Catalog
Why use HSV space instead of RGB space?
4. Obtaining binary maps in HSV space
1. Get the value of the slider bar
2. Transfer to HSV (three channels: H, S, V)
3. To binary (single channel threshold processing)
4. Combining the three channels of HSV to get the final binary graph
2. Binary Map from HSV Color Space
4. Open Operational Noise Reduction
6-2, Get the center and radius coordinates
Basic Theory (HSV)
Why use HSV space instead of RGB space?
Because the RGB channel does not reflect the specific color information of the object very well.
HSV space can very intuitively express the shade, hue, and vividness of colors, and facilitate the comparison between colors.
(RGB is heavily influenced by light, so HSV is used)
The purpose of using HSV here is to obtain an appropriate binary graph.
HSV
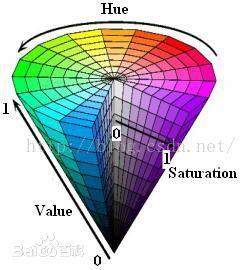
Hue (H): Hue, hue (specific color)
Saturation (S): Saturation, color purity
Value (V): luminosity
Hue range is [0,179], saturation range is [0,255], value range is [0,255]
(I made a foolish mistake when I wrote the code: I set all three to 179 and found that they were out of tune)
1. Hue (hue)
Hue: Hue (specific color)
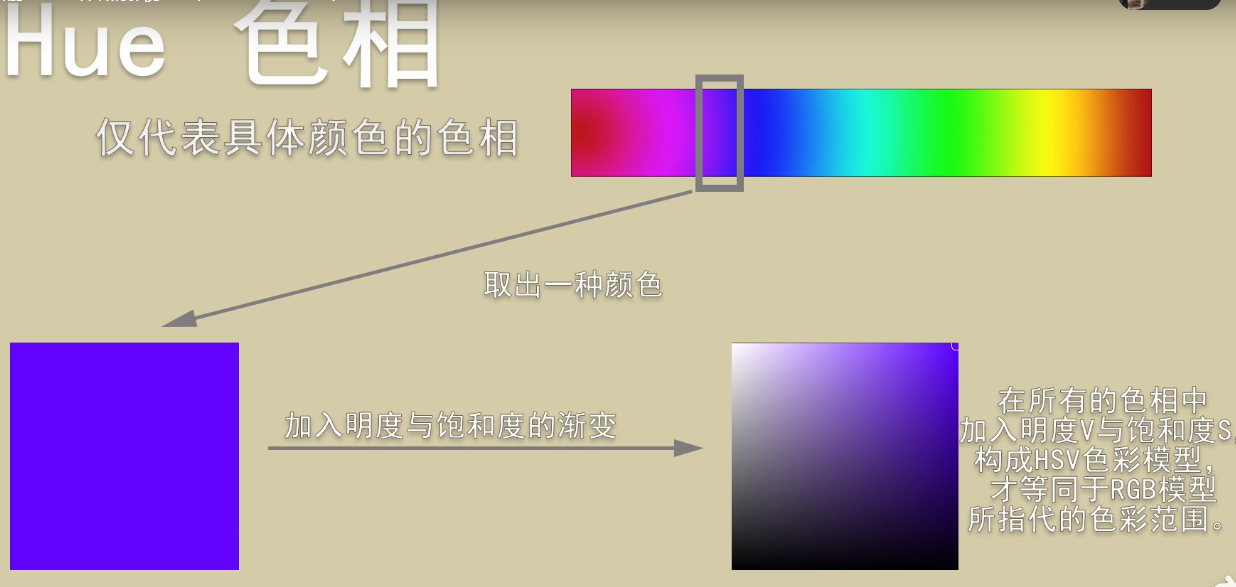
2. Value (lightness)
Brightness: The brightness of a color, the brightness of a single channel (not equal to the overall amount of light).
(The brighter the brightness, the whiter the lightness, the lower the darkness, generally improving the brightness will also improve the R, G, B channel values)
3. Saturation
Saturation: Saturation, color purity (lower gray, higher purity).
(Higher saturation generally decreases the relatively low values in RGB, highlighting the purity of the main color.)

Video Explanation at Station B:
Short Animation Slow Speech Speed of 1 Minute Explains the Basic Principle of Color Formation in Movie and TV Color Matching--RGB and HSV
Effect Display




I. Initialization
Slider initialization
In addition to the initialization of the motor, the rudder, the window, and so on, there is also the initial setup of the slider bar.
Before creating the slider bar:
1. You need to set the name of the window, otherwise you will not be able to set the slider bar without any windows.
2. Create callback functions.
1. Create callback functions
def nothing(*arg):
pass2. Window Settings (Name)
def Trackbar_Init():
# 1 create windows
cv2.namedWindow('h_binary')
cv2.namedWindow('s_binary')
cv2.namedWindow('v_binary')3. Slider bar settings
# 2 Create Trackbar
cv2.createTrackbar('hmin', 'h_binary', 6, 179, nothing)
cv2.createTrackbar('hmax', 'h_binary', 26, 179, nothing)
cv2.createTrackbar('smin', 's_binary', 110, 255, nothing)
cv2.createTrackbar('smax', 's_binary', 255, 255, nothing)
cv2.createTrackbar('vmin', 'v_binary', 140, 255, nothing)
cv2.createTrackbar('vmax', 'v_binary', 255, 255, nothing)
# Create Slider Slider Value Name Window Name Slider Value Slider Threshold Callback FunctionCode
def Motor_Init():
global L_Motor, R_Motor
L_Motor= GPIO.PWM(l_motor,100)
R_Motor = GPIO.PWM(r_motor,100)
L_Motor.start(0)
R_Motor.start(0)
def Direction_Init():
GPIO.setup(left_back,GPIO.OUT)
GPIO.setup(left_front,GPIO.OUT)
GPIO.setup(l_motor,GPIO.OUT)
GPIO.setup(right_front,GPIO.OUT)
GPIO.setup(right_back,GPIO.OUT)
GPIO.setup(r_motor,GPIO.OUT)
def Servo_Init():
global pwm_servo
pwm_servo=Adafruit_PCA9685.PCA9685()
def Trackbar_Init():
# 1 create windows
cv2.namedWindow('h_binary')
cv2.namedWindow('s_binary')
cv2.namedWindow('v_binary')
# 2 Create Trackbar
cv2.createTrackbar('hmin', 'h_binary', 6, 179, nothing)
cv2.createTrackbar('hmax', 'h_binary', 26, 179, nothing)
cv2.createTrackbar('smin', 's_binary', 110, 255, nothing)
cv2.createTrackbar('smax', 's_binary', 255, 255, nothing)
cv2.createTrackbar('vmin', 'v_binary', 140, 255, nothing)
cv2.createTrackbar('vmax', 'v_binary', 255, 255, nothing)
# Create Slider Slider Value Name Window Name Slider Value Slider Threshold Callback Function
def Init():
GPIO.setwarnings(False)
GPIO.setmode(GPIO.BCM)
Direction_Init()
Servo_Init()
Motor_Init()
Trackbar_Init()
# callback
def nothing(*arg):
pass
2. Motion Functions
General operations: forward, backward, left, right, stop.
def Front(speed):
L_Motor.ChangeDutyCycle(speed)
GPIO.output(left_front,1) #left_front
GPIO.output(left_back,0) #left_back
R_Motor.ChangeDutyCycle(speed)
GPIO.output(right_front,1) #right_front
GPIO.output(right_back,0) #right_back
def Back(speed):
L_Motor.ChangeDutyCycle(speed)
GPIO.output(left_front,0) #left_front
GPIO.output(left_back,1) #left_back
R_Motor.ChangeDutyCycle(speed)
GPIO.output(right_front,0) #right_front
GPIO.output(right_back,1) #right_back
def Left(speed):
L_Motor.ChangeDutyCycle(speed)
GPIO.output(left_front,0) #left_front
GPIO.output(left_back,1) #left_back
R_Motor.ChangeDutyCycle(speed)
GPIO.output(right_front,1) #right_front
GPIO.output(right_back,0) #right_back
def Right(speed):
L_Motor.ChangeDutyCycle(speed)
GPIO.output(left_front,1) #left_front
GPIO.output(left_back,0) #left_back
R_Motor.ChangeDutyCycle(speed)
GPIO.output(right_front,0) #right_front
GPIO.output(right_back,1) #right_back
def Stop():
L_Motor.ChangeDutyCycle(0)
GPIO.output(left_front,0) #left_front
GPIO.output(left_back,0) #left_back
R_Motor.ChangeDutyCycle(0)
GPIO.output(right_front,0) #right_front
GPIO.output(right_back,0) #right_back 3. Helicopter Control
def set_servo_angle(channel,angle):
angle=4096*((angle*11)+500)/20000
pwm_servo.set_pwm_freq(50) #frequency==50Hz (servo)
pwm_servo.set_pwm(channel,0,int(angle))set_servo_angle(4, 110) #top servo lengthwise
#0:back 180:front
set_servo_angle(5, 90) #bottom servo crosswise
#0:left 180:right
4. Obtaining binary maps in HSV space
1. Get the value of the slider bar
# 1 get trackbar's value
hmin = cv2.getTrackbarPos('hmin', 'h_binary')
hmax = cv2.getTrackbarPos('hmax', 'h_binary')
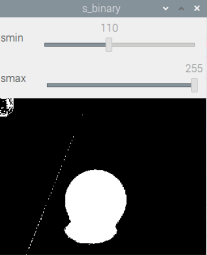
smin = cv2.getTrackbarPos('smin', 's_binary')
smax = cv2.getTrackbarPos('smax', 's_binary')
vmin = cv2.getTrackbarPos('vmin', 'v_binary')
vmax = cv2.getTrackbarPos('vmax', 'v_binary')2. Transfer to HSV (three channels: H, S, V)
# 2 to HSV
hsv = cv2.cvtColor(image, cv2.COLOR_BGR2HSV)
cv2.imshow('hsv', hsv)
h, s, v = cv2.split(hsv)

3. To binary (single channel threshold processing)
H, S, V thresholds are processed separately:
# 3 set threshold (binary image)
# if value in (min, max):white; otherwise:black
h_binary = cv2.inRange(np.array(h), np.array(hmin), np.array(hmax))
s_binary = cv2.inRange(np.array(s), np.array(smin), np.array(smax))
v_binary = cv2.inRange(np.array(v), np.array(vmin), np.array(vmax))
# 5 Show
cv2.imshow('h_binary', h_binary)
cv2.imshow('s_binary', s_binary)
cv2.imshow('v_binary', v_binary)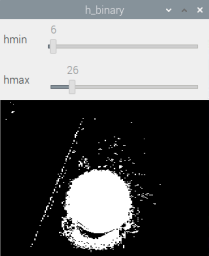

4. Combining the three channels of HSV to get the final binary graph
For H, S, V channels and operations.
# 4 get binary
binary = cv2.bitwise_and(h_binary, cv2.bitwise_and(s_binary, v_binary))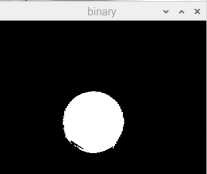
Code
# Obtaining binary images in HSV color space
def Get_HSV(image):
# 1 get trackbar's value
hmin = cv2.getTrackbarPos('hmin', 'h_binary')
hmax = cv2.getTrackbarPos('hmax', 'h_binary')
smin = cv2.getTrackbarPos('smin', 's_binary')
smax = cv2.getTrackbarPos('smax', 's_binary')
vmin = cv2.getTrackbarPos('vmin', 'v_binary')
vmax = cv2.getTrackbarPos('vmax', 'v_binary')
# 2 to HSV
hsv = cv2.cvtColor(image, cv2.COLOR_BGR2HSV)
cv2.imshow('hsv', hsv)
h, s, v = cv2.split(hsv)
# 3 set threshold (binary image)
# if value in (min, max):white; otherwise:black
h_binary = cv2.inRange(np.array(h), np.array(hmin), np.array(hmax))
s_binary = cv2.inRange(np.array(s), np.array(smin), np.array(smax))
v_binary = cv2.inRange(np.array(v), np.array(vmin), np.array(vmax))
# 4 get binary (for H, S, V channels and operation)
binary = cv2.bitwise_and(h_binary, cv2.bitwise_and(s_binary, v_binary))
# 5 Show
cv2.imshow('h_binary', h_binary)
cv2.imshow('s_binary', s_binary)
cv2.imshow('v_binary', v_binary)
cv2.imshow('binary', binary)
return binary5. Image Processing (General)
1. Turn on the camera
# 1 Capture the frames
ret, frame = camera.read()
image = frame
cv2.imshow('frame', frame)
2. Binary Map from HSV Color Space
(Get_HSV(frame) is actually step 4 HSV processing)
# 2 get HSV
binary = Get_HSV(frame)3. Gauss filter
# 3 Gausi blur
blur = cv2.GaussianBlur(binary,(9,9),0)4. Open Operational Noise Reduction
# 4 Open
kernel = cv2.getStructuringElement(cv2.MORPH_RECT, (9,9))
Open = cv2.morphologyEx(blur, cv2.MORPH_OPEN, kernel)
cv2.imshow('Open',Open)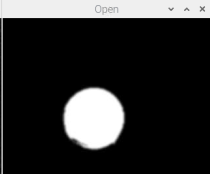
5. Closed operations
# 5 Close
Close = cv2.morphologyEx(Open, cv2.MORPH_CLOSE, kernel)
cv2.imshow('Close',Close) 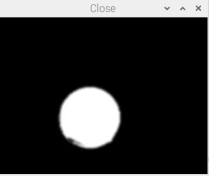
6. Hoff circle detection
principle
Hoff transform circle detection is based on image gradient:
Principle of center detection: A center is the junction of the circumferential normal lines. Set a threshold value at which the number of intersecting straight lines at a point is greater than this threshold, and the junction is considered to be the center of the circle.
The principle of determining the radius of a circle: the distance from the center to the circumference (radius) is the same. Set a threshold value which is considered the radius of the circle as long as the number of identical distances is greater than the threshold.
API
def HoughCircles(image: Any,
method: Any,
dp: Any,
minDist: Any,
circles: Any = None,
param1: Any = None,
param2: Any = None,
minRadius: Any = None,
maxRadius: Any = None) -> NoneParameters:
- The second parameter, method of type int, is currently available in OpenCV as one of the Hoff gradient methods, and its identifier is CV_HOUGH_GRADIENT. Fill in this parameter with this identifier.
- The third parameter, the double type dp, is used to detect the reciprocal resolution of the accumulator image to the ratio of the input image, and this parameter allows the creation of an accumulator with a lower resolution than the input image. If the above text is not easy to understand, take an example. For example, if dp=If dp=2, the accumulator will have half the width and height of the input image.
- The fourth parameter, minDist of type double, is the minimum distance between the centers of the circles detected by the Hough transformation, that is, the minimum distance between two distinct circles that our algorithm can clearly distinguish. If this parameter is too small, multiple adjacent circles may be incorrectly detected as a coincident circle. Conversely, if this parameter is set too large, some circles cannot be detected.Detected.
- The fifth parameter, circles of type InputArray, stores the output vectors of the detected circles after calling the HoughCircles function. Each vector is represented by a floating-point vector (x, y, radius) containing three elements.
- The sixth parameter, param1 of type double, has a default value of 100. It is the corresponding parameter for the detection method set by the third parameter method. For the current unique method, Hough gradient CV_HOUGH_GRADIENT, it represents the high threshold passed to the canny edge detection operator, while the low threshold is half of the high threshold.
- The seventh parameter, param2 of the double type, also has a default value of 100. It is the corresponding parameter for the detection method set by the third parameter method. For the current unique method, Hough gradient CV_HOUGH_GRADIENT, it represents the accumulator threshold for the center of the circle in the detection phase. The smaller it is, more circles that do not exist at all can be detected, and the larger it is, it can pass the detection.The circle is closer to the perfect circle.
- The eighth parameter, minRadius of type int, has a default value of 0, which represents the minimum radius of a circle.
- The ninth parameter, maxRadius of type int, also has a default value of 0, which represents the maximum radius of a circle.
6-1, Hoff circle detection
# 6 Hough Circle detect
circles = cv2.HoughCircles(Close,cv2.HOUGH_GRADIENT,2,120,param1=120,param2=20,minRadius=20,maxRadius=0)
# param2: Determines whether a circle can be detected (fewer circles are easier to detect, but corresponding circles are more prone to error)6-2, Get the center and radius coordinates
# 1 Get the center and radius of a circle
x, y, r = int(circles[0][0][0]),int(circles[0][0][1]),int(circles[0][0][2])
print(x, y, r)6-3, Draw a circle
# 2 Draw circles
cv2.circle(image, (x, y), r, (255,0,255),5)
cv2.imshow('image', image)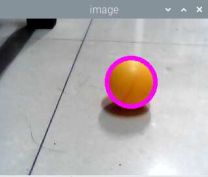
Code
# image processing
def Image_Processing():
global h, s, v
# 1 Capture the frames
ret, frame = camera.read()
image = frame
cv2.imshow('frame', frame)
# 2 get HSV
binary = Get_HSV(frame)
# 3 Gausi blur
blur = cv2.GaussianBlur(binary,(9,9),0)
# 4 Open
kernel = cv2.getStructuringElement(cv2.MORPH_RECT, (9,9))
Open = cv2.morphologyEx(blur, cv2.MORPH_OPEN, kernel)
cv2.imshow('Open',Open)
# 5 Close
Close = cv2.morphologyEx(Open, cv2.MORPH_CLOSE, kernel)
cv2.imshow('Close',Close)
# 6 Hough Circle detect
circles = cv2.HoughCircles(Close,cv2.HOUGH_GRADIENT,2,120,param1=120,param2=20,minRadius=20,maxRadius=0)
# param2: Determines whether a circle can be detected (fewer circles are easier to detect, but corresponding circles are more prone to error)
# judge if circles is exist
if circles is not None:
# 1 Get the center and radius of a circle
x, y, r = int(circles[0][0][0]),int(circles[0][0][1]),int(circles[0][0][2])
print(x, y, r)
# 2 Draw circles
cv2.circle(image, (x, y), r, (255,0,255),5)
cv2.imshow('image', image)
else:
(x,y),r = (0,0), 0
return (x,y), r6. Motion Control
According to the detected circle, the obtained coordinates and radius are used for motion control.
Here you can track the balls, and the foreground and the backwards will work together, "The enemy enters and retreats, the enemy retreats and enters."
# Motion Control (Tracking balls, foreground and retreat work together here, "Enemy advancing and retreating, Enemy retreating and advancing")
def Move((x,y), r):
low_xlimit = width/4
high_xlimit = 0.75 * width
#low_ylimit = 3/4 * height
ylimit = 0.75 * height
print(high_xlimit, ylimit)
# No detection, no movement
if x==0:
Stop()
# Detected in area above 0.75 (normal distance)
elif x>low_xlimit and x<high_xlimit and y<ylimit:
Front(60)
# Detected areas below 0.75 (too close, back)
elif x>low_xlimit and x<high_xlimit and y>=ylimit:
Back(60)
# Track left in area 0.25
elif x<low_xlimit:
Left(60)
# Track right in area 0.25
elif x>high_xlimit:
Right(60)Total Code
#Ball Tracking(HSV)
import RPi.GPIO as GPIO
import time
import Adafruit_PCA9685
import numpy as np
import cv2
#set capture window
width, height = 320, 240
camera = cv2.VideoCapture(0)
camera.set(3,width)
camera.set(4,height)
l_motor = 18
left_front = 22
left_back = 27
r_motor = 23
right_front = 25
right_back = 24
def Motor_Init():
global L_Motor, R_Motor
L_Motor= GPIO.PWM(l_motor,100)
R_Motor = GPIO.PWM(r_motor,100)
L_Motor.start(0)
R_Motor.start(0)
def Direction_Init():
GPIO.setup(left_back,GPIO.OUT)
GPIO.setup(left_front,GPIO.OUT)
GPIO.setup(l_motor,GPIO.OUT)
GPIO.setup(right_front,GPIO.OUT)
GPIO.setup(right_back,GPIO.OUT)
GPIO.setup(r_motor,GPIO.OUT)
def Servo_Init():
global pwm_servo
pwm_servo=Adafruit_PCA9685.PCA9685()
def Trackbar_Init():
# 1 create windows
cv2.namedWindow('h_binary')
cv2.namedWindow('s_binary')
cv2.namedWindow('v_binary')
# 2 Create Trackbar
cv2.createTrackbar('hmin', 'h_binary', 6, 179, nothing)
cv2.createTrackbar('hmax', 'h_binary', 26, 179, nothing)
cv2.createTrackbar('smin', 's_binary', 110, 255, nothing)
cv2.createTrackbar('smax', 's_binary', 255, 255, nothing)
cv2.createTrackbar('vmin', 'v_binary', 140, 255, nothing)
cv2.createTrackbar('vmax', 'v_binary', 255, 255, nothing)
# Create Slider Slider Value Name Window Name Slider Value Slider Threshold Callback Function
def Init():
GPIO.setwarnings(False)
GPIO.setmode(GPIO.BCM)
Direction_Init()
Servo_Init()
Motor_Init()
Trackbar_Init()
def Front(speed):
L_Motor.ChangeDutyCycle(speed)
GPIO.output(left_front,1) #left_front
GPIO.output(left_back,0) #left_back
R_Motor.ChangeDutyCycle(speed)
GPIO.output(right_front,1) #right_front
GPIO.output(right_back,0) #right_back
def Back(speed):
L_Motor.ChangeDutyCycle(speed)
GPIO.output(left_front,0) #left_front
GPIO.output(left_back,1) #left_back
R_Motor.ChangeDutyCycle(speed)
GPIO.output(right_front,0) #right_front
GPIO.output(right_back,1) #right_back
def Left(speed):
L_Motor.ChangeDutyCycle(speed)
GPIO.output(left_front,0) #left_front
GPIO.output(left_back,1) #left_back
R_Motor.ChangeDutyCycle(speed)
GPIO.output(right_front,1) #right_front
GPIO.output(right_back,0) #right_back
def Right(speed):
L_Motor.ChangeDutyCycle(speed)
GPIO.output(left_front,1) #left_front
GPIO.output(left_back,0) #left_back
R_Motor.ChangeDutyCycle(speed)
GPIO.output(right_front,0) #right_front
GPIO.output(right_back,1) #right_back
def Stop():
L_Motor.ChangeDutyCycle(0)
GPIO.output(left_front,0) #left_front
GPIO.output(left_back,0) #left_back
R_Motor.ChangeDutyCycle(0)
GPIO.output(right_front,0) #right_front
GPIO.output(right_back,0) #right_back
def set_servo_angle(channel,angle):
angle=4096*((angle*11)+500)/20000
pwm_servo.set_pwm_freq(50) #frequency==50Hz (servo)
pwm_servo.set_pwm(channel,0,int(angle))
# callback
def nothing(*arg):
pass
# Obtaining binary images in HSV color space
def Get_HSV(image):
# 1 get trackbar's value
hmin = cv2.getTrackbarPos('hmin', 'h_binary')
hmax = cv2.getTrackbarPos('hmax', 'h_binary')
smin = cv2.getTrackbarPos('smin', 's_binary')
smax = cv2.getTrackbarPos('smax', 's_binary')
vmin = cv2.getTrackbarPos('vmin', 'v_binary')
vmax = cv2.getTrackbarPos('vmax', 'v_binary')
# 2 to HSV
hsv = cv2.cvtColor(image, cv2.COLOR_BGR2HSV)
cv2.imshow('hsv', hsv)
h, s, v = cv2.split(hsv)
# 3 set threshold (binary image)
# if value in (min, max):white; otherwise:black
h_binary = cv2.inRange(np.array(h), np.array(hmin), np.array(hmax))
s_binary = cv2.inRange(np.array(s), np.array(smin), np.array(smax))
v_binary = cv2.inRange(np.array(v), np.array(vmin), np.array(vmax))
# 4 get binary (for H, S, V channels and operation)
binary = cv2.bitwise_and(h_binary, cv2.bitwise_and(s_binary, v_binary))
# 5 Show
cv2.imshow('h_binary', h_binary)
cv2.imshow('s_binary', s_binary)
cv2.imshow('v_binary', v_binary)
cv2.imshow('binary', binary)
return binary
# image processing
def Image_Processing():
global h, s, v
# 1 Capture the frames
ret, frame = camera.read()
image = frame
cv2.imshow('frame', frame)
# 2 get HSV
binary = Get_HSV(frame)
# 3 Gausi blur
blur = cv2.GaussianBlur(binary,(9,9),0)
# 4 Open
kernel = cv2.getStructuringElement(cv2.MORPH_RECT, (9,9))
Open = cv2.morphologyEx(blur, cv2.MORPH_OPEN, kernel)
cv2.imshow('Open',Open)
# 5 Close
Close = cv2.morphologyEx(Open, cv2.MORPH_CLOSE, kernel)
cv2.imshow('Close',Close)
# 6 Hough Circle detect
circles = cv2.HoughCircles(Close,cv2.HOUGH_GRADIENT,2,120,param1=120,param2=20,minRadius=20,maxRadius=0)
# param2: Determines whether a circle can be detected (fewer circles are easier to detect, but corresponding circles are more prone to error)
# judge if circles is exist
if circles is not None:
# 1 Get the center and radius of a circle
x, y, r = int(circles[0][0][0]),int(circles[0][0][1]),int(circles[0][0][2])
print(x, y, r)
# 2 Draw circles
cv2.circle(image, (x, y), r, (255,0,255),5)
cv2.imshow('image', image)
else:
(x,y),r = (0,0), 0
return (x,y), r
# Motion Control (Tracking balls, foreground and retreat work together here, "Enemy advancing and retreating, Enemy retreating and advancing")
def Move((x,y), r):
low_xlimit = width/4
high_xlimit = 0.75 * width
#low_ylimit = 3/4 * height
ylimit = 0.75 * height
print(high_xlimit, ylimit)
# No detection, no movement
if x==0:
Stop()
# Detected in area above 0.75 (normal distance)
elif x>low_xlimit and x<high_xlimit and y<ylimit:
Front(60)
# Detected areas below 0.75 (too close, back)
elif x>low_xlimit and x<high_xlimit and y>=ylimit:
Back(60)
# Track left in area 0.25
elif x<low_xlimit:
Left(60)
# Track right in area 0.25
elif x>high_xlimit:
Right(60)
if __name__ == '__main__':
Init()
set_servo_angle(4, 110) #top servo lengthwise
#0:back 180:front
set_servo_angle(5, 90) #bottom servo crosswise
#0:left 180:right
while 1:
# 1 Image Process
(x,y), r = Image_Processing()
# 2 Move
Move((x,y), r)
# must include this codes(otherwise you can't open camera successfully)
if cv2.waitKey(1) & 0xFF == ord('q'):
Stop()
GPIO.cleanup()
break
Here the HSV is adjusted according to my own current situation, after changing the scene, you may need to re-adjust the threshold of H, S, V channels (max & & min)
Basic visual detection + motion, not too many motion control algorithms (PID and so on) are involved. Have good ideas and suggestions Welcome to the discussion, Thanks