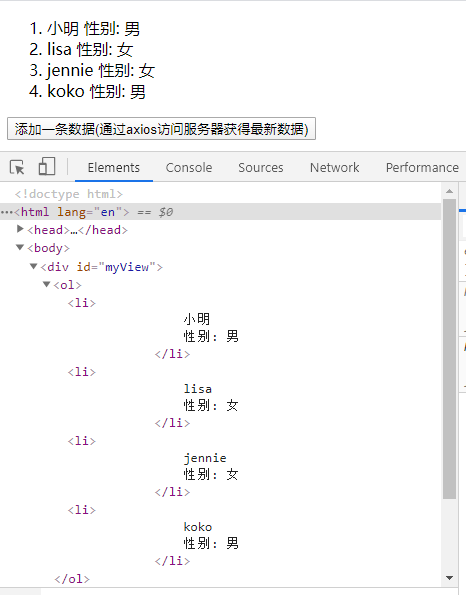
12. Add a piece of data
<div id="aa"> <button onclick="pp()">Add a piece of data(adopt axios Access the server to get the latest data)</button> </div> </body> <script> const myModel = { stuList: [ { name: 'Xiao Ming', sex: 'male' }, { name: 'lisa', sex: 'female' }, { name: 'jennie', sex: 'female' }] } const myvue = new Vue({ el: '#myView', data: myModel }); console.log(myvue); const pp = function () { myModel.stuList.push({ name: 'koko', sex: 'male' }) } </script>
console:
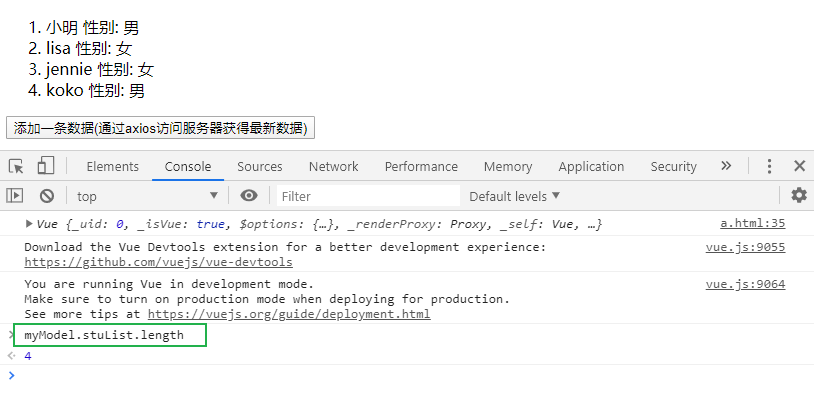
13.
<div id="aa">
< button onclick = "pp()" > add a piece of data (get the latest data through axios access server) < / button >
</div>
<script> const myvue = new Vue({ el: '#myView', data: { stuList: [ { name: 'Xiao Ming', sex: 'male' }, { name: 'lisa', sex: 'female' }, { name: 'jennie', sex: 'female' }] } }); console.log(myvue); const pp = function () { myvue.$data.stuList.push({ name: 'koko', sex: 'male' }) } </script>
console: