1, HOG feature extraction principle
HOG feature extraction process can be divided into five parts: detection window, normalized image, calculating gradient, statistical histogram, normalization of gradient histogram, and obtaining HOG feature vector.
-
Detection window:
HOG divides the image through window and block. By taking the cell as the unit, the pixel value of a certain area of the image is mathematically calculated and processed. Here we first introduce the concepts of window, block and cell and the relationship between them.Window: divide the image into multiple identical windows according to a certain size and slide.
Block: divide each window into multiple identical blocks according to a certain size and slide.
Cell: each window is divided into multiple identical cells according to a certain size. It belongs to the unit of feature extraction and is stationary.
Image - > win - > block - > cell -
Normalized image
normalization is divided into gamma space and color space normalization. In order to reduce the influence of illumination factors, the whole image is normalized (normalized), which can avoid the large proportion of local surface exposure contribution in the texture intensity of the image. -
Calculated gradient
calculate the gradient in the abscissa and ordinate directions of the image, and calculate the gradient direction according to the gradient in the abscissa and ordinate. -
Constructing gradient histogram
HOG construction direction gradient histogram completed in cell: bins (it can be understood as the number of divisions) determines the division of the direction. Generally, bins takes 9 and divides the gradient direction into 9 intervals. For example, assuming that the size of a cell is 6 * 6, for 36 pixels in the cell, first judge the interval of the gradient direction of the pixel, and then weight the corresponding gradient direction interval according to the gradient amplitude and gradient direction of the pixel . -
Cell normalized gradient histogram was performed within the block
the change of local illumination and foreground background contrast make the gradient intensity change in a wide range, which needs to be normalized here. -
Generate HOG eigenvector
finally, all blocks are combined to generate feature vectors: for example, for a 64128 window, every 88 pixels form a cell and every 22 cells form a block. Each block has 94 features. With 8 pixels as steps, there will be 7 scanning windows in the horizontal direction and 15 scanning windows in the vertical direction. Therefore, a 64128 window has 367 * 15 = 3780 features, and a hog descriptor in the code is for a detection window.
2, Code implementation
- Import related libraries
# Import package import numpy as np import cv2 import dlib import random#Construct random test set and training set from sklearn.svm import SVC #Import svm from sklearn.svm import LinearSVC #Import linear svm from sklearn.pipeline import Pipeline #Import pipes in python import os import joblib#Save model from sklearn.preprocessing import StandardScaler,PolynomialFeatures #Import polynomial regression and standardization import tqdm
- Define path
folder_path='./genki4k/' label='labels.txt'#Label file pic_folder='files/'#Picture file path
- Obtain the default face detector and trained face 68 feature point detector
#Obtain the default face detector and trained face 68 feature point detector
def get_detector_and_predicyor():
#Use the front that comes with dlib_ face_ Detector as our feature extractor
detector = dlib.get_frontal_face_detector()
"""
Function: face detection frame
Parameters: PythonFunction and in Classes
in classes Indicates the number of sampling times. The more the number of times, the more the number of faces obtained, but it is easier to frame errors
The return value is the coordinates of the rectangle, and each rectangle is a human face (the default face detector)
"""
#Return to the trained face 68 feature point detector
predictor = dlib.shape_predictor('shape_predictor_68_face_landmarks.dat')
return detector,predictor
#Acquisition detector
detector,predictor=get_detector_and_predicyor()
- Function of intercepting face
def cut_face(img,detector,predictor):
#Intercept face
img_gry=cv2.cvtColor(img,cv2.COLOR_BGR2GRAY)
rects = detector(img_gry, 0)
if len(rects)!=0:
mouth_x=0
mouth_y=0
landmarks = np.matrix([[p.x, p.y] for p in predictor(img,rects[0]).parts()])
for i in range(47,67):#Mouth range
mouth_x+=landmarks[i][0,0]
mouth_y+=landmarks[i][0,1]
mouth_x=int(mouth_x/20)
mouth_y=int(mouth_y/20)
#Crop picture
img_cut=img_gry[mouth_y-20:mouth_y+20,mouth_x-20:mouth_x+20]
return img_cut
else:
return 0#If the face is not detected, 0 is returned
- Extract eigenvalue function
#Extract eigenvalues
def get_feature(files_train,face,face_feature):
for i in tqdm.tqdm(range(len(files_train))):
img=cv2.imread(folder_path+pic_folder+files_train[i])
cut_img=cut_face(img,detector,predictor)
if type(cut_img)!=int:
face.append(True)
cut_img=cv2.resize(cut_img,(64,64))
#Padding: padding for boundary processing
padding=(8,8)
winstride=(16,16)
hogdescrip=hog.compute(cut_img,winstride,padding).reshape((-1,))
face_feature.append(hogdescrip)
else:
face.append(False)#No face detected
face_feature.append(0)
- Filter function
def filtrate_face(face,face_feature,face_site): #Remove the features of the image that cannot detect the face, and return the feature array and the corresponding label
face_features=[]
#Get label
label_flag=[]
with open(folder_path+label,'r') as f:
lines=f.read().splitlines()
#Select the that can detect the face, and collect the corresponding label
for i in tqdm.tqdm(range(len(face_site))):
if face[i]:#Determine whether a face is detected
#After pop, you need to delete the current element and move the following elements forward, so you can extract the first one every time
face_features.append(face_feature.pop(0))
label_flag.append(int(lines[face_site[i]][0]))
else:
face_feature.pop(0)
datax=np.float64(face_features)
datay=np.array(label_flag)
return datax,datay
- Polynomial kernel SVM function
def PolynomialSVC(degree,c=10):#Polynomial svm
return Pipeline([
# Mapping source data to third-order polynomials
("poly_features", PolynomialFeatures(degree=degree)),
# Standardization
("scaler", StandardScaler()),
# SVC linear classifier
("svm_clf", LinearSVC(C=10, loss="hinge", random_state=42,max_iter=10000))
])
- Gaussian kernel SVM function
#svm Gaussian kernel
def RBFKernelSVC(gamma=1.0):
return Pipeline([
('std_scaler',StandardScaler()),
('svc',SVC(kernel='rbf',gamma=gamma))
])
- Training function
def train(files_train,train_site):#train
'''
files_train:Collection of training file names
train_site :Location of training files in the folder
'''
#Is a face detected
train_face=[]
#Face feature array
train_feature=[]
#Extracting feature array of training set
get_feature(files_train,train_face,train_feature)
#Filter out the feature array of undetectable faces
train_x,train_y=filtrate_face(train_face,train_feature,train_site)
svc=PolynomialSVC(degree=1)
svc.fit(train_x,train_y)
return svc#Return to the trained model
- Test function
def test(files_test,test_site,svc):#Forecast, viewing result set
'''
files_train:Collection of training file names
train_site :Location of training files in the folder
'''
#Is a face detected
test_face=[]
#Face feature array
test_feature=[]
#Extracting feature array of training set
get_feature(files_test,test_face,test_feature)
#Filter out the feature array of undetectable faces
test_x,test_y=filtrate_face(test_face,test_feature,test_site)
pre_y=svc.predict(test_x)
ac_rate=0
for i in range(len(pre_y)):
if(pre_y[i]==test_y[i]):
ac_rate+=1
ac=ac_rate/len(pre_y)*100
print("The accuracy is"+str(ac)+"%")
return ac
- HOG feature extractor
#Set the parameters of the hog winsize=(64,64) blocksize=(32,32) blockstride=(16,16) cellsize=(8,8) nbin=9 #Define hog hog=cv2.HOGDescriptor(winsize,blocksize,blockstride,cellsize,nbin) #Get which files are in the folder files=os.listdir(folder_path+pic_folder)
- The random 9 / 10 of the data set is used as the training set, and the remaining 1 / 10 is used as the test set for ten times
ac=float(0)
for j in range(10):
site=[i for i in range(4000)]
#The location of the sample used for training
train_site=random.sample(site,3600)
#Predict the location of the sample used
test_site=[]
for i in range(len(site)):
if site[i] not in train_site:
test_site.append(site[i])
files_train=[]
#Training set, accounting for nine tenths of the total
for i in range(len(train_site)):
files_train.append(files[train_site[i]])
#Test set
files_test=[]
for i in range(len(test_site)):
files_test.append(files[test_site[i]])
svc=train(files_train,train_site)
ac=ac+test(files_test,test_site,svc)
save_path='./train/second'+str(j)+'(hog).pkl'
joblib.dump(svc,save_path)
ac=ac/10
print("The average accuracy is"+str(ac)+"%")
- Detection function
def test1(files_test,test_site,svc):#Forecast, viewing result set
'''
files_train:Collection of training file names
train_site :Location of training files in the folder
'''
#Is a face detected
test_face=[]
#Face feature array
test_feature=[]
#Extracting feature array of training set
get_feature(files_test,test_face,test_feature)
#Filter out the feature array of undetectable faces
test_x,test_y=filtrate_face(test_face,test_feature,test_site)
pre_y=svc.predict(test_x)
tp=0
tn=0
for i in range(len(pre_y)):
if pre_y[i]==test_y[i] and pre_y[i]==1:
tp+=1
elif pre_y[i]==test_y[i] and pre_y[i]==0:
tn+=1
f1=2*tp/(tp+len(pre_y)-tn)
print(f1)
svc7=joblib.load('./train/second9(hog).pkl')
site=[i for i in range(4000)]
#The location of the sample used for training
train_site=random.sample(site,3600)
#Predict the location of the sample used
test_site=[]
for i in range(len(site)):
if site[i] not in train_site:
test_site.append(site[i])
#Test set
files_test=[]
for i in range(len(test_site)):
files_test.append(files[test_site[i]])
test1(files_test,test_site,svc7)

- Smiley face detection function
def smile_detector(img,svc):
cut_img=cut_face(img,detector,predictor)
a=[]
if type(cut_img)!=int:
cut_img=cv2.resize(cut_img,(64,64))
#Padding: padding for boundary processing
padding=(8,8)
winstride=(16,16)
hogdescrip=hog.compute(cut_img,winstride,padding).reshape((-1,))
a.append(hogdescrip)
result=svc.predict(a)
a=np.array(a)
return result[0]
else :
return 2
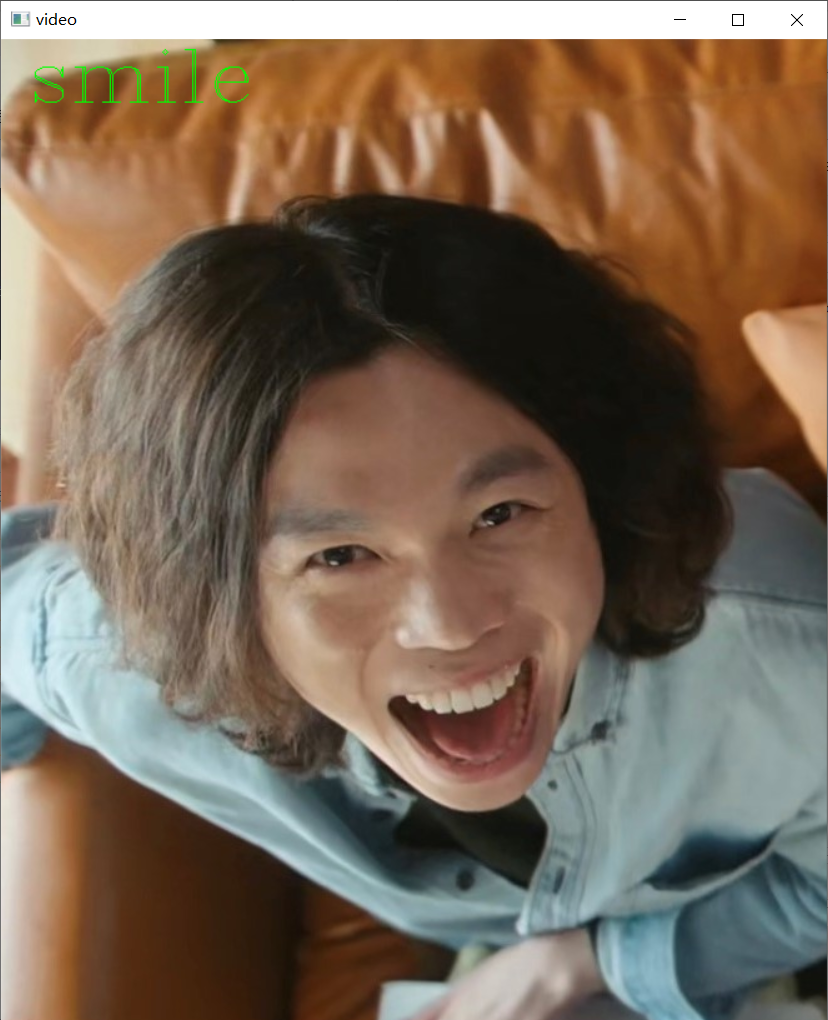
- Picture test
##Image detection
pic_path='2.png'
img=cv2.imread(pic_path)
result=smile_detector(img,svc7)
if result==1:
img=cv2.putText(img,'smile',(21,50),cv2.FONT_HERSHEY_COMPLEX,2.0,(0,255,0),1)
elif result==0:
img=cv2.putText(img,'no smile',(21,50),cv2.FONT_HERSHEY_COMPLEX,2.0,(0,255,0),1)
else:
img=cv2.putText(img,'no face',(21,50),cv2.FONT_HERSHEY_COMPLEX,2.0,(0,255,0),1)
cv2.imshow('video', img)
cv2.waitKey(0)


3, Summary
this paper realizes face smile recognition by using SVM algorithm.
4, Reference
https://blog.csdn.net/weixin_56102526/article/details/121926814