Key value pair
Key value pair writing format
In key value pairs, the key must be a string, but the value can be of type bool/string/int/float:
#Key value pair KeyValueBool: true #bool KeyValueStr: "abc" #string
When writing key value pairs, there is no space between key and: but there is a space between value and:.
Replace sub tags in launch within yaml file:
#Key value pair KeyValueBool: true #bool KeyValueStr: "$(optenv ROS_NAMESPACE NULL)" #string
Use with the rosparam sub tag in the launch file. See:
roslaunch/XML - ROS Wiki http://wiki.ros.org/roslaunch/XML#substitution_args
http://wiki.ros.org/roslaunch/XML#substitution_args
The most detailed implementation of launch file and meta function package in ROS (example + code + parameter analysis)_ Super powerful blog - CSDN blog https://blog.csdn.net/weixin_45590473/article/details/122647788 Note: when the double quotation mark / single quotation mark of value contains "single quotation mark" or "double quotation mark", the transfer character \:
https://blog.csdn.net/weixin_45590473/article/details/122647788 Note: when the double quotation mark / single quotation mark of value contains "single quotation mark" or "double quotation mark", the transfer character \:
#Key value pair KeyValueBool: true #bool KeyValueStr: "ss\'\"" #string
Reference to key value pair
The reference format is as follows: VAR_ name: &refer_ name
#Key value pair KeyValueBool: &KeyValueBool true #bool
When writing a reference, there must be a space between the reference symbol & and:, and no space between & and the variable reference alias.
Cast type
yaml currently supports the following data type conversions:
| Source data type | Target data type | Cast type converter |
| string | Int | !!int |
| string | float | !!float |
| Int | string | !!str |
| float | string | !!str |
Note: when converting string to int type, there can be no decimal point in the string!
#String to integer StringToInt: !!int "122" #String to floating point StringToFloat: !!float "122.0" #Floating point to string FloatToString: !!float 122.3 #Integer to string IntToString: !!int 122
array
Normal array
The elements in the array can be key value pairs of type / bool/string/int/float:
In the array, in order to represent the hierarchical relationship, you must use the TAB key! The following error example:
ArrayOfKeyValue02: - KeyValueBool: false #bool - KeyValueStr: "string02" #string - KeyValueFloat: 1.1 #float
The reason for the error is that the tab key is not used to display the hierarchical relationship!
Key value pair array
#Key value pair array ArrayOfKeyValue01: &ArrayOfKeyValue01 - KeyValueBool: true #bool - KeyValueStr: "string01" #string - KeyValueFloat: 1.05 #float
Array reference
#Key value pair array ArrayOfKeyValue01: &ArrayOfKeyValue01 - KeyValueBool: true #bool - KeyValueStr: "string01" #string - KeyValueFloat: 1.05 #float
Note: "-" represents the dimension. Each element in the above one-dimensional array is placed under a "-".
The application of array reference is as follows:
#Key value pair array ArrayOfKeyValue01: &ArrayOfKeyValue01 - KeyValueBool: true #bool - KeyValueStr: "string01" #string - KeyValueFloat: 1.05 #float ArrayOfKeyValue02: &ArrayOfKeyValue02 - KeyValueBool: false #bool - KeyValueStr: "string02" #string - KeyValueFloat: 1.1 #float #High dimensional array MuliArray: - *ArrayOfKeyValue01 - *ArrayOfKeyValue02
The meaning of * Arrag is the same as that of the reference coincidence & dereference symbol * in C language_ Name means "all elements under array arrag_name".
Multidimensional array
ArrayOfKeyValue01: - - KeyValueBool: true - KeyValueStr: string01 - KeyValueFloat: 1.05 - - KeyValueBool: false - KeyValueStr: string02 - KeyValueFloat: 1.1
The high-dimensional array structure is shown in the following figure:
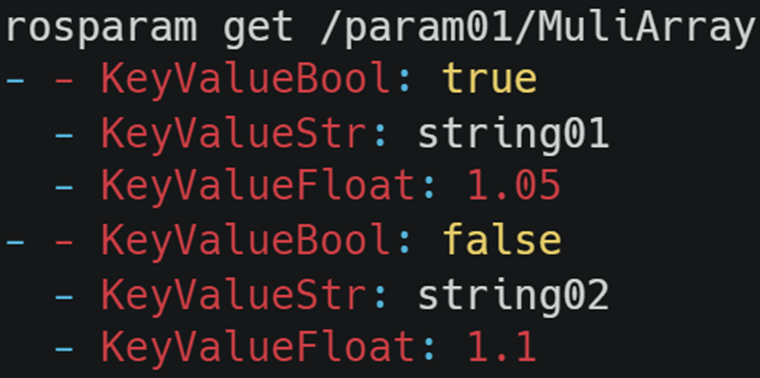
In fact, we can also use reference to build a high-dimensional array:
#Key value pair array ArrayOfKeyValue01: &ArrayOfKeyValue01 - KeyValueBool: true #bool - KeyValueStr: "string01" #string - KeyValueFloat: 1.05 #float ArrayOfKeyValue02: &ArrayOfKeyValue02 - KeyValueBool: false #bool - KeyValueStr: "string02" #string - KeyValueFloat: 1.1 #float #High dimensional array MuliArray: - *ArrayOfKeyValue01 - *ArrayOfKeyValue02
Namespace
Assignment method of common variables under namespace
#Prefix namespace / variable namespace01: &namespace01 var1: 'a' var2: 1.2
In fact, we will use a prefix in the namespace structure of variables of different types, which is more like C
| Base_name | Namespace | name |
| Var1 | Namespace01 | Namespace01/var1 |
| Var2 | Namespace01 | Namespace01/var2 |
Use references to assign values to variables under namespaces
#Array Arrag01: &Arrag01 -""Xiao Ming" -""Li Hua" -"Daqiang“ #Prefix namespace / variable namespace01: &namespace01 var1: 'a' var2: *Arrag01
After using * to dereference Arrag01, assign all the values in Arrag01 array to var2 variable under namespace01 namespace, which is equivalent to:
#Prefix namespace / variable namespace01: &namespace01 var1: 'a' var2: -""Xiao Ming" -""Li Hua" -"Daqiang“
Use references to import variables into namespaces
The above is to import the contents of one variable into another variable. Now, we import the contents of one variable into the namespace, but remember that "the imported contents must be composed of variables":
#Prefix namespace / variable namespace01: &namespace01 var1: 'a' var2: *Arrag01 #Key value pair array ArrayOfKeyValue01: &ArrayOfKeyValue01 - KeyValueBool: true #bool - KeyValueStr: "string01" #string - KeyValueFloat: 1.05 #float #Quote Arrag02: <<: *ArrayOfKeyValue01 <<: *namespace01
How to understand "all imported contents must be composed of variables"? Let's take an example to see if the following example can run?
#Array Arrag01: &Arrag01 -""Xiao Ming" -""Li Hua" -"Daqiang“ #Quote Arrag02: <<: *Arrag01
It seems feasible. Let's expand it to see:
#Quote Arrag02: ""Xiao Ming" ""Li Hua" "Daqiang“
Is that right? Obviously, there is no variable under the Arrag02 namespace (variables in yaml exist in the form of key value pairs)! Then we are implementing the following example:
#Key value pair KeyValueBool: &KeyValueBool true #bool #Quote Arrag02: <<: *KeyValueBool
Errors will also be reported, because when we expand, we will find:
#Quote Arrag02: true #bool
There is also no complete variable under the Arrag02 namespace. Therefore, we draw the following conclusions:
When using < <: * refer_ When name imports variables into the namespace, refer_name cannot be a reference to a key value pair, nor can it be a reference to an ordinary array. Generally, refer_name is a reference to multidimensional array / namespace.